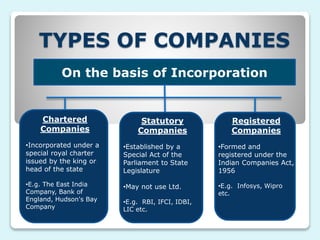
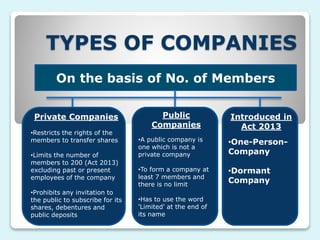
The document provides a comprehensive overview of companies, defining them as artificial legal entities with distinct features such as perpetual succession and limited liability. It categorizes companies based on incorporation, liability, membership, ownership, and nationality, detailing types like private, public, and foreign companies. It also outlines the three levels of management within companies: top-level, middle-level, and lower-level management, along with their respective roles and responsibilities.

![COMPANY
Definition:
“A company can be defined as an "artificial person",
invisible, intangible, created by or under law, with a discrete legal
entity, perpetual succession and a common seal.[citation needed]
It is not affected by the death, insanity or insolvency of an
individual member”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/company-160729110458/85/Company-Definition-Meaning-Features-Types-and-Structure-2-320.jpg)