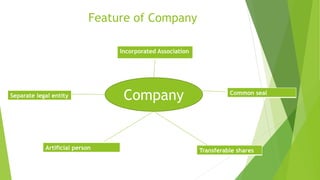
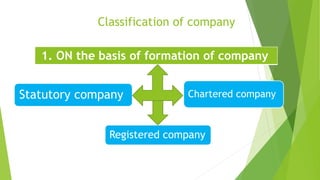
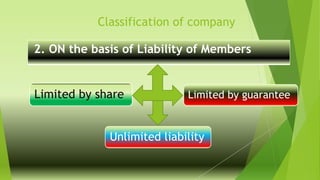
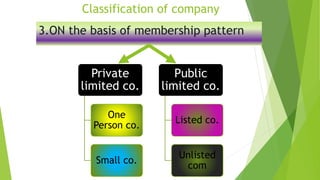
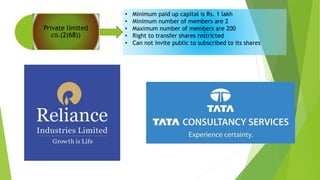
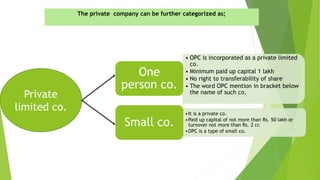
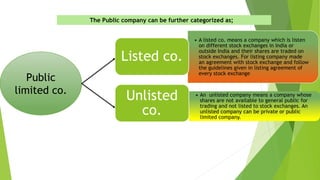
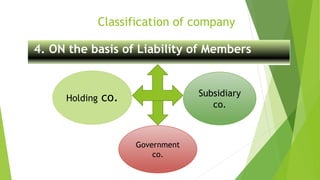
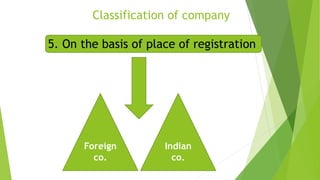
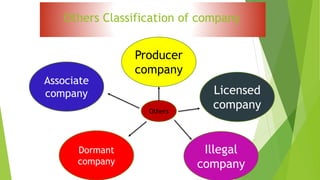
This document presents a presentation on the classification of companies. It discusses various ways companies can be classified, including by formation (statutory, registered, chartered), liability (limited by shares, guarantee, unlimited), membership (private, public, one person), control (holding, subsidiary, government), place (foreign, Indian), and others (dormant, licensed, producer, illegal, associate). The key classifications discussed are private and public limited companies, with private limited having fewer members and transferability restrictions, while public limited must invite public investment and have no member limits. The document provides details on features of companies and examples and definitions of the different classifications.