The document discusses different types of companies based on various classifications:
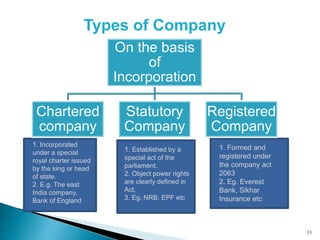
1. Based on incorporation, companies can be registered, chartered, or statutory. Registered companies are formed under the Company Act, while chartered companies are formed by royal charter and statutory companies are established by a special act of parliament.
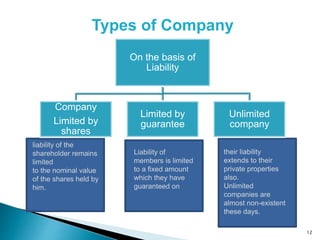
2. Based on liability, companies can be limited by shares, limited by guarantee, or unlimited. For limited companies, shareholder liability is limited to share capital, while unlimited companies' liability extends to private properties.
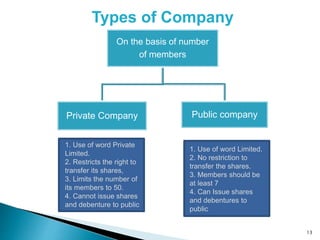
3. Based on number of members, companies are either private (restricted transfer of shares and fewer than 50 members) or public (no restriction on share transfers and minimum 7 members).