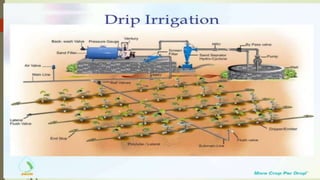
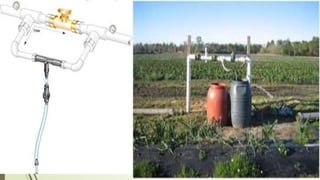
Drip irrigation is a type of micro-irrigation system that slowly delivers water directly to plant roots through a network of valves, pipes, tubing, and emitters. It allows for highly efficient watering by reducing evaporation, runoff, and over-watering. The key components of a drip irrigation system include a water source, pumping system, distribution pipes, drip tape with emitters, injectors for fertilizers, and filters to prevent clogging. Drip irrigation provides numerous advantages like maximizing crop yields, minimizing water and fertilizer use, reducing labor costs, and preventing soil erosion. It is well-suited for row crops, orchards, vineyards, and other agricultural and landscape applications.