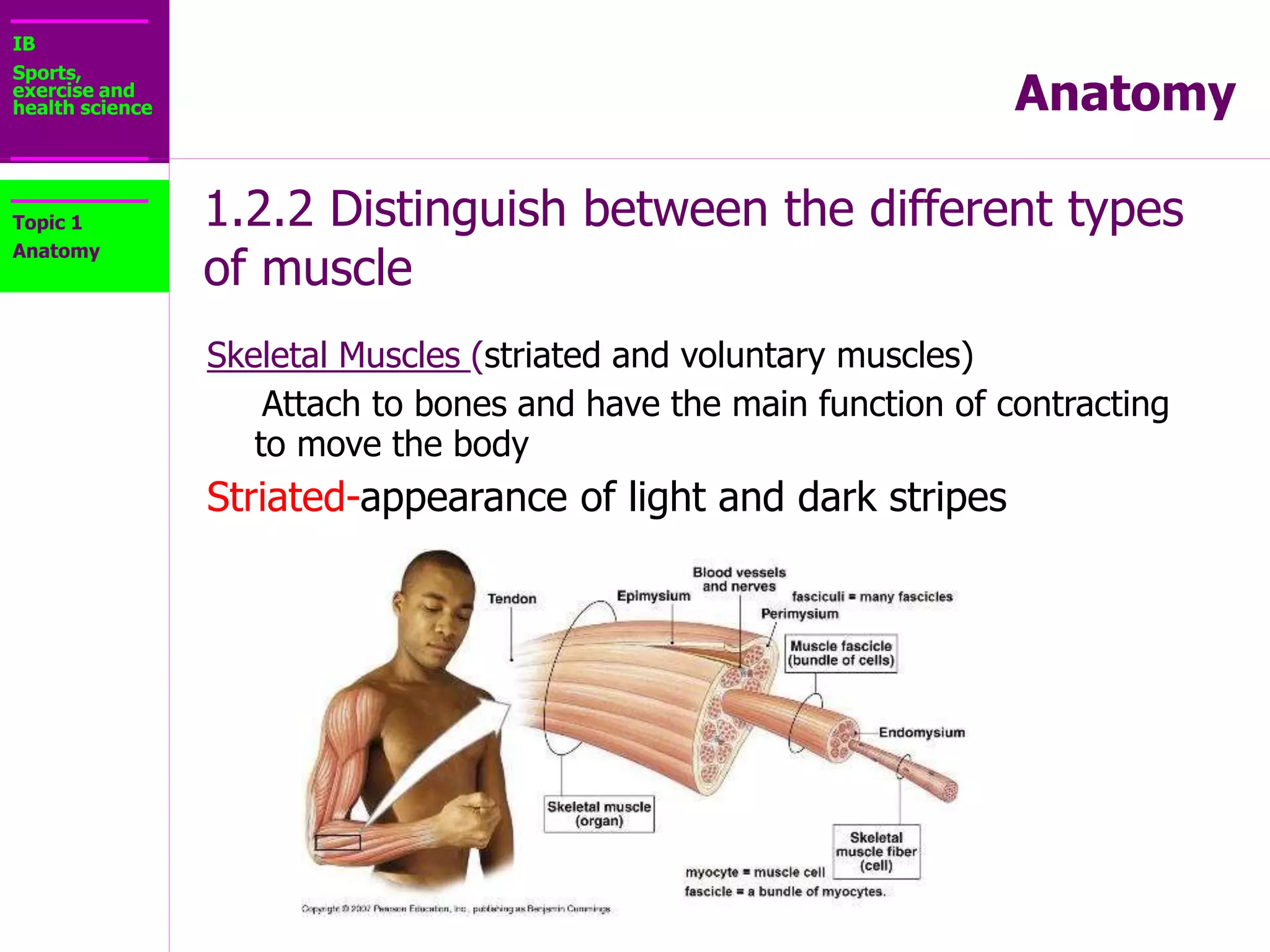
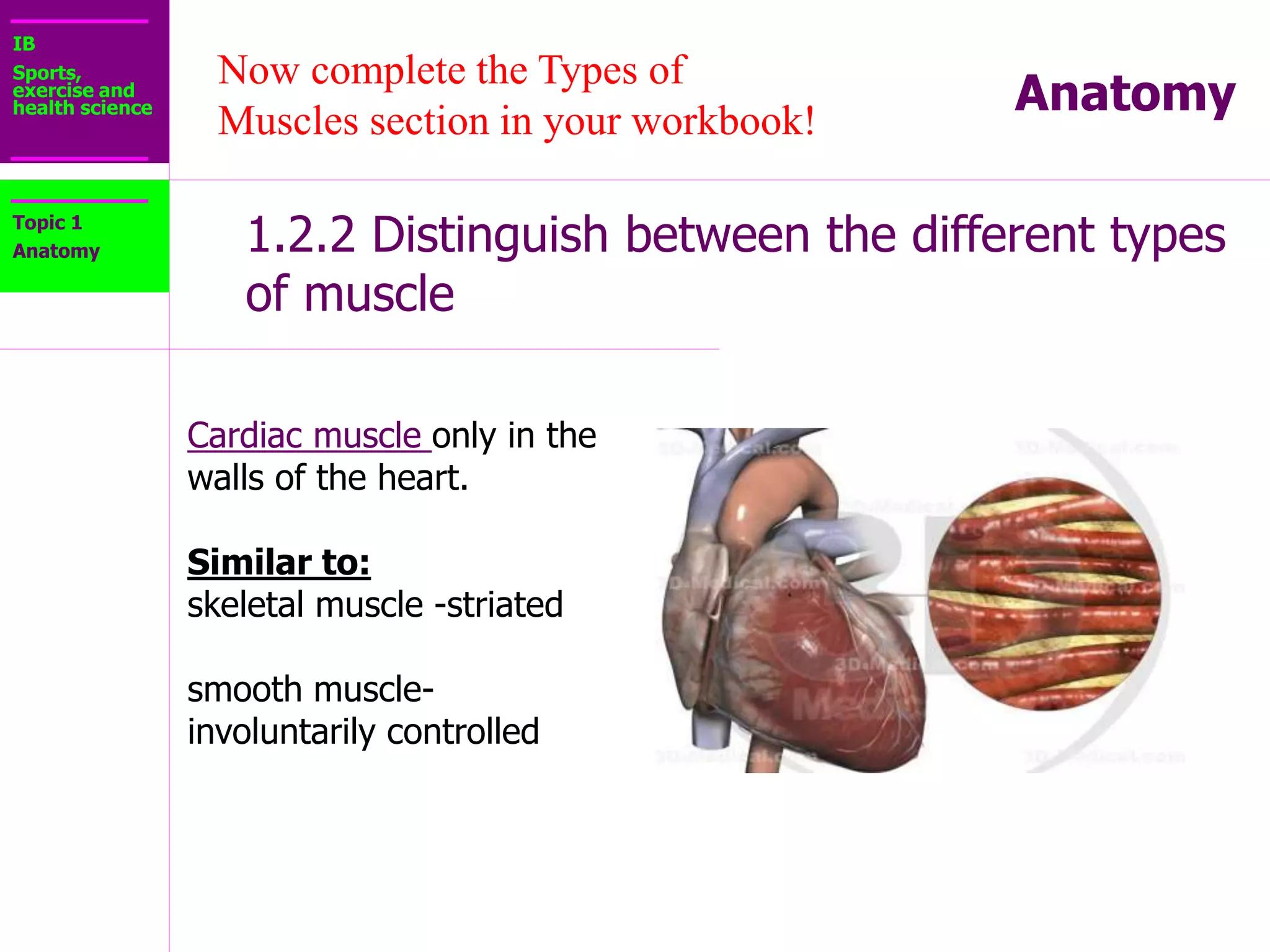
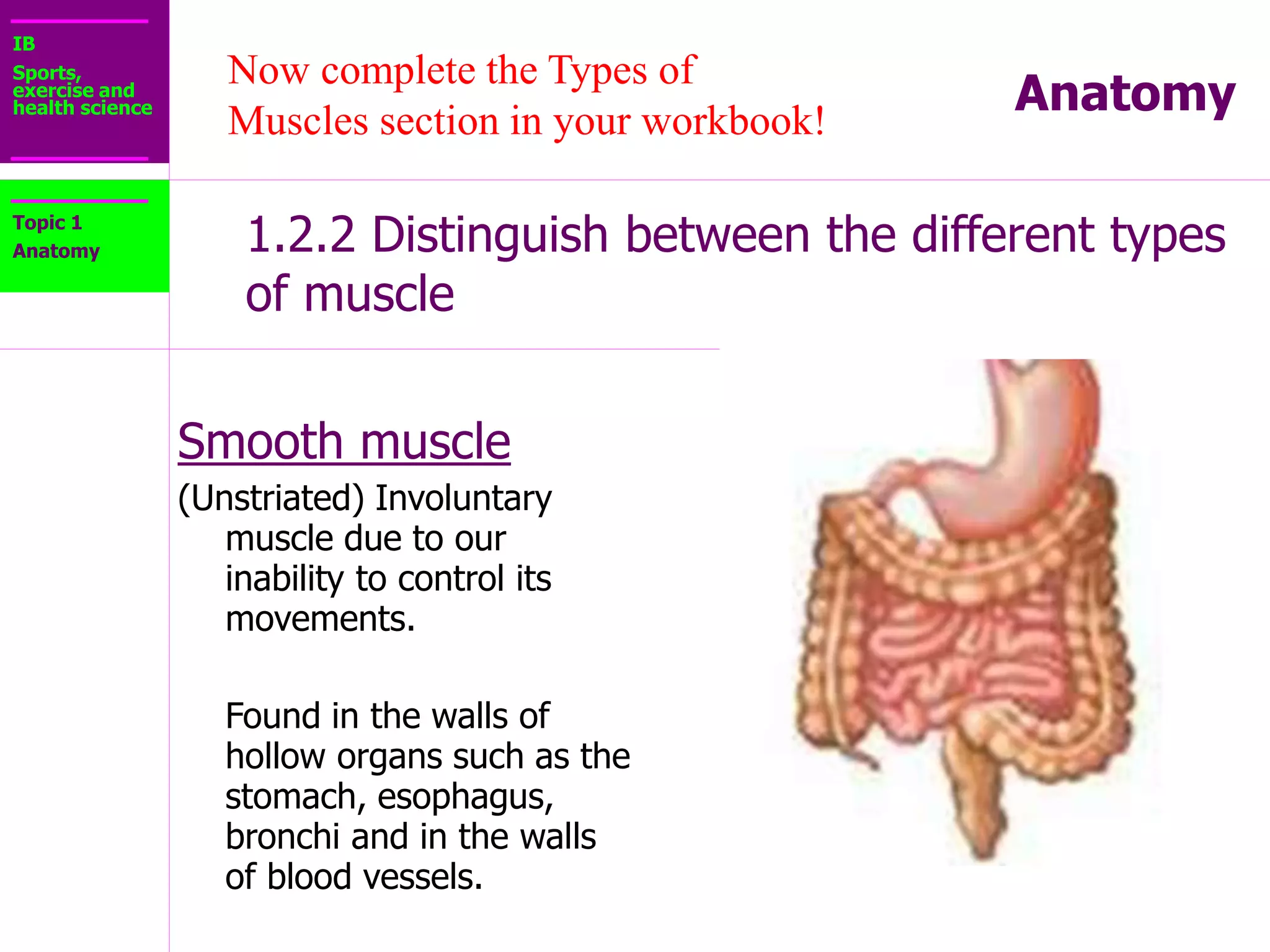
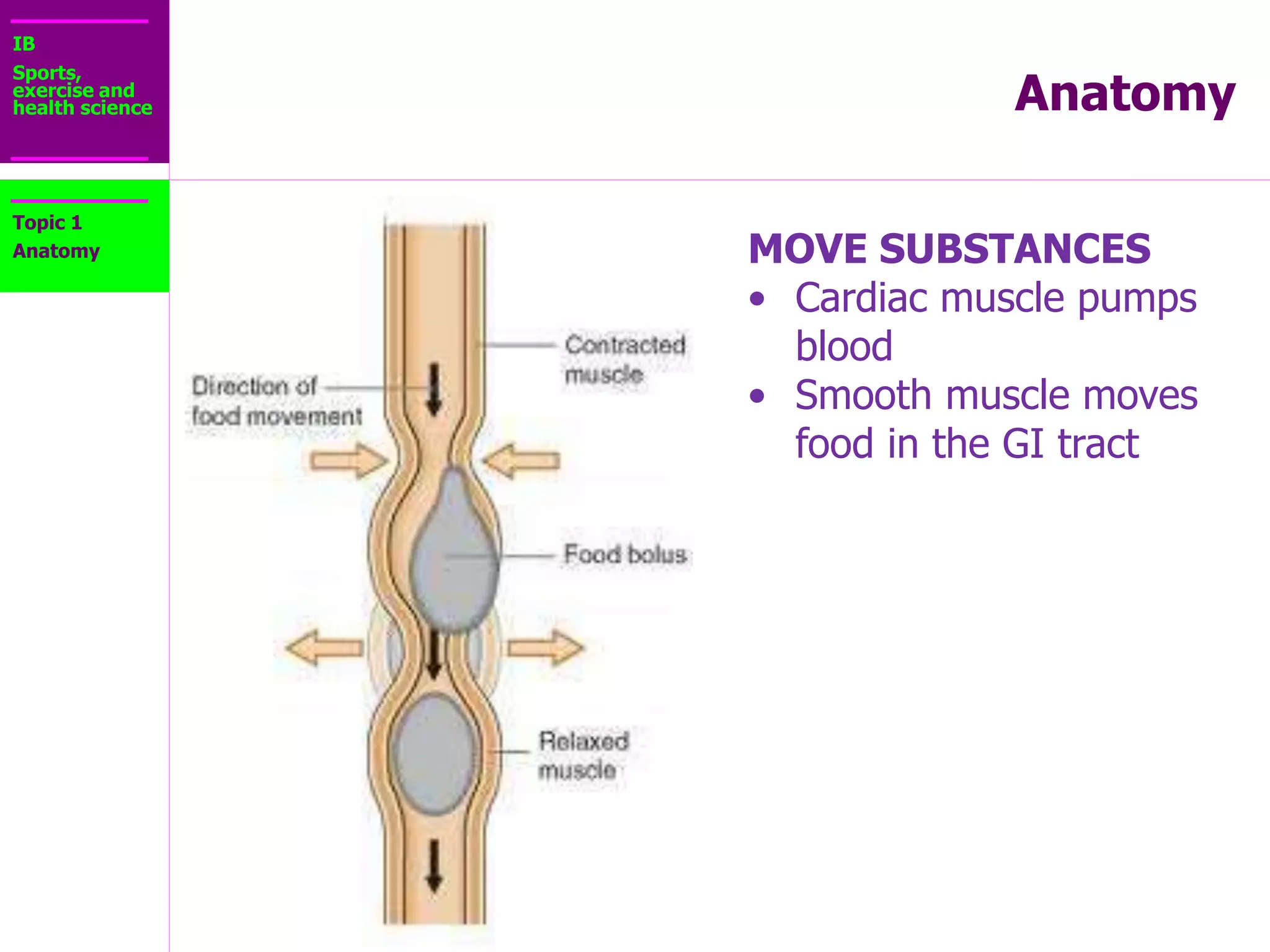
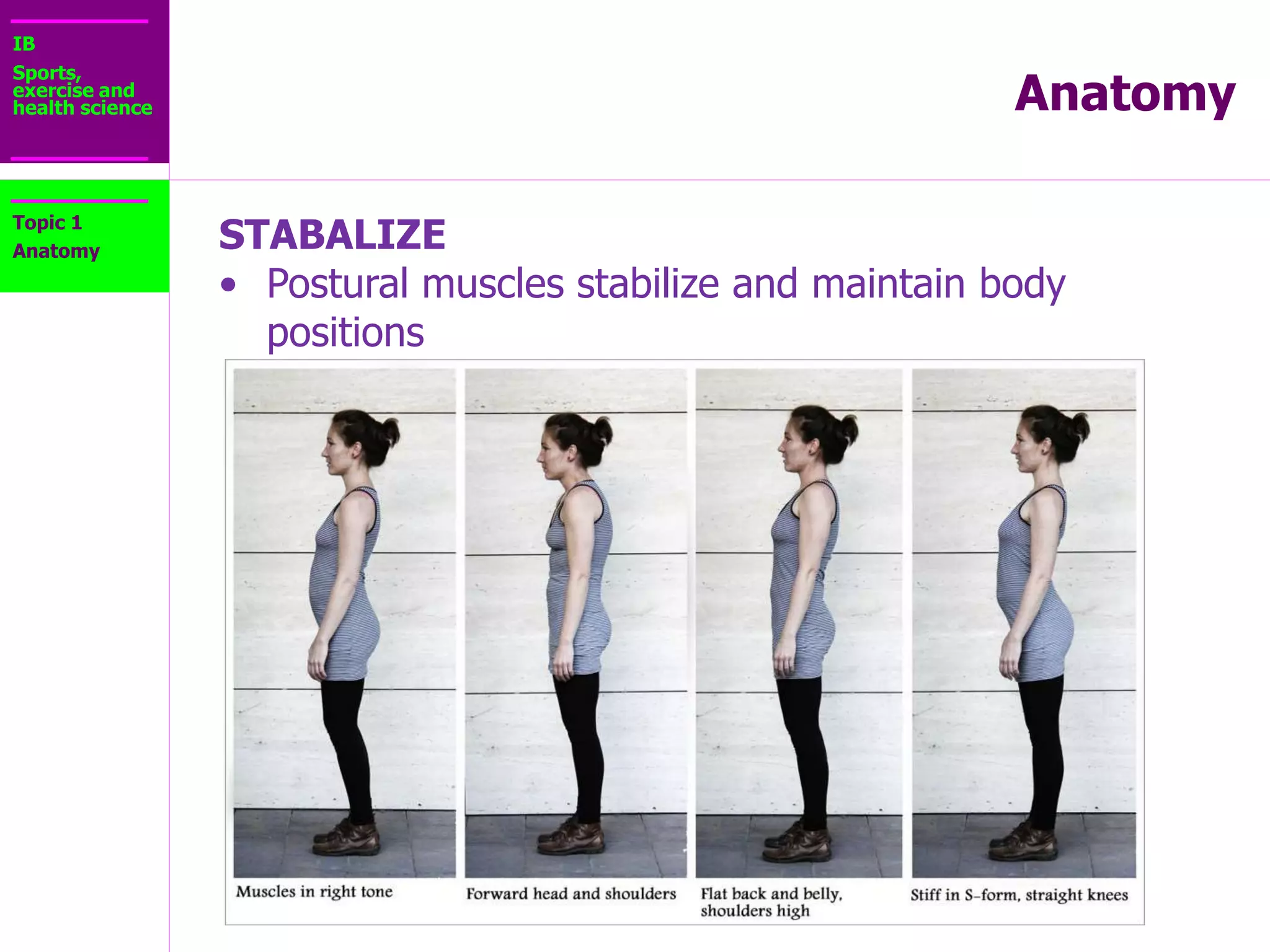
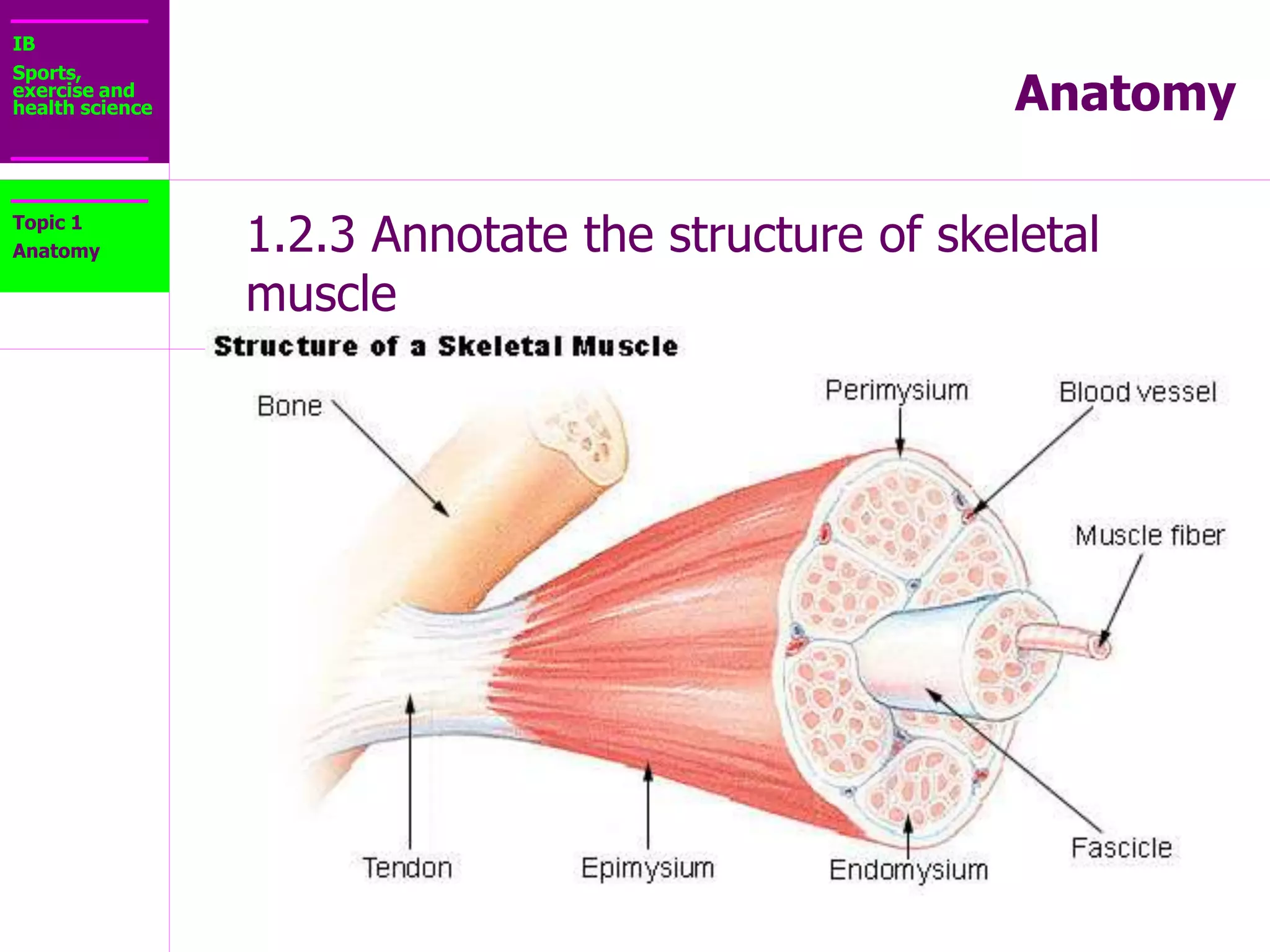
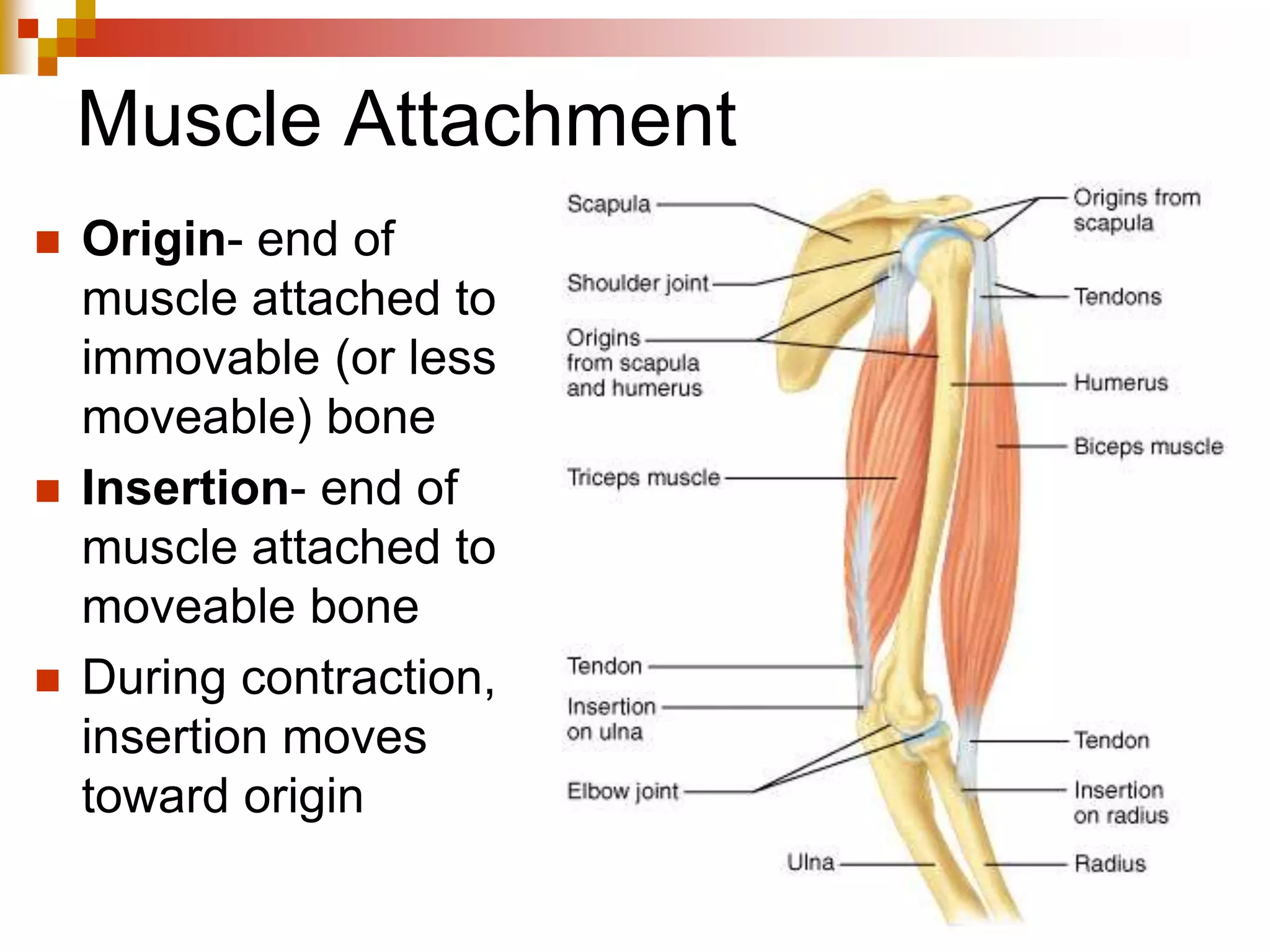
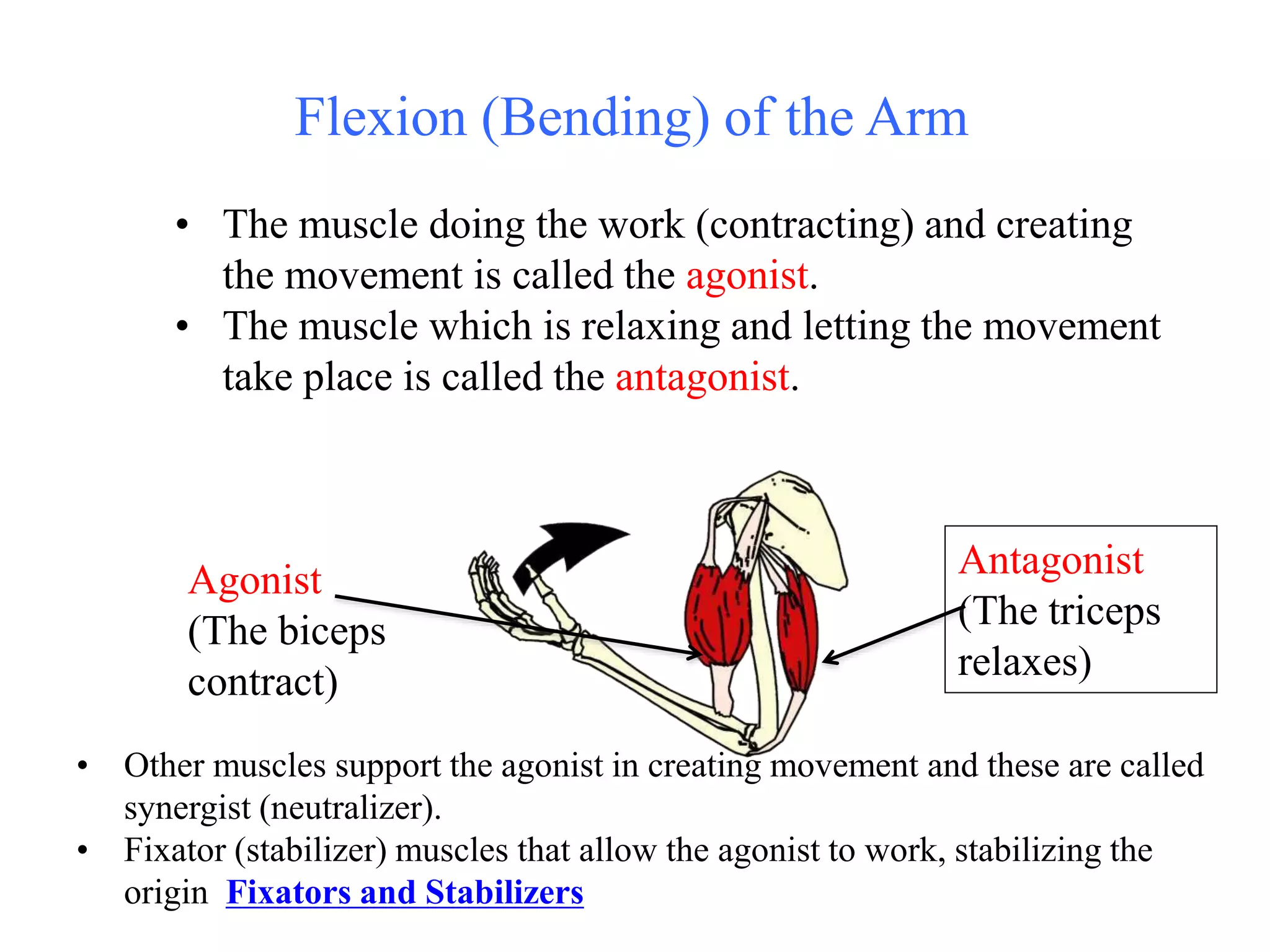
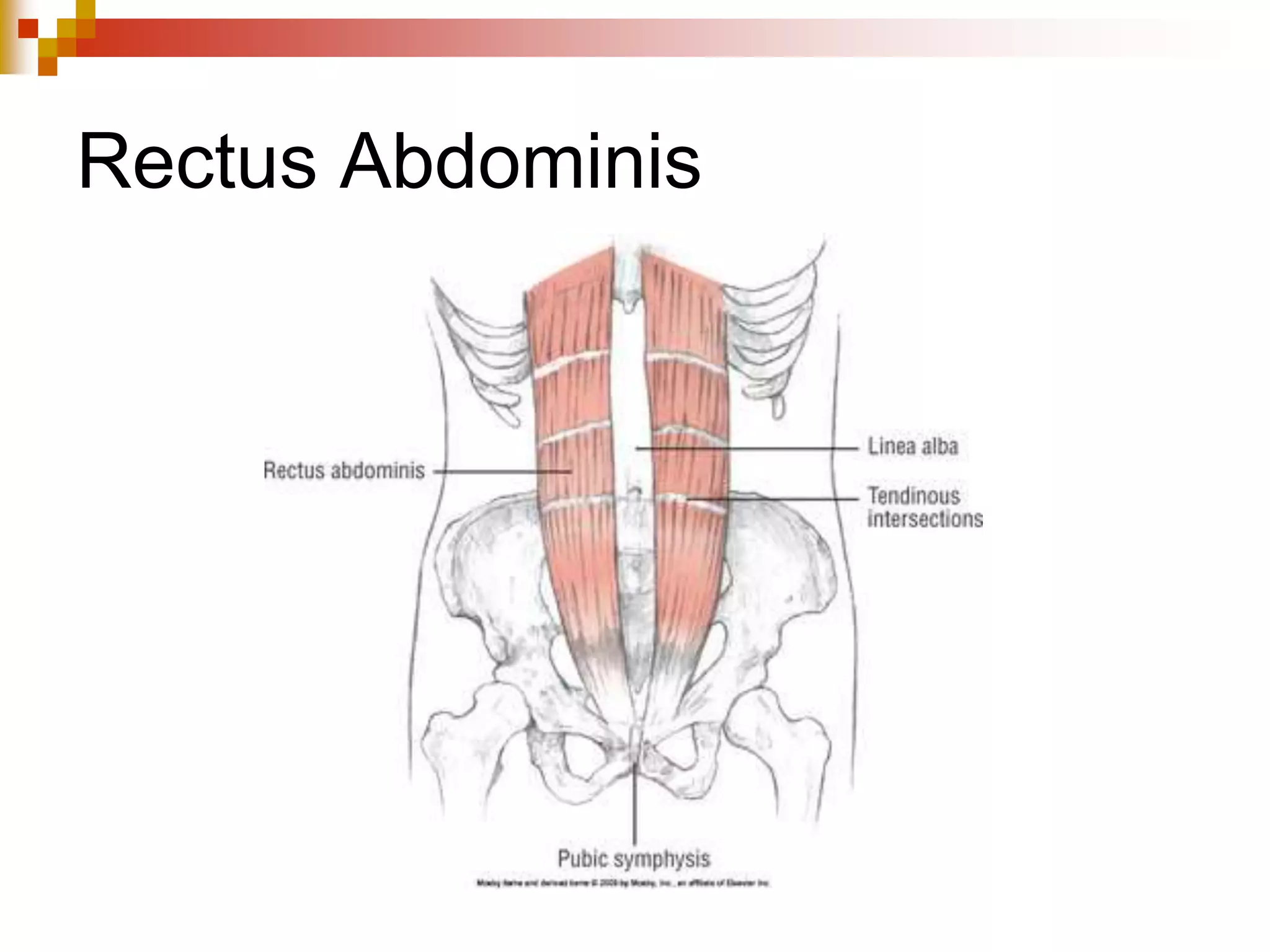
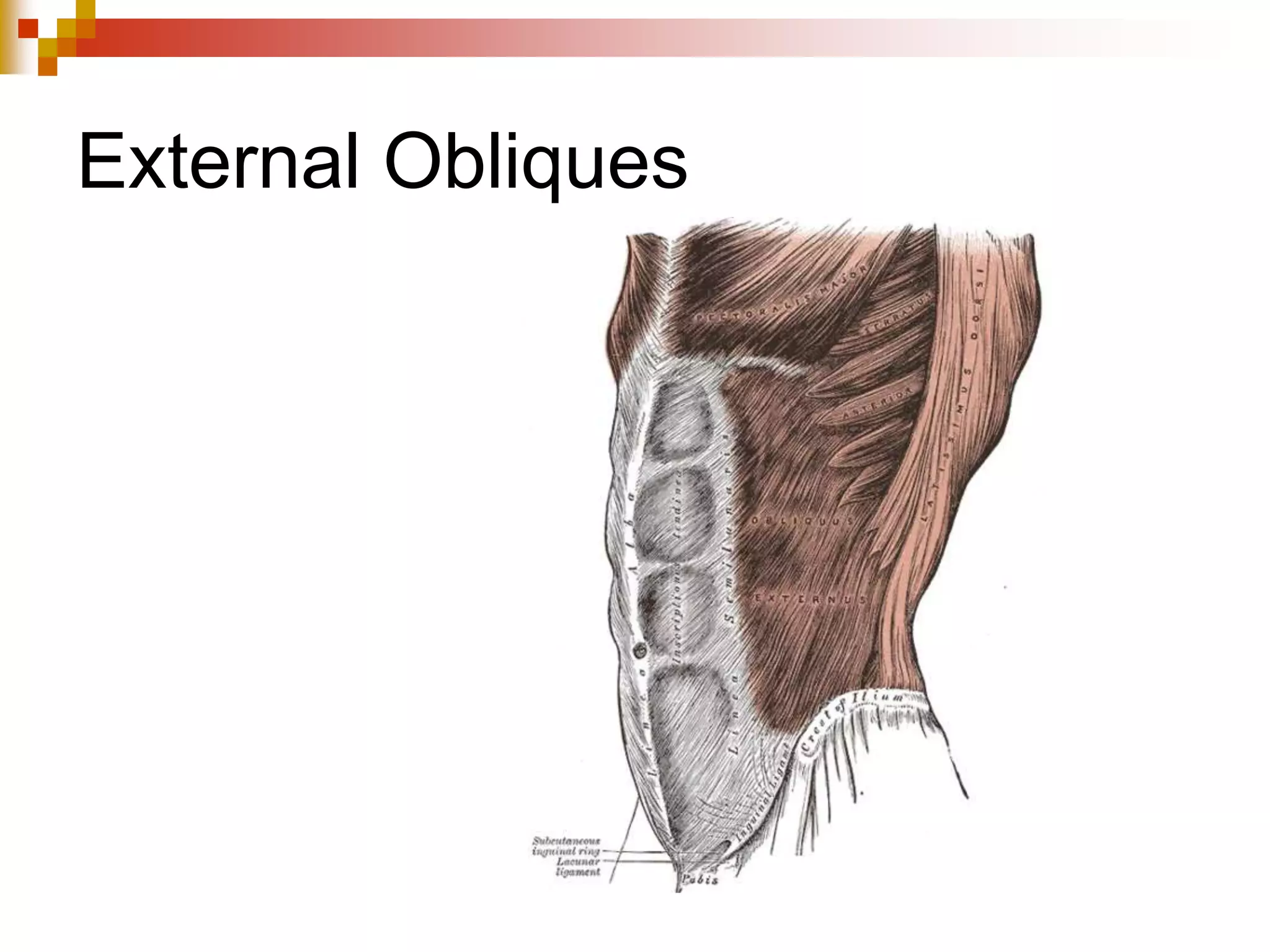
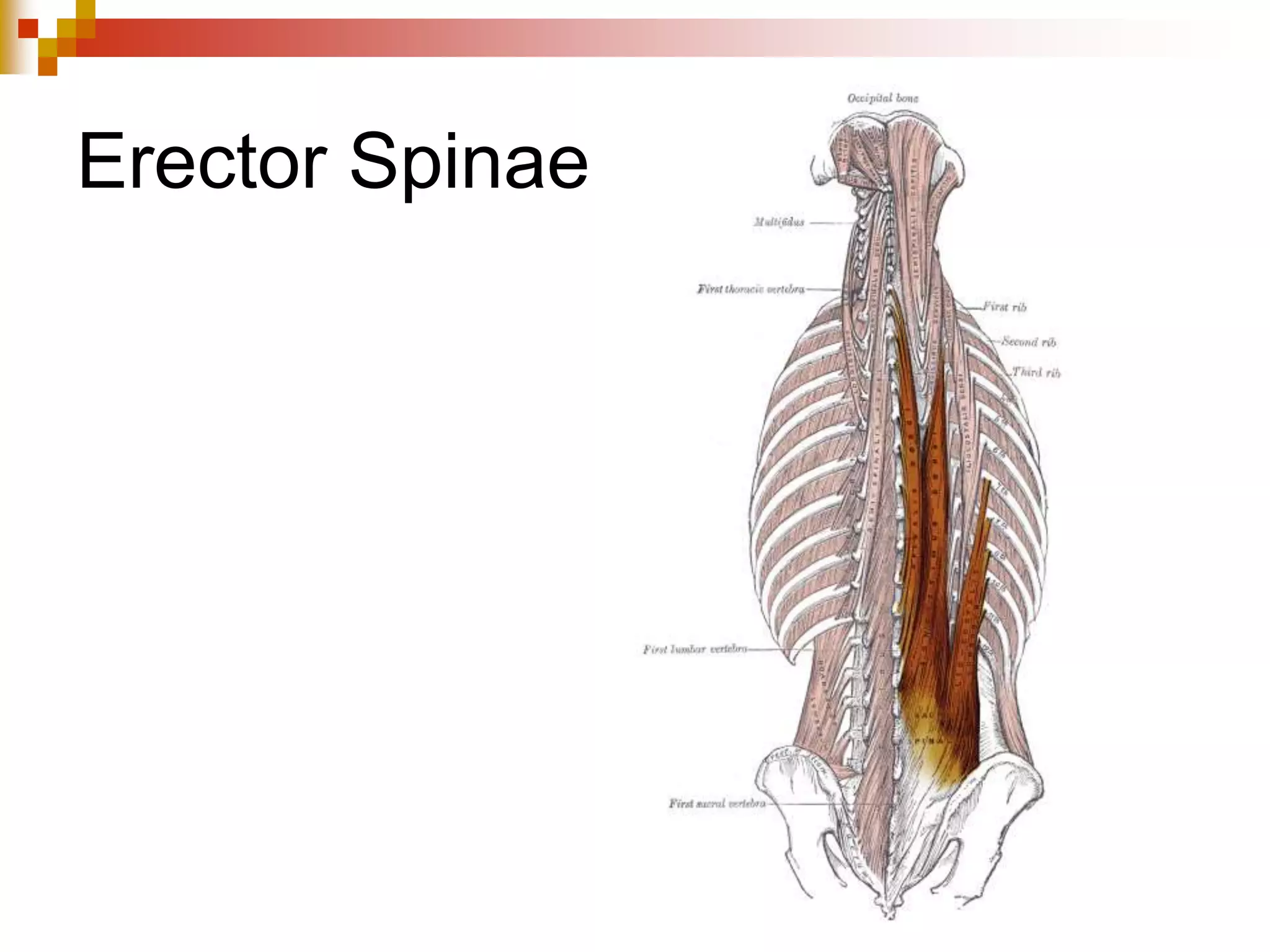
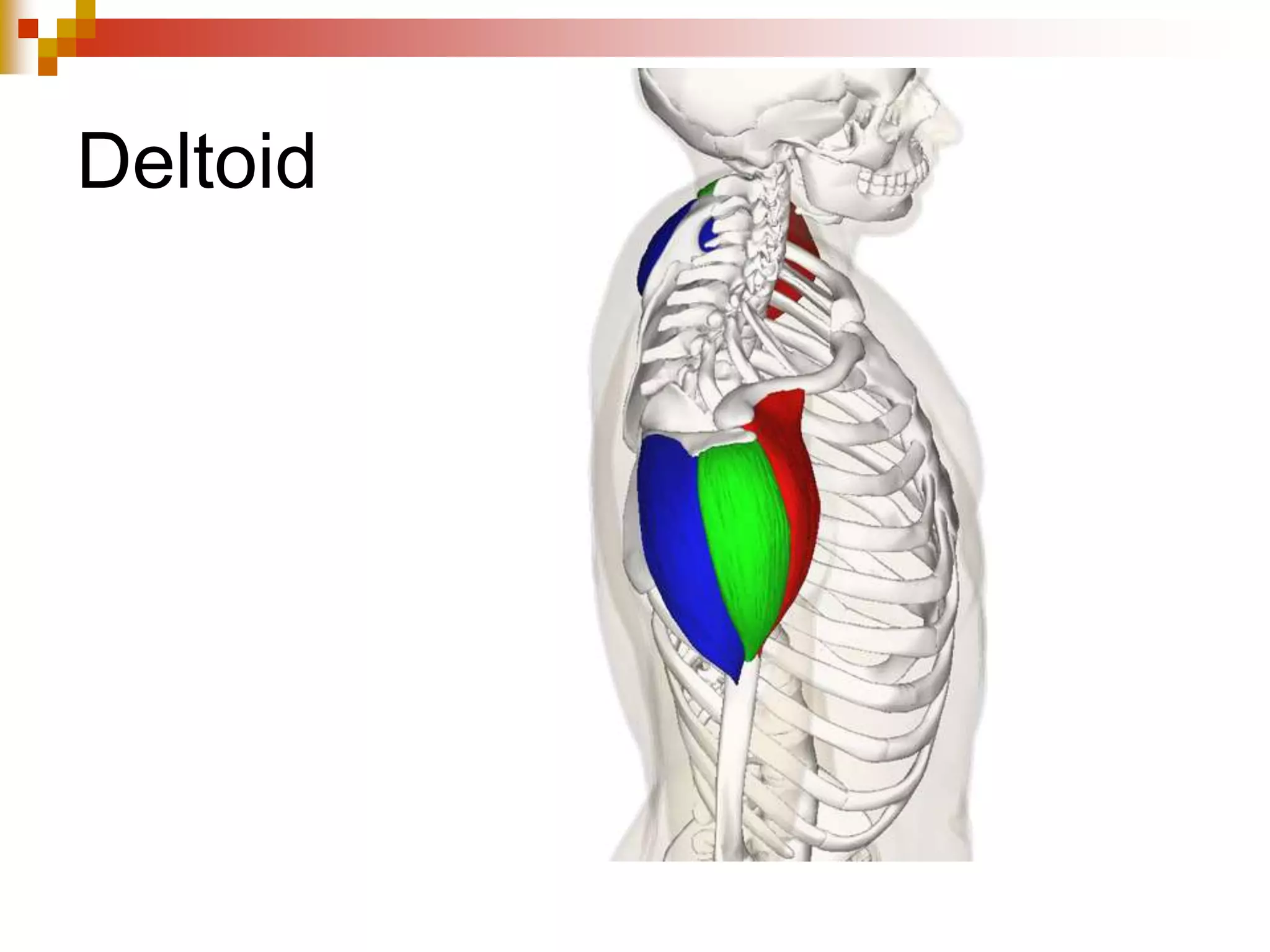
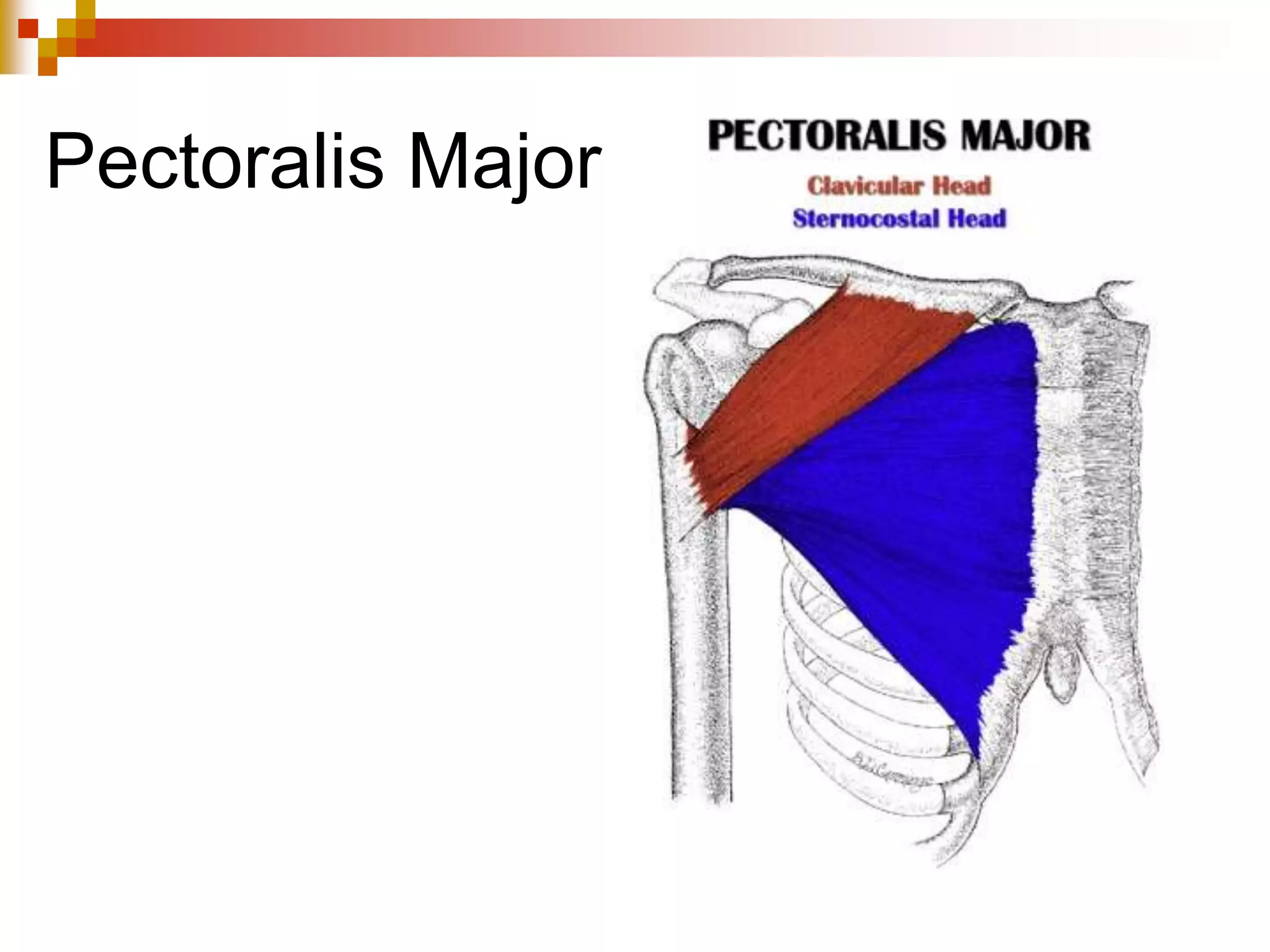
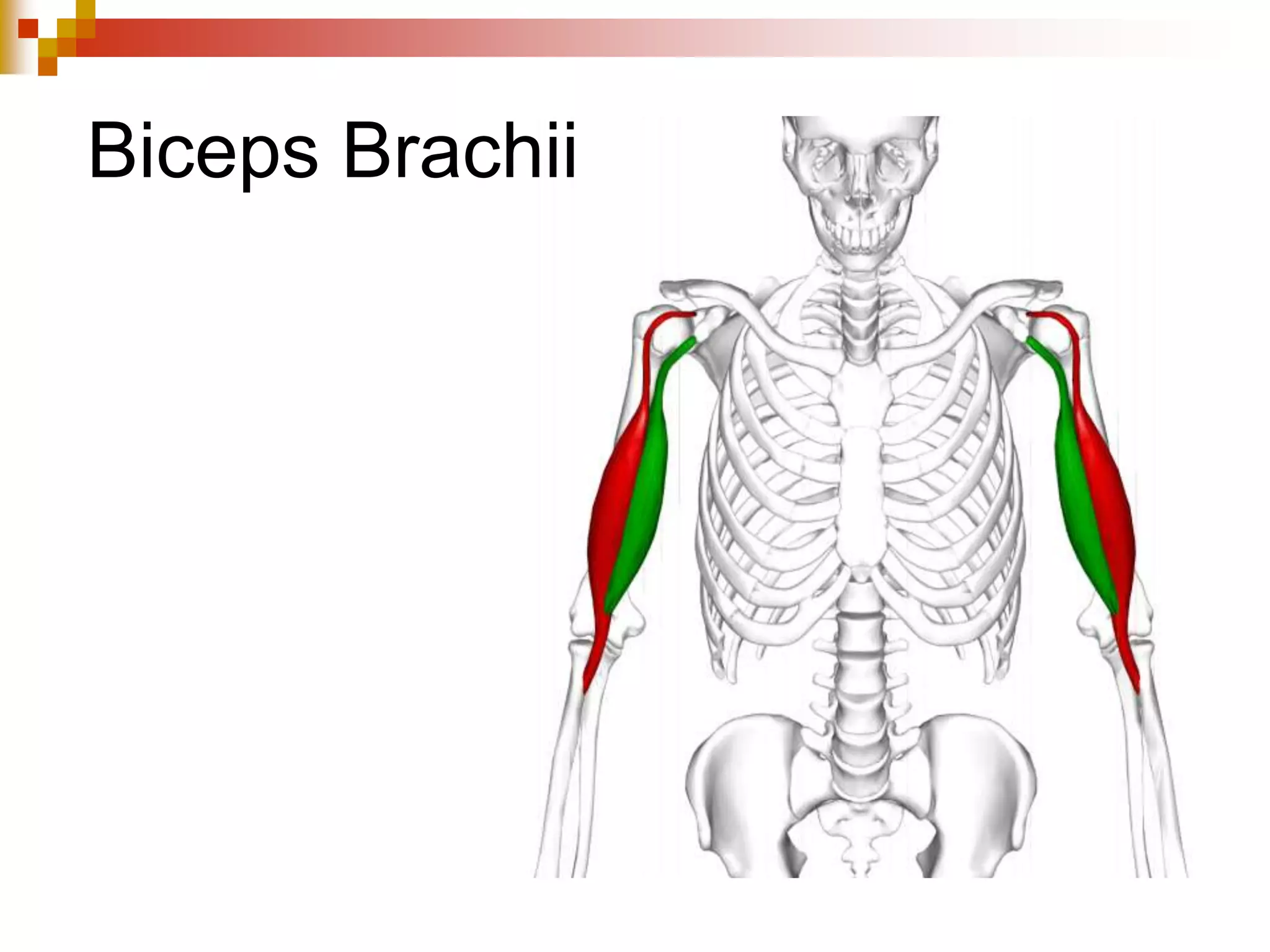
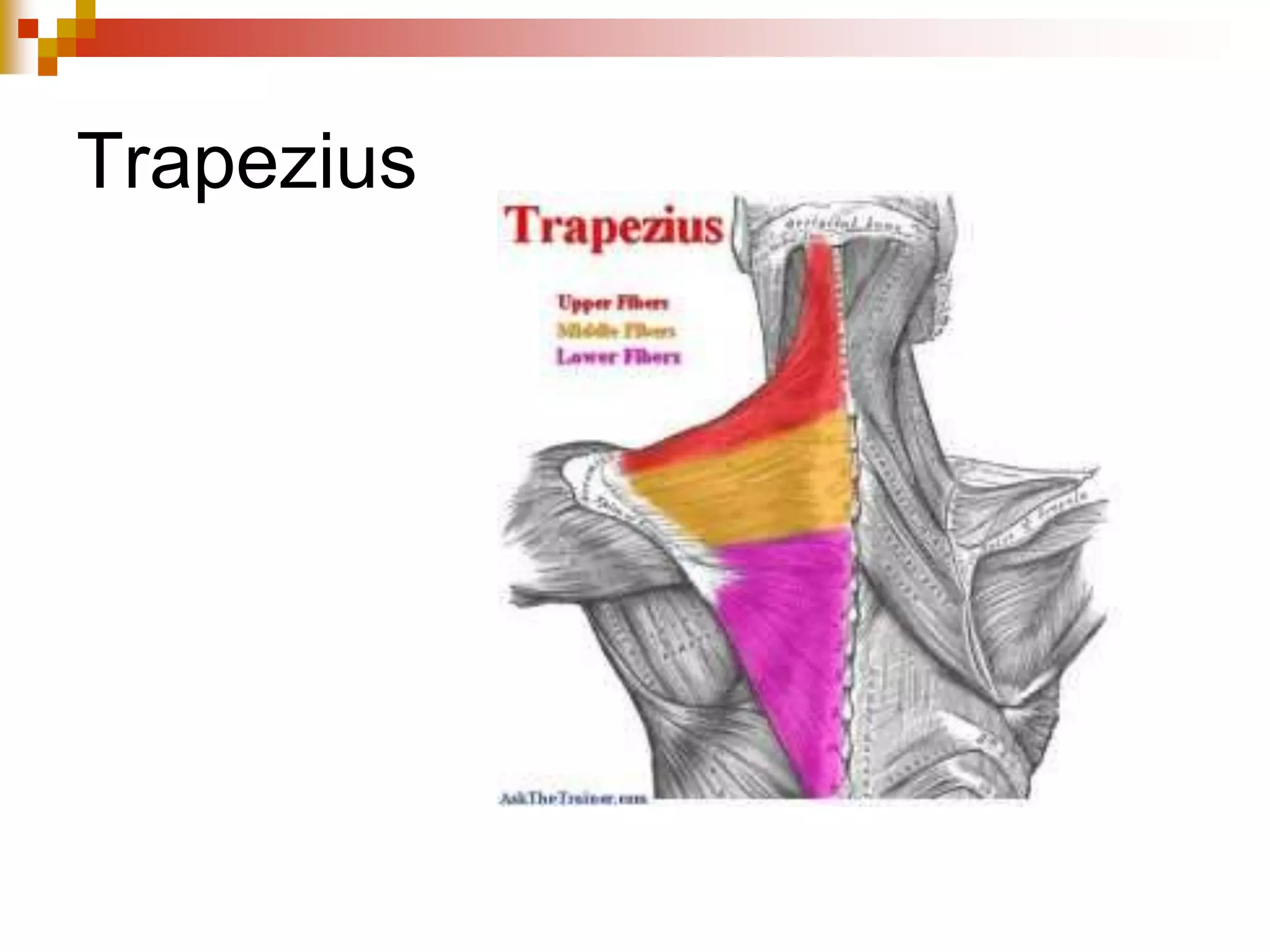
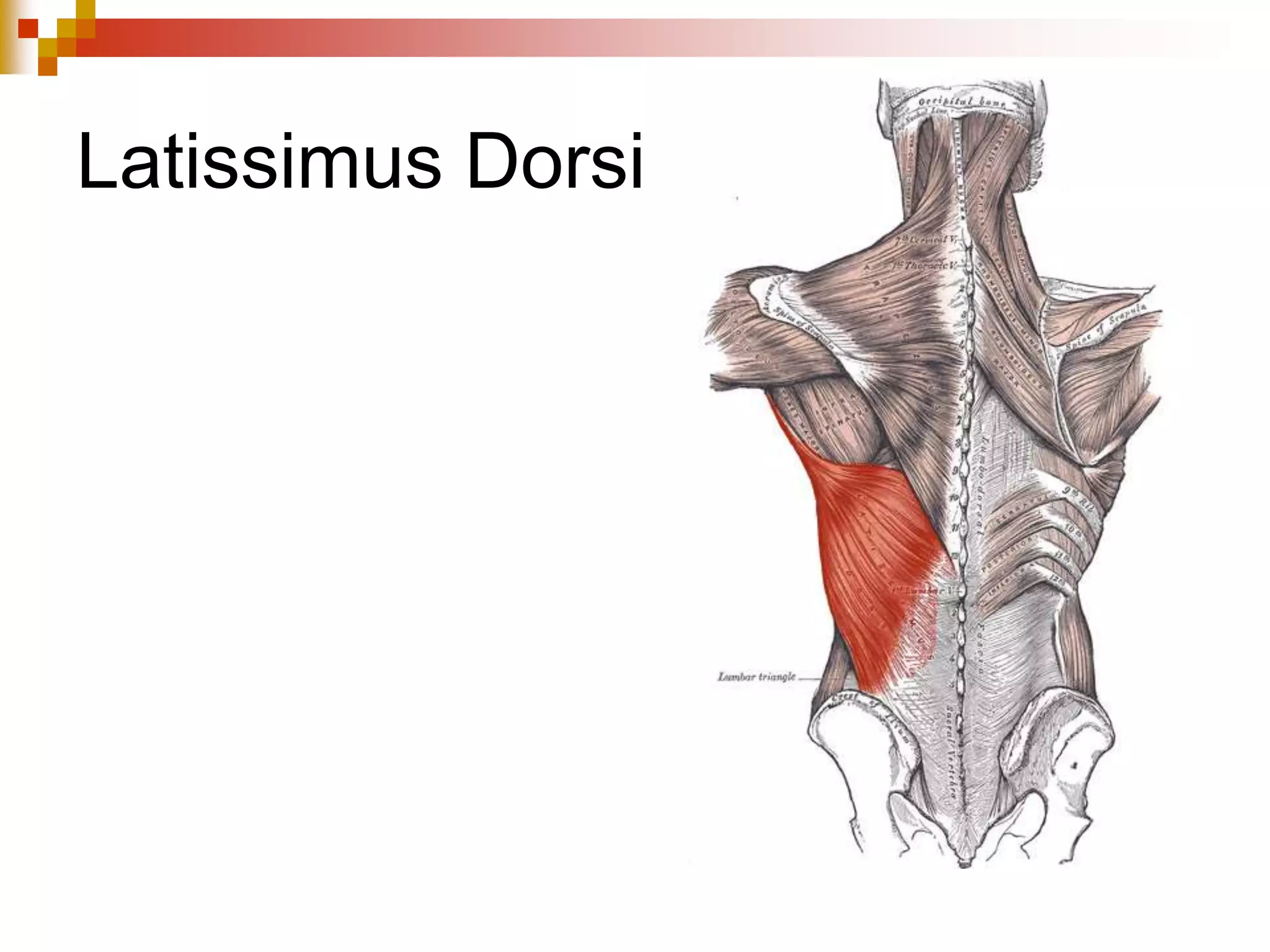
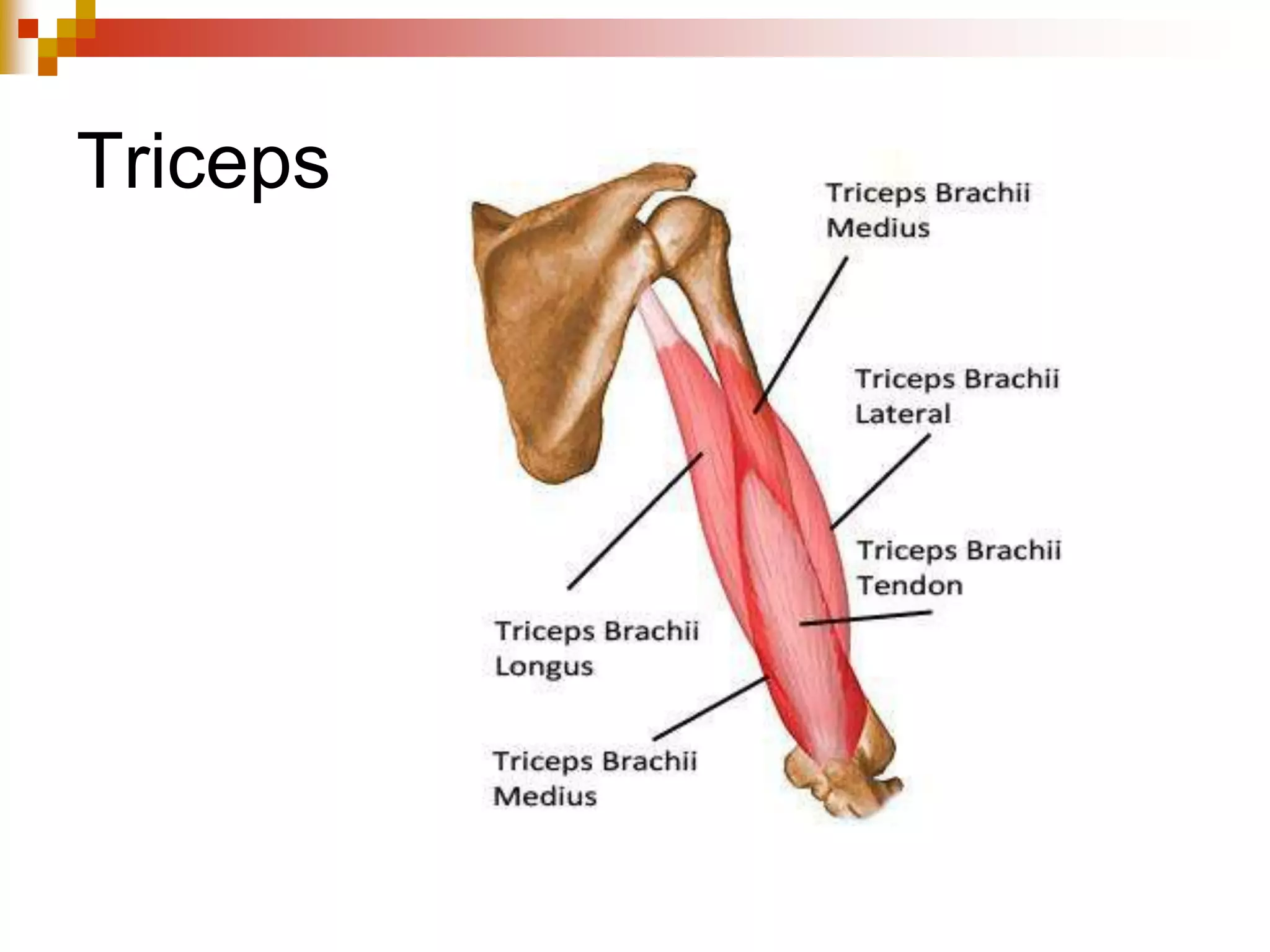
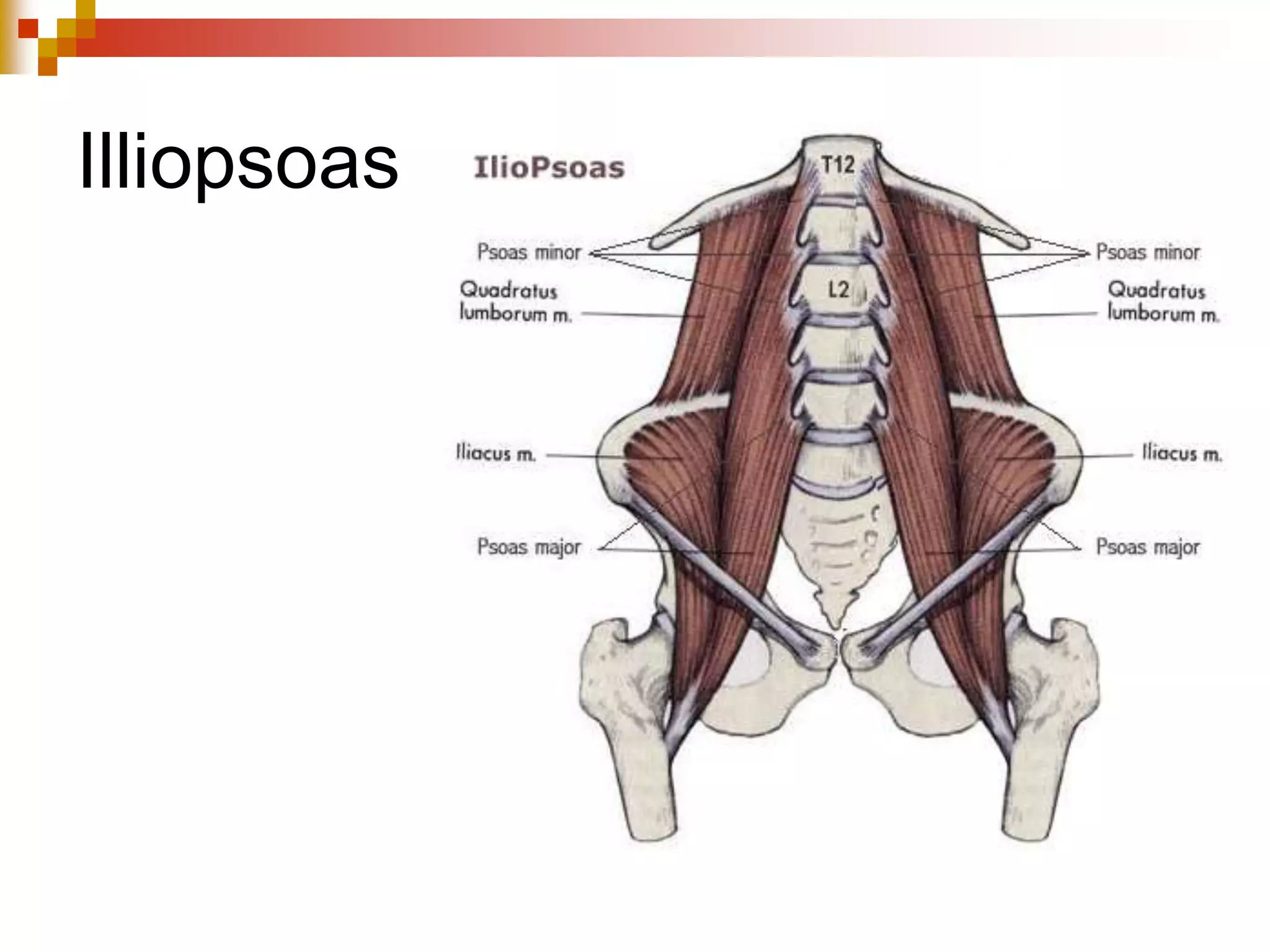
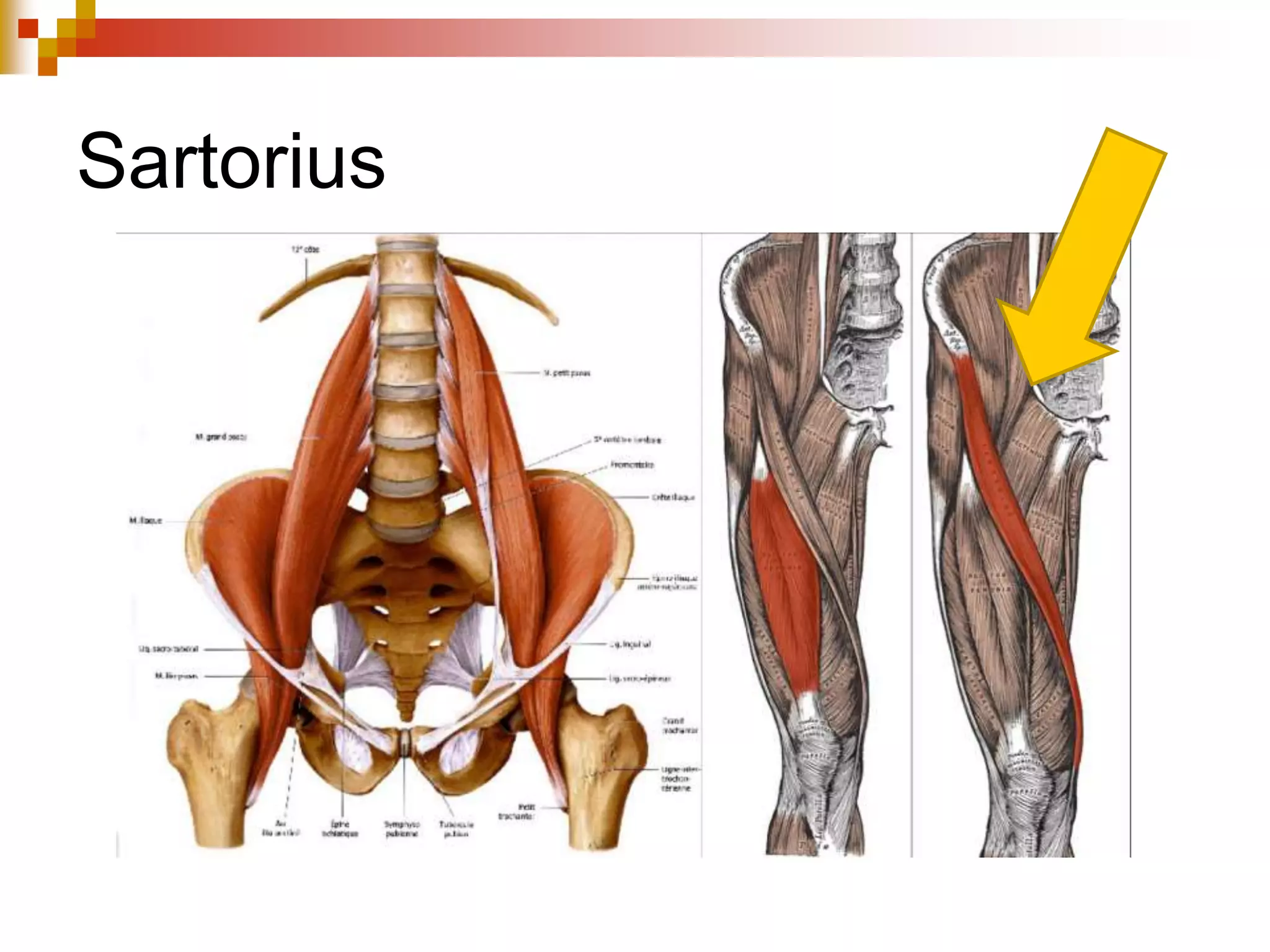
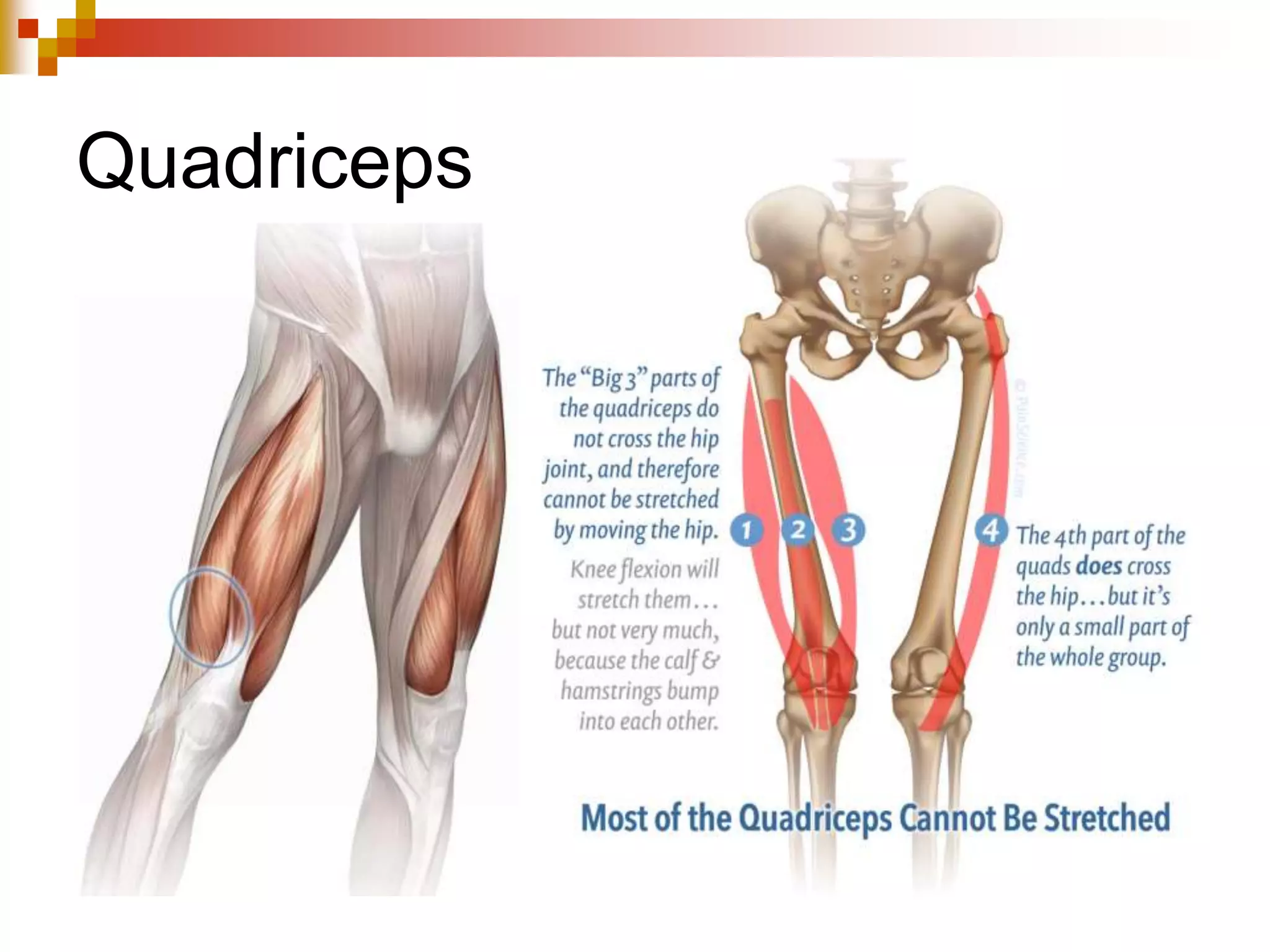
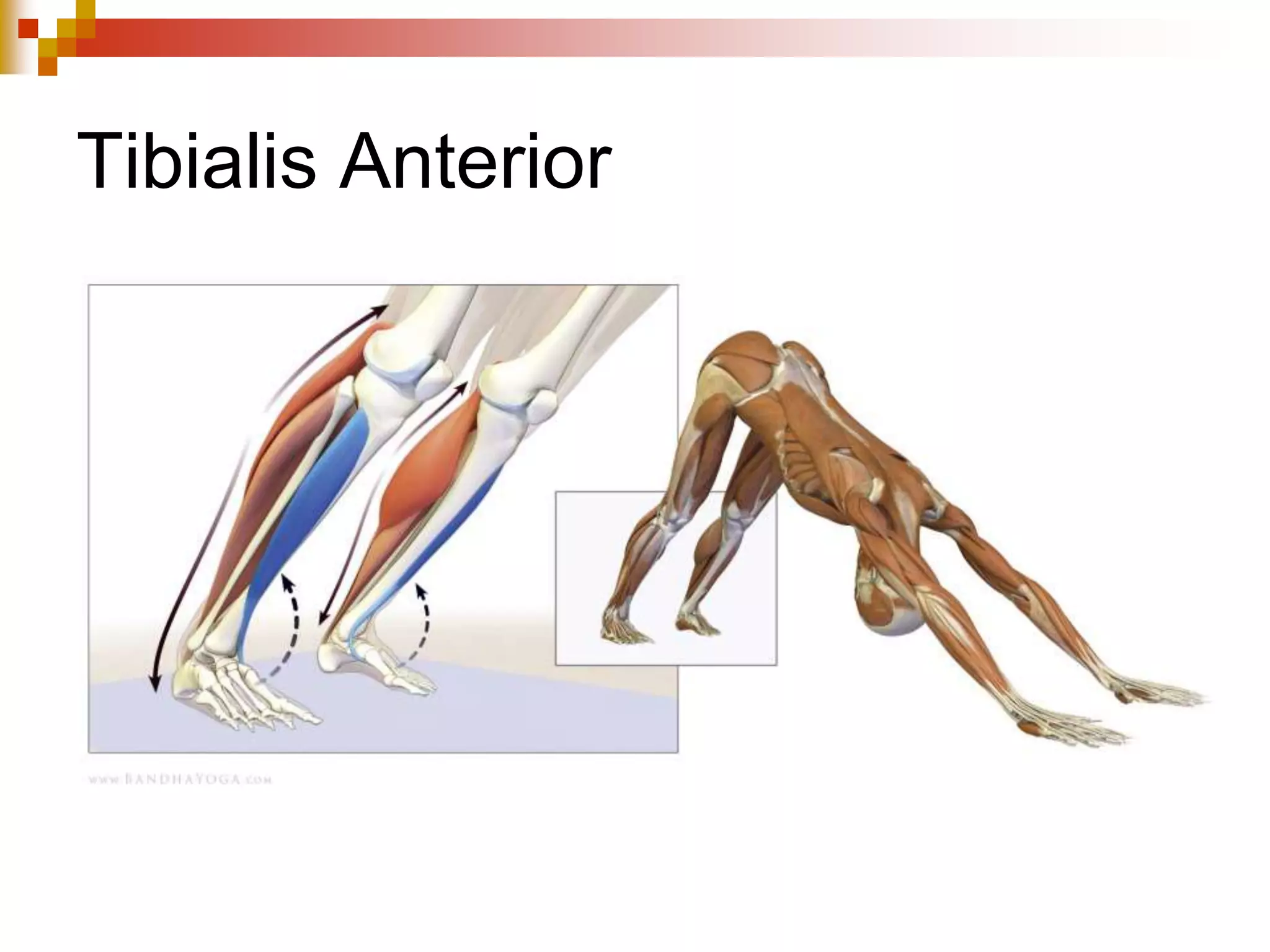
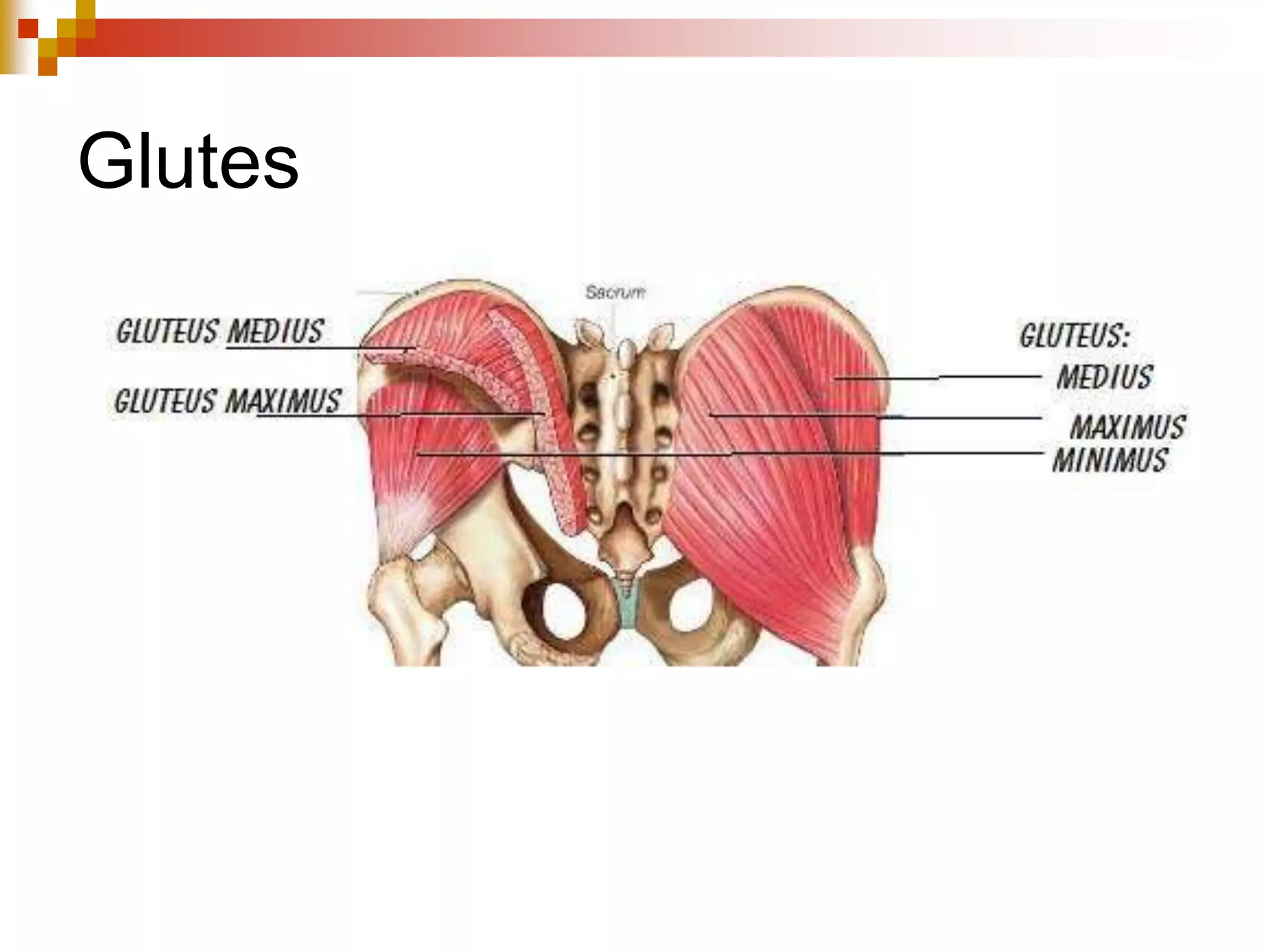
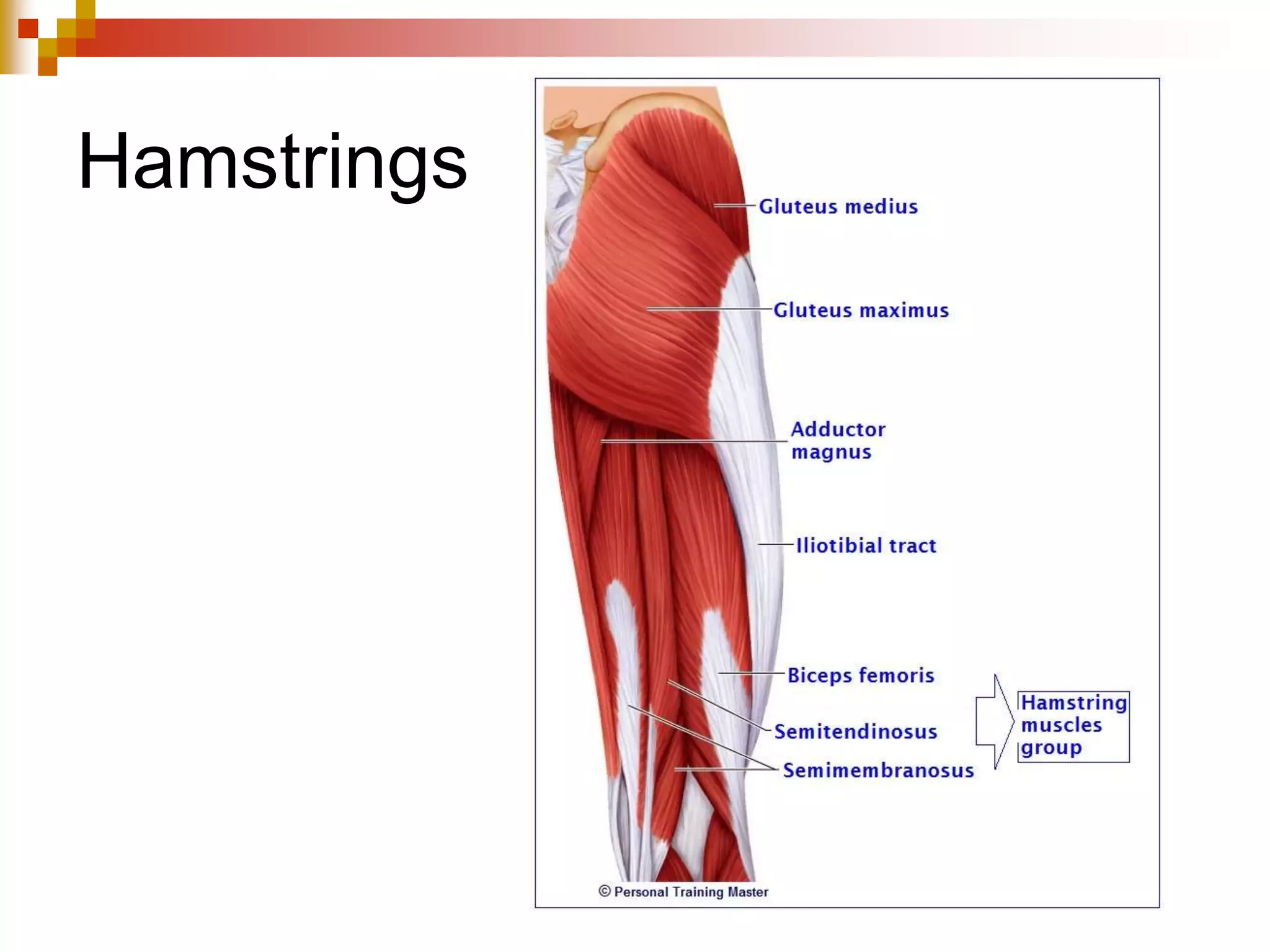
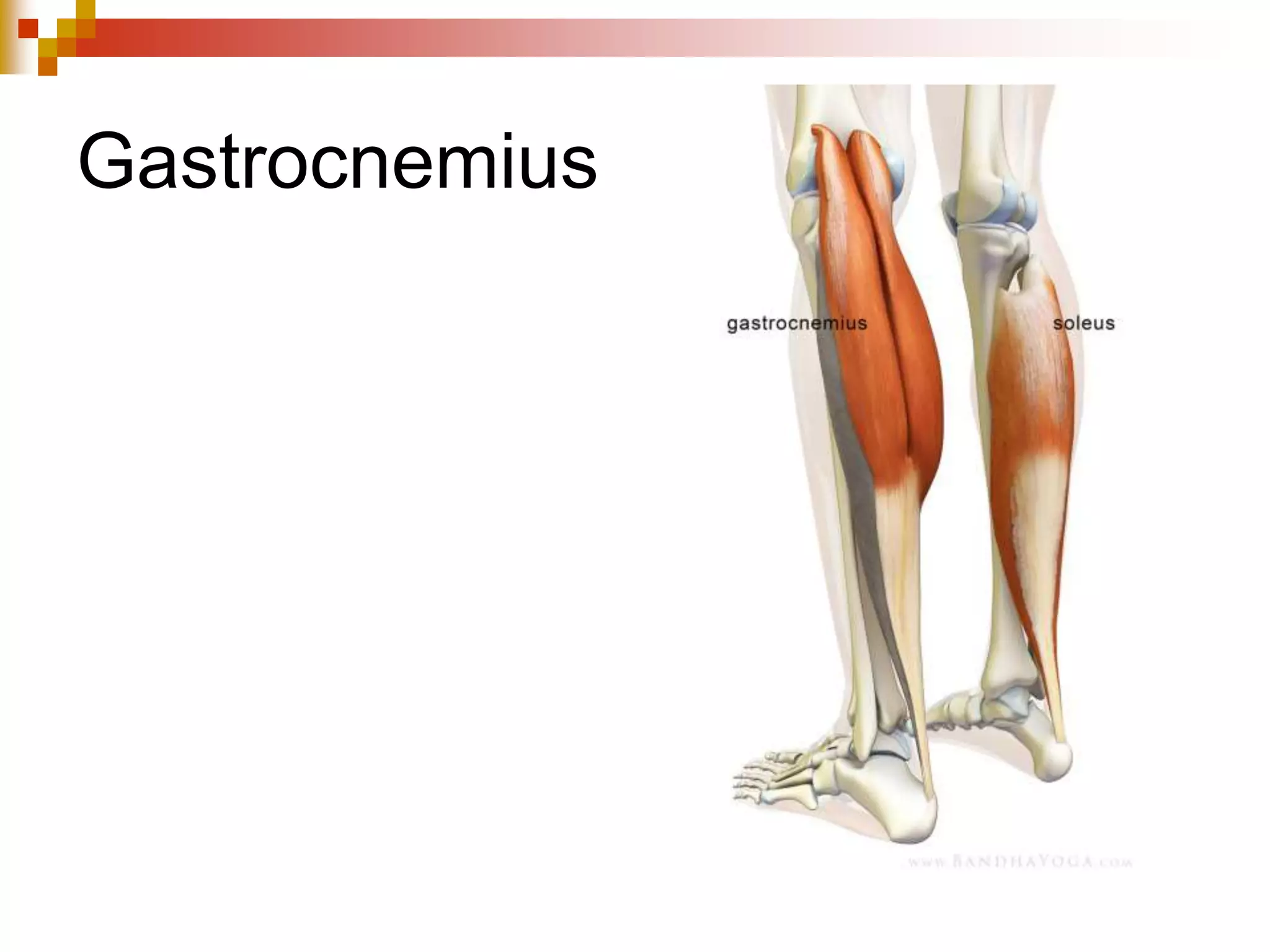
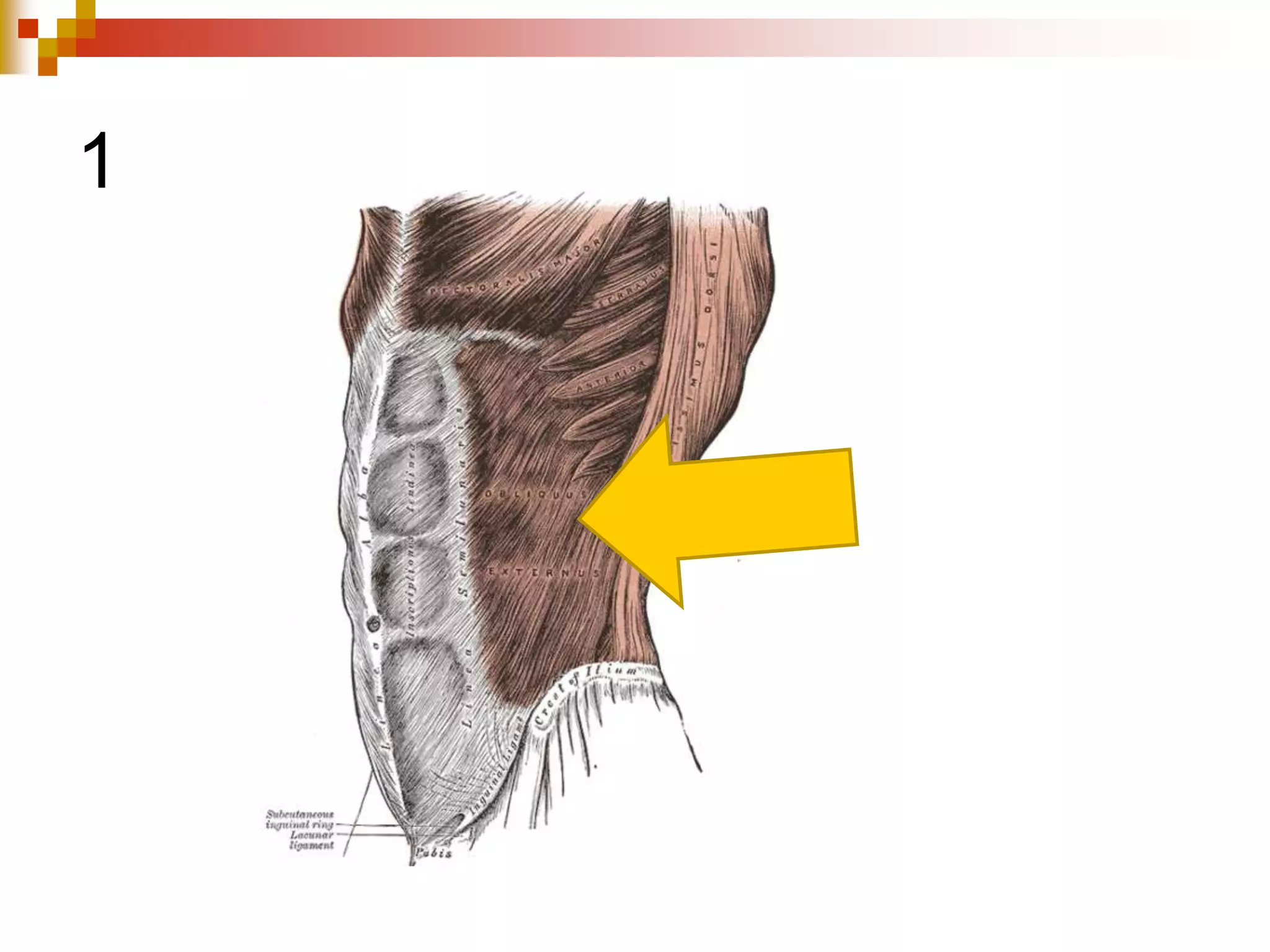
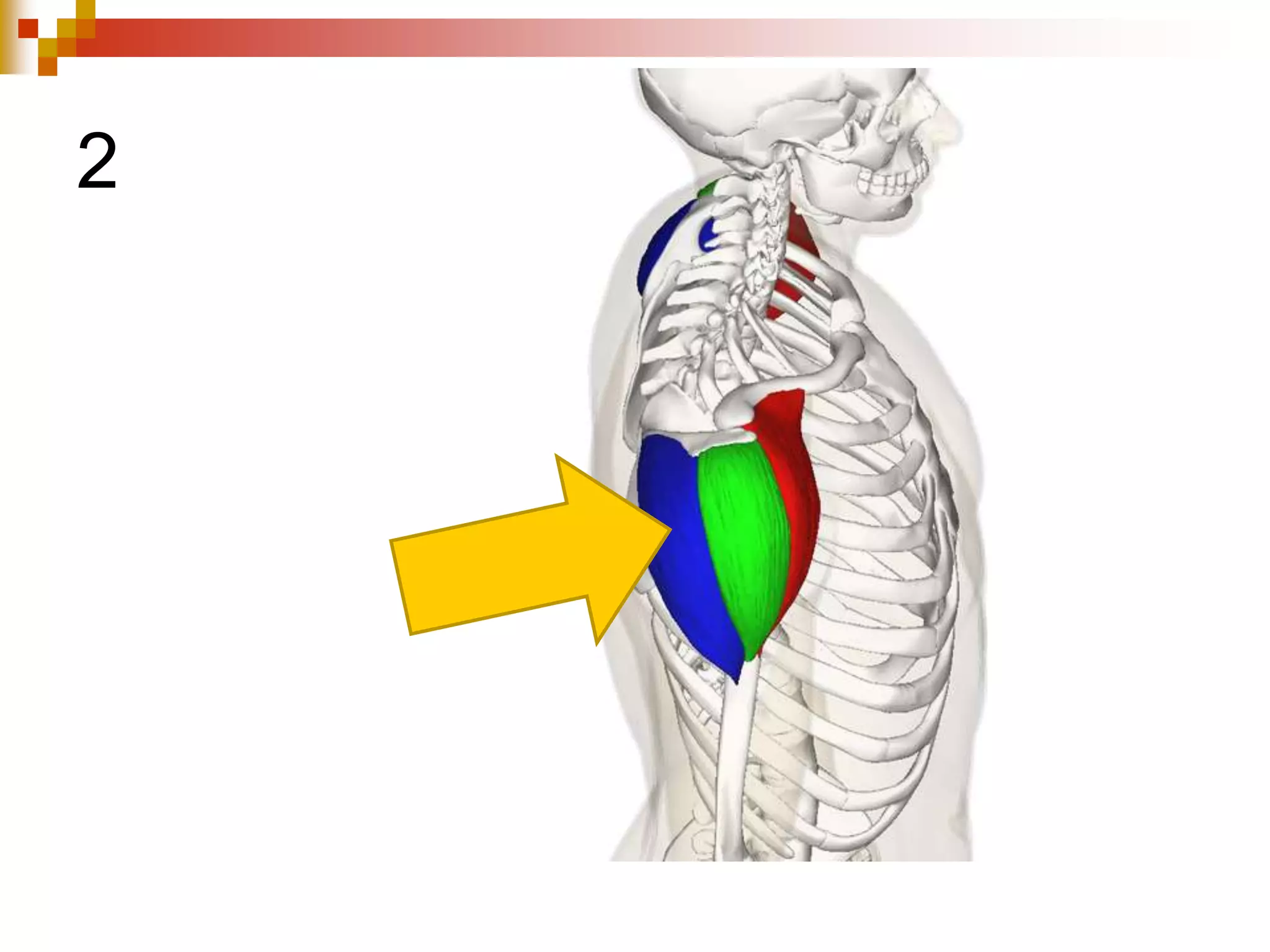
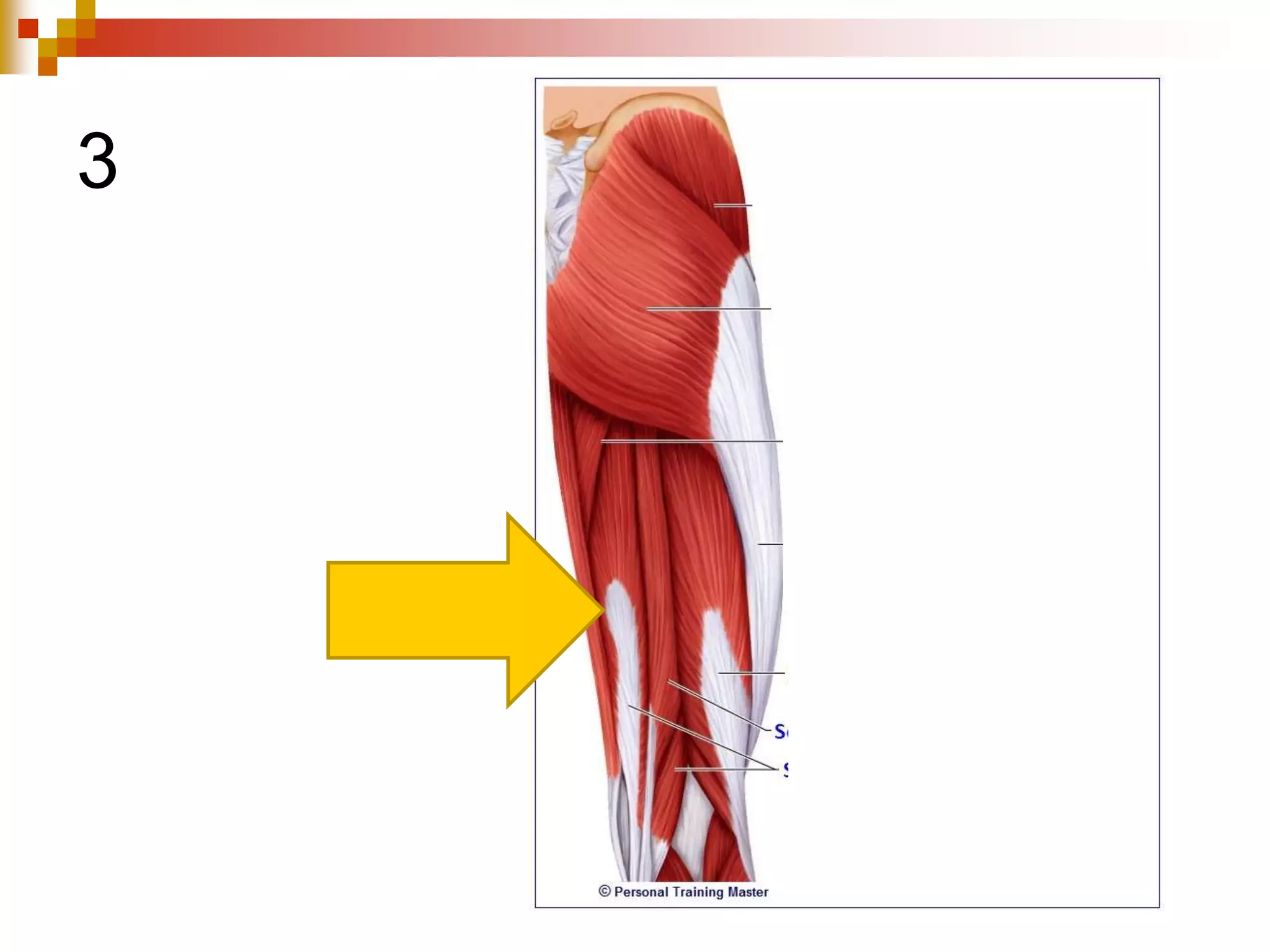
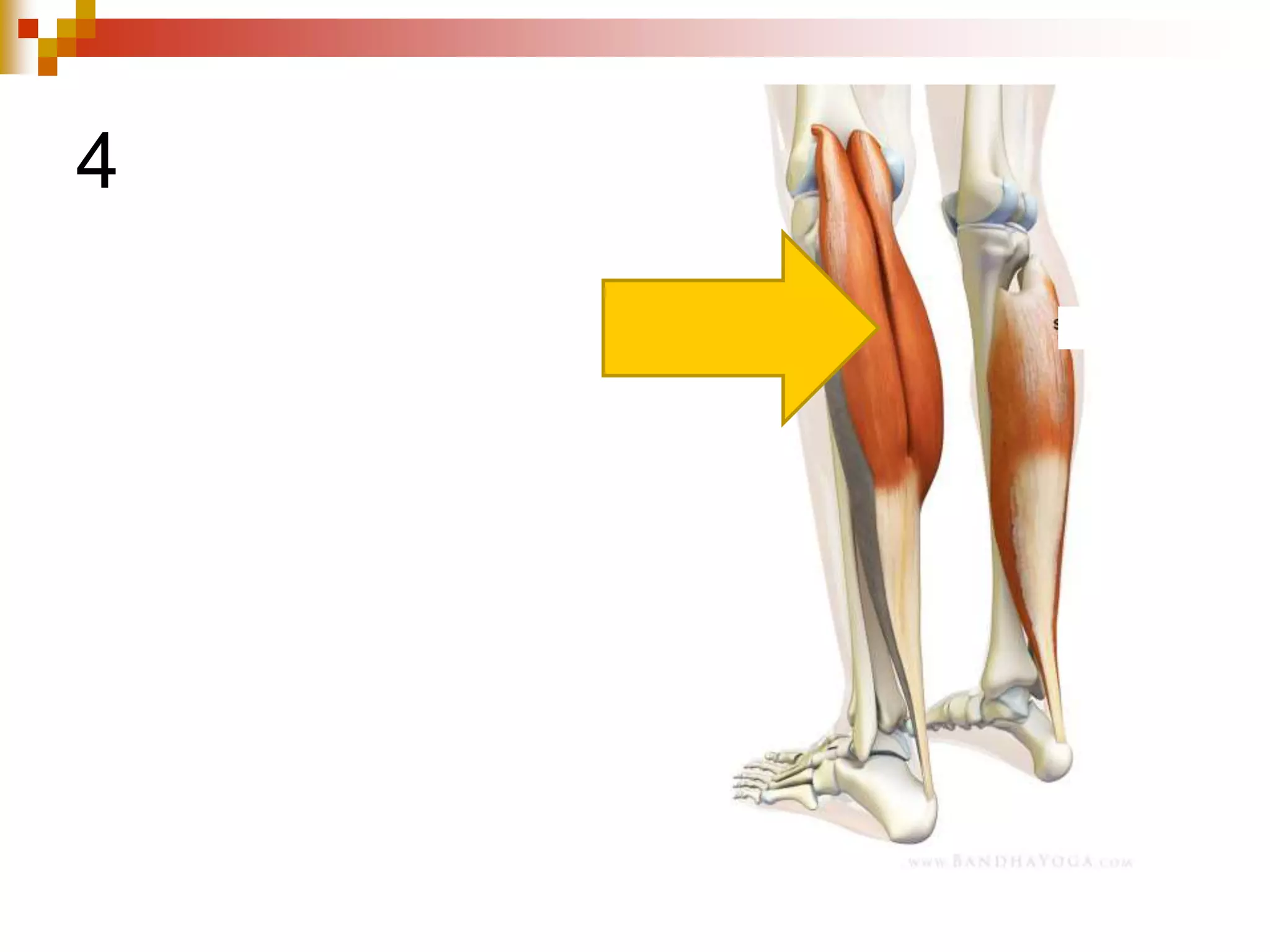
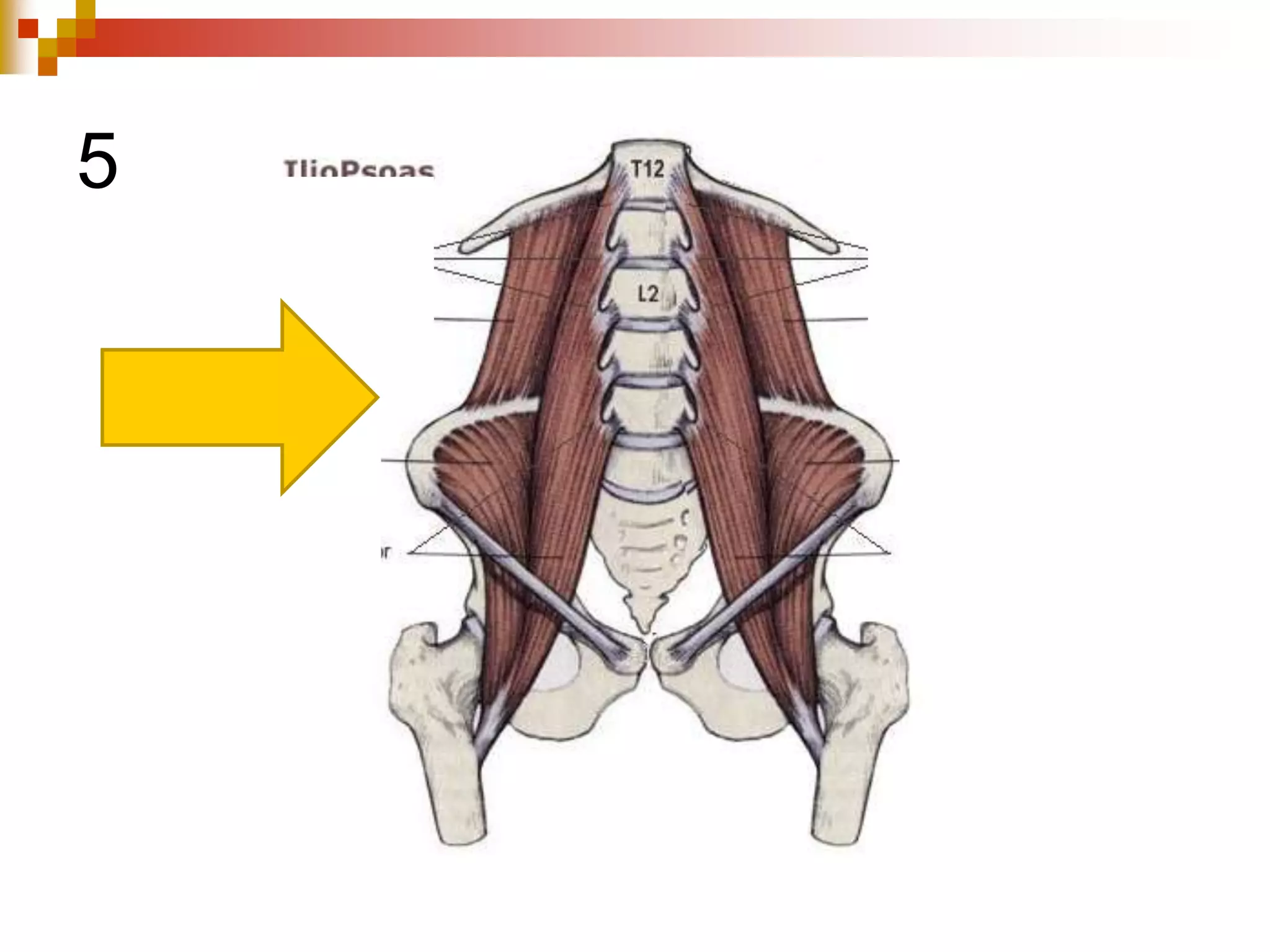
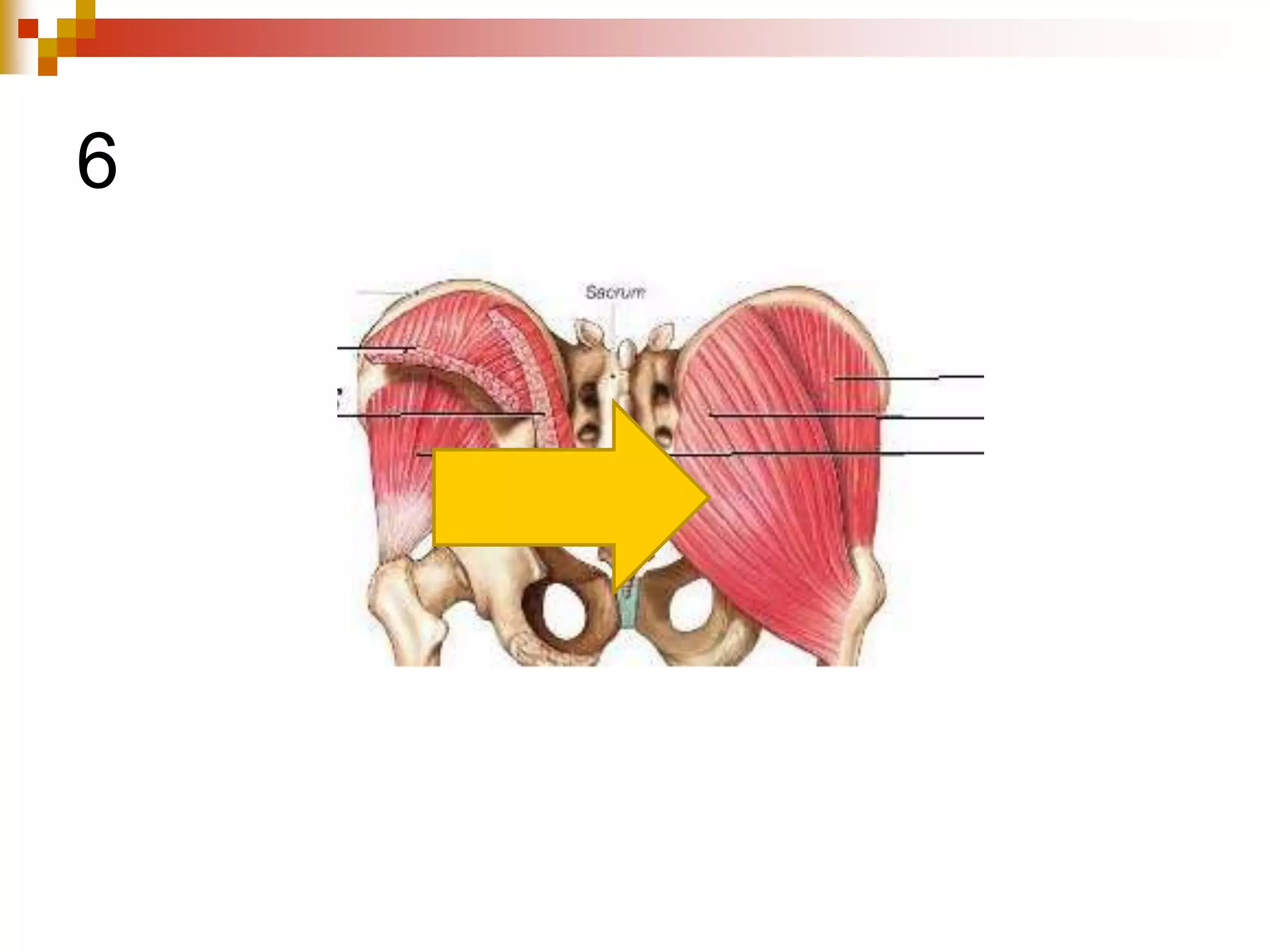
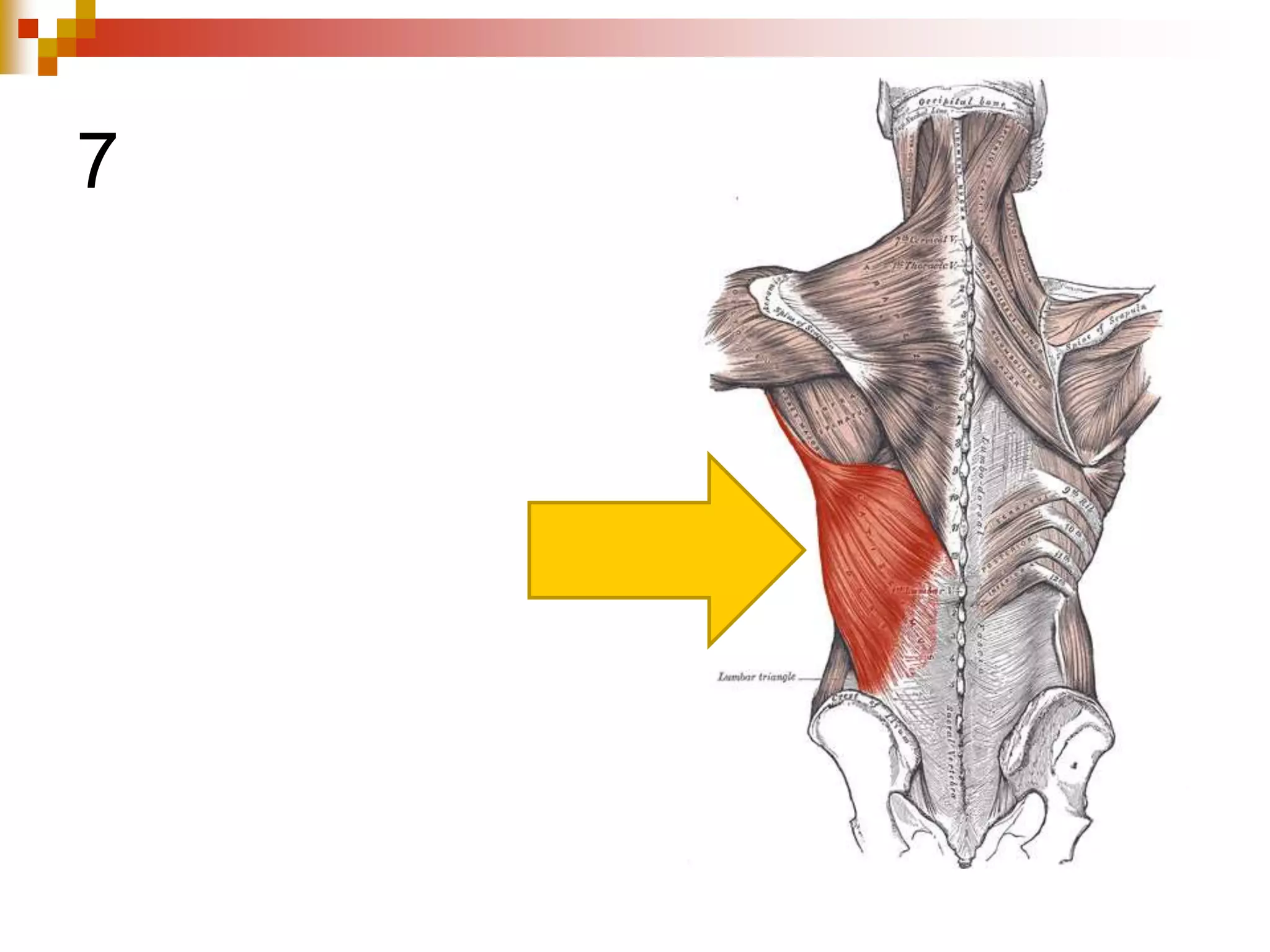
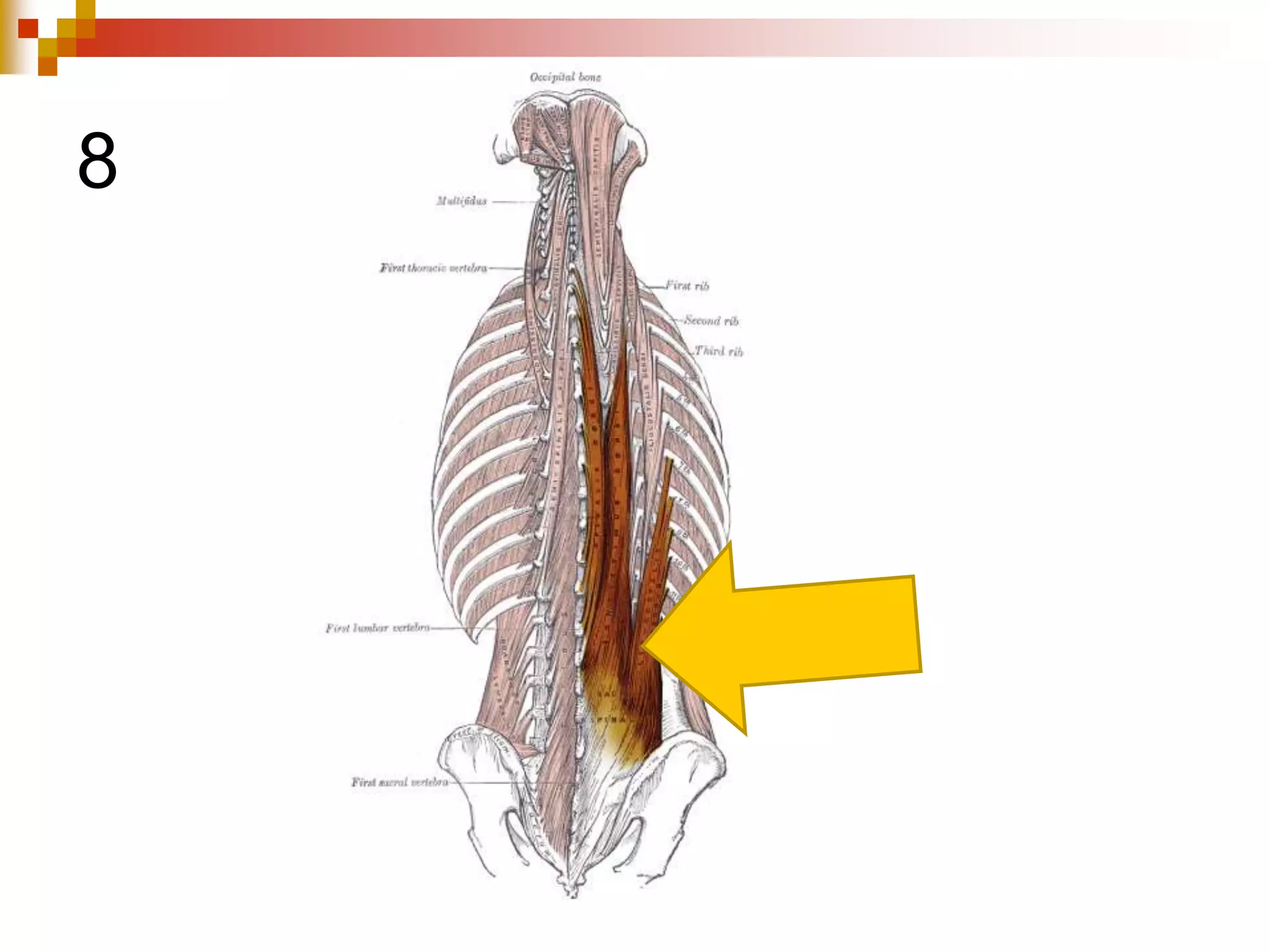
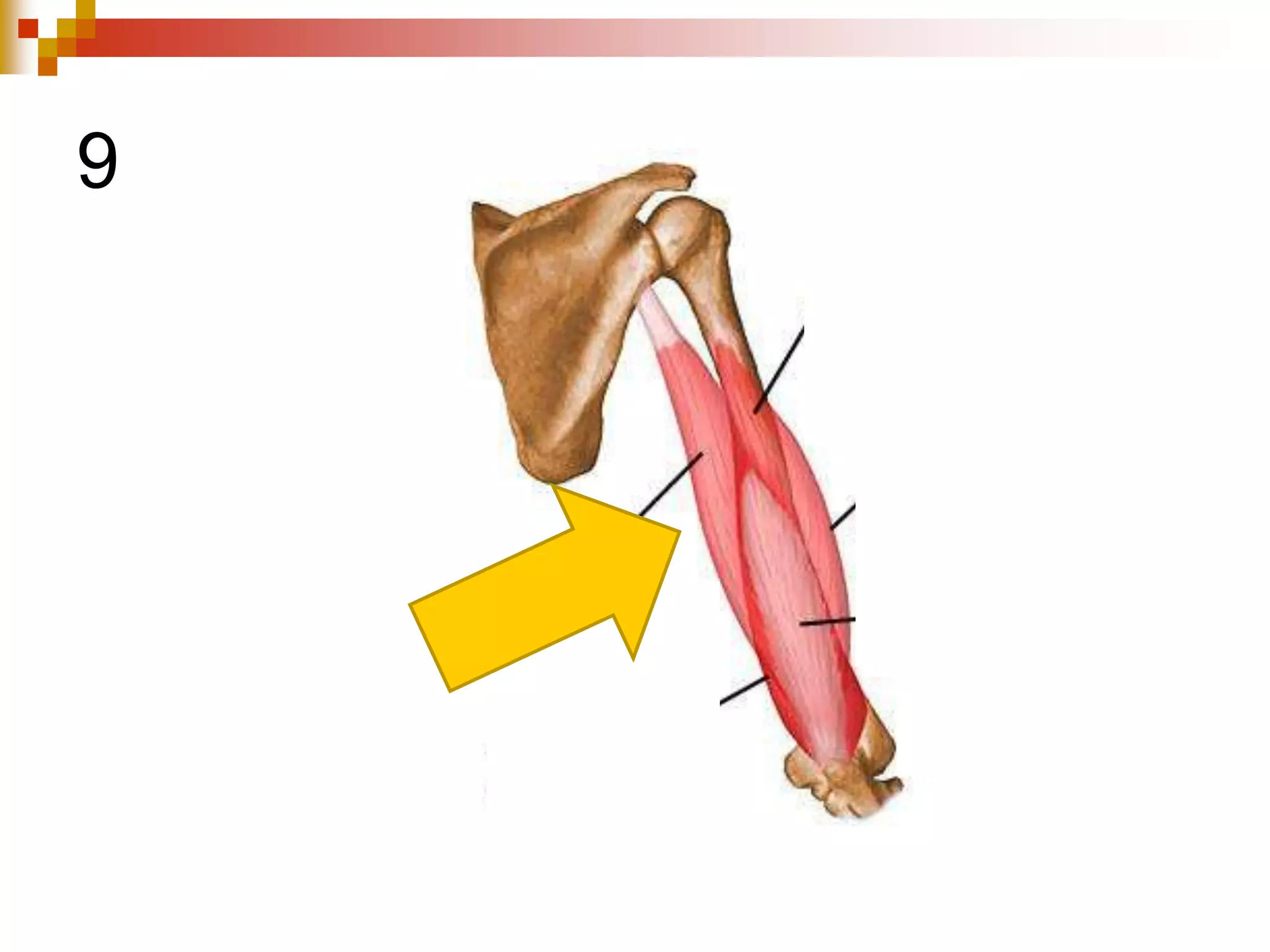
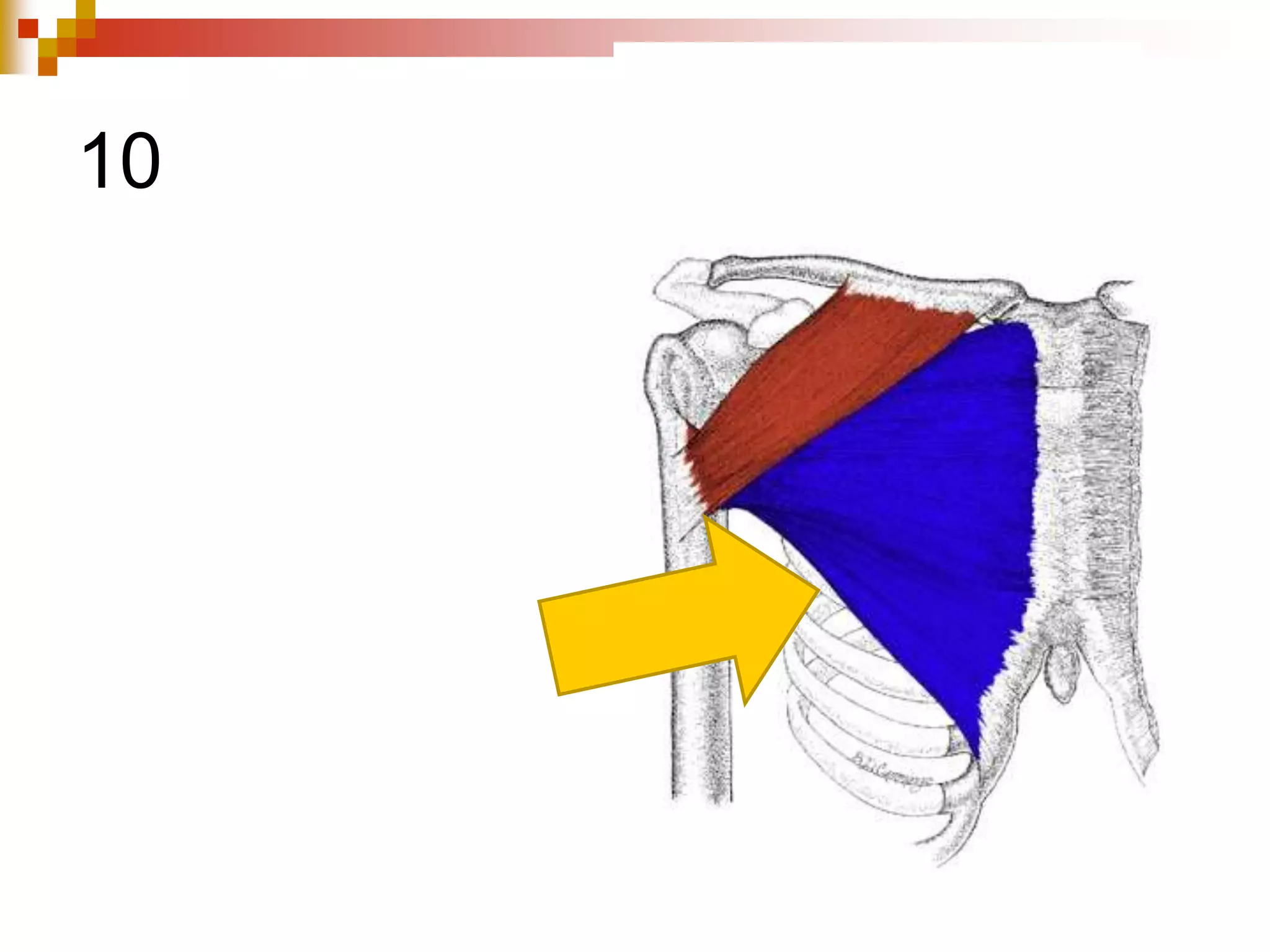
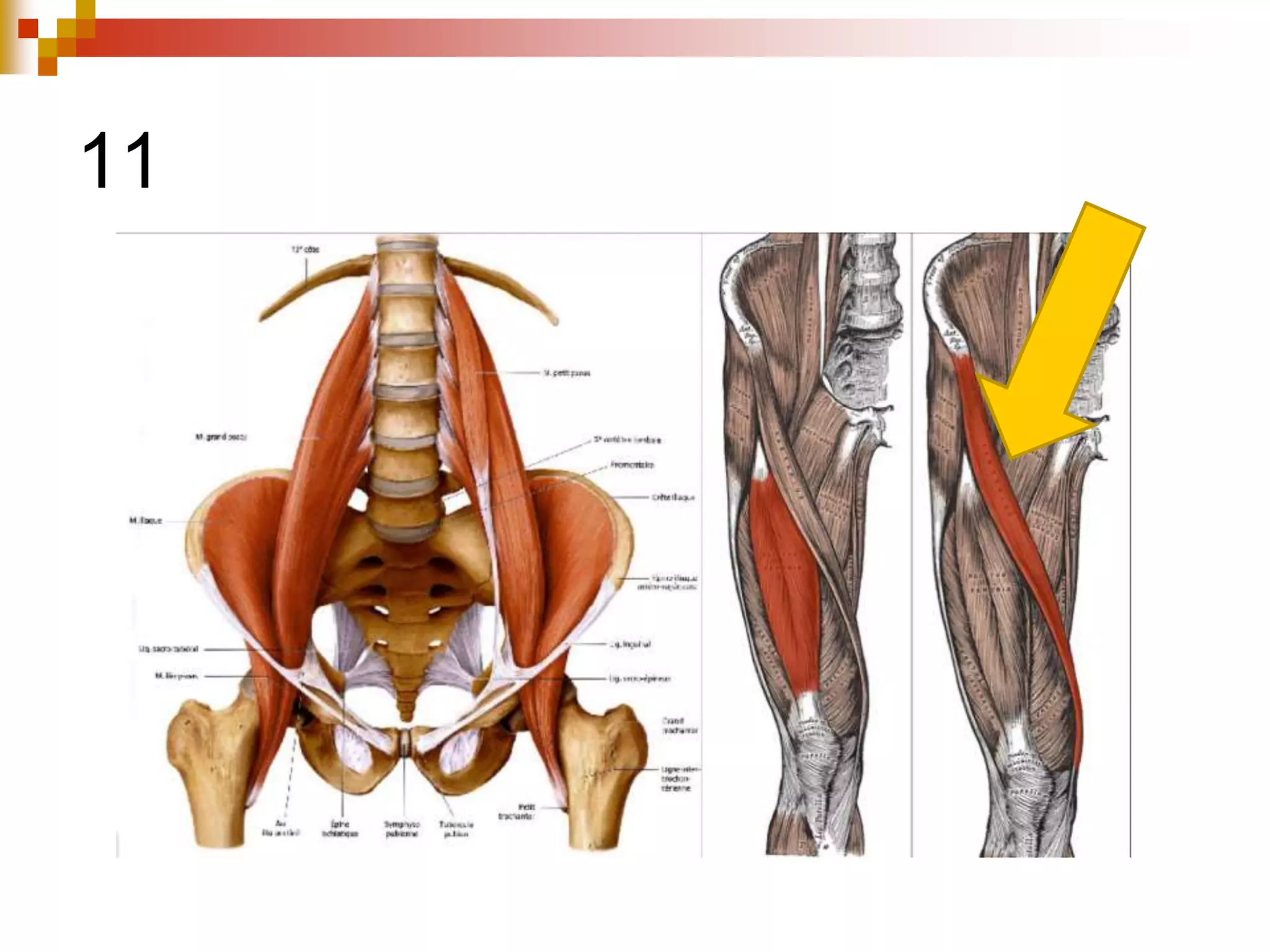
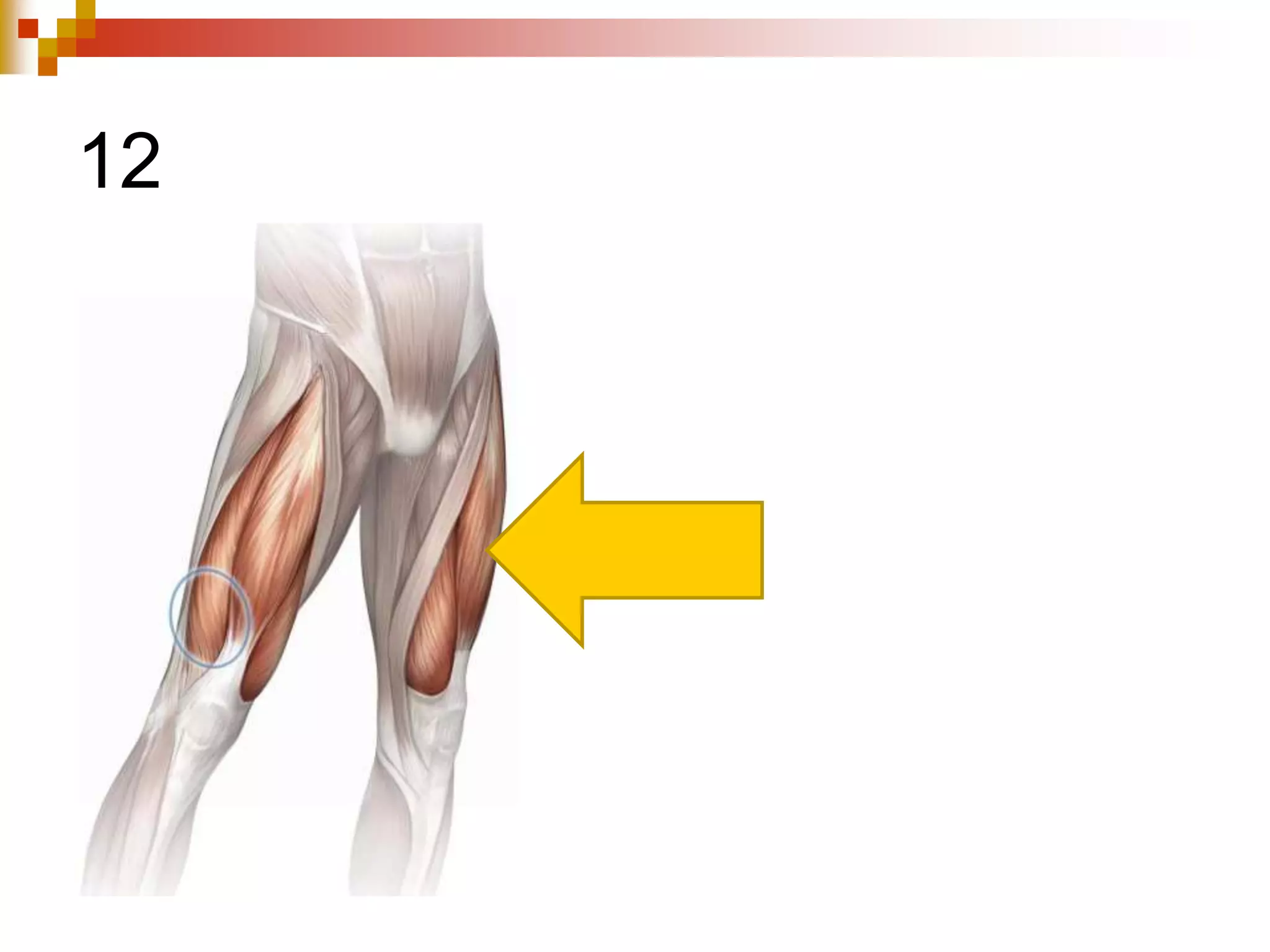
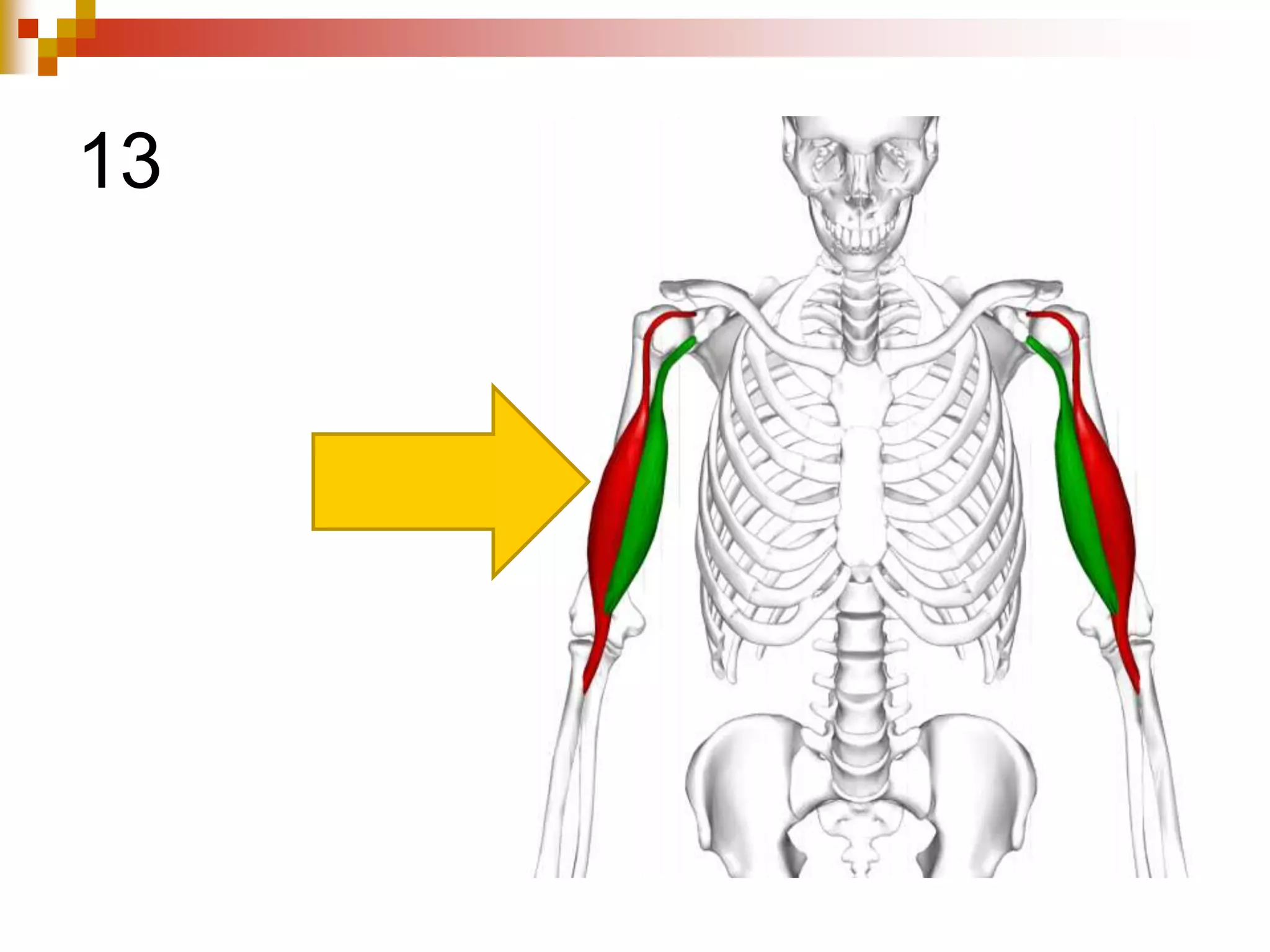
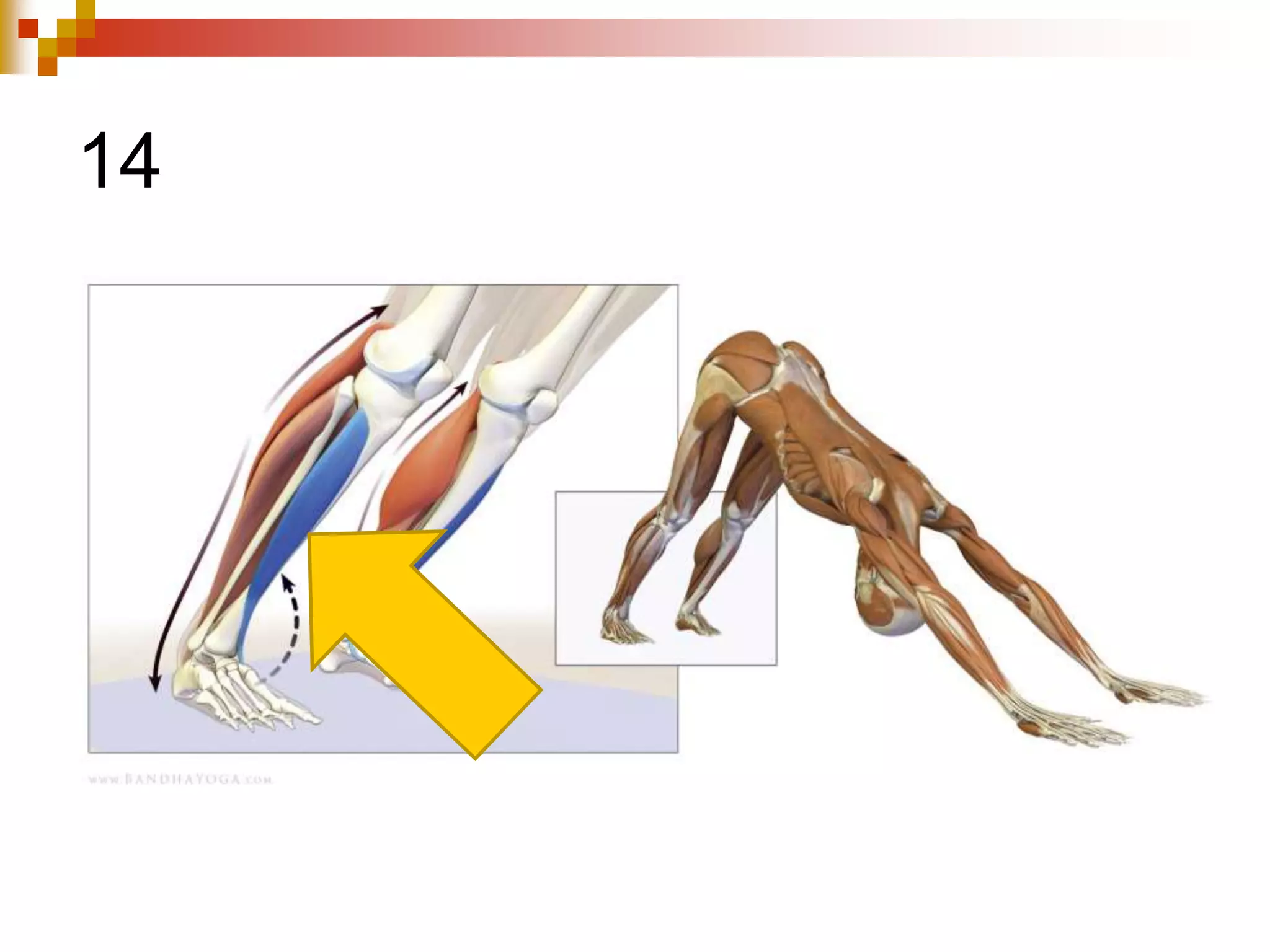
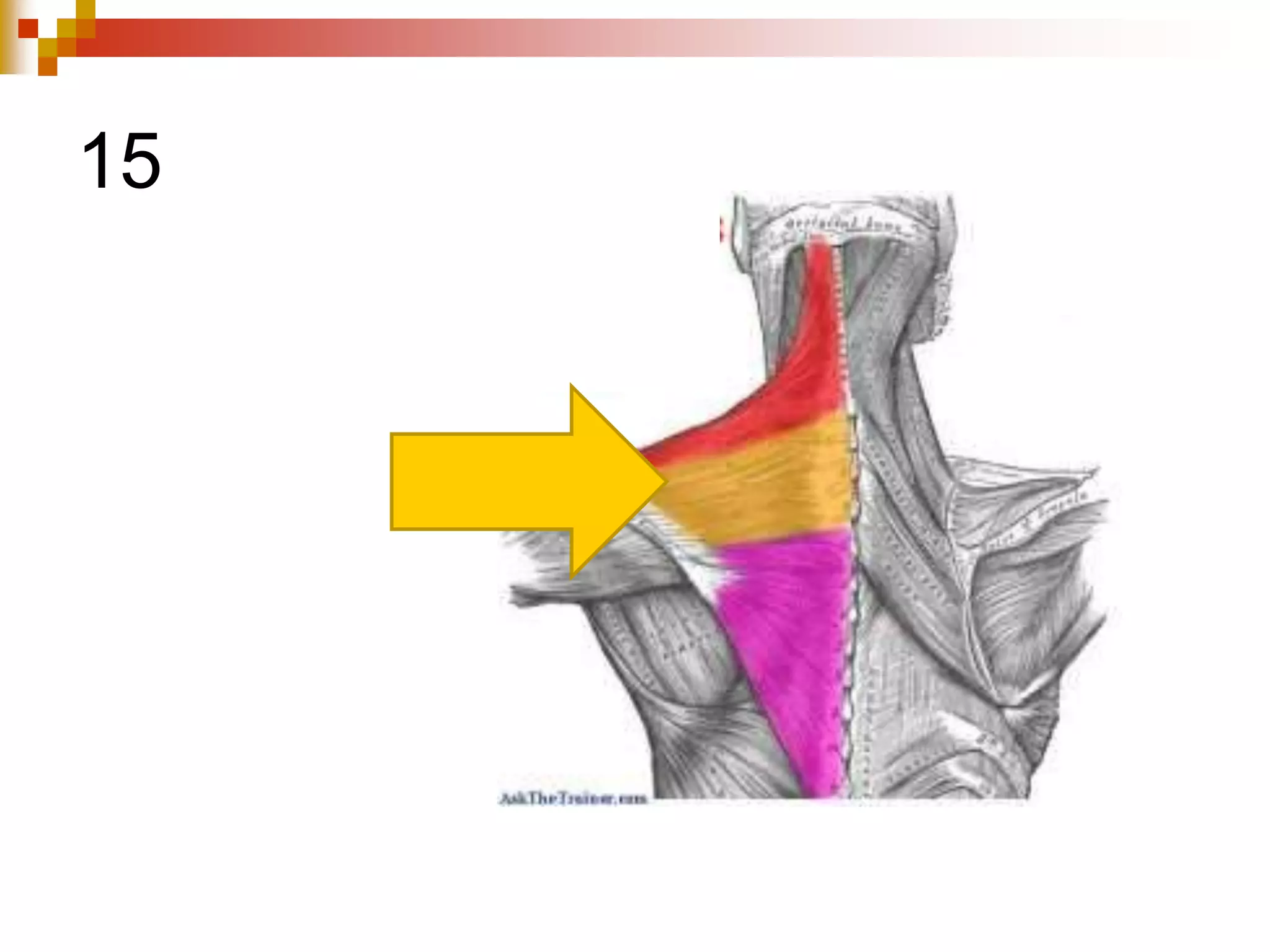
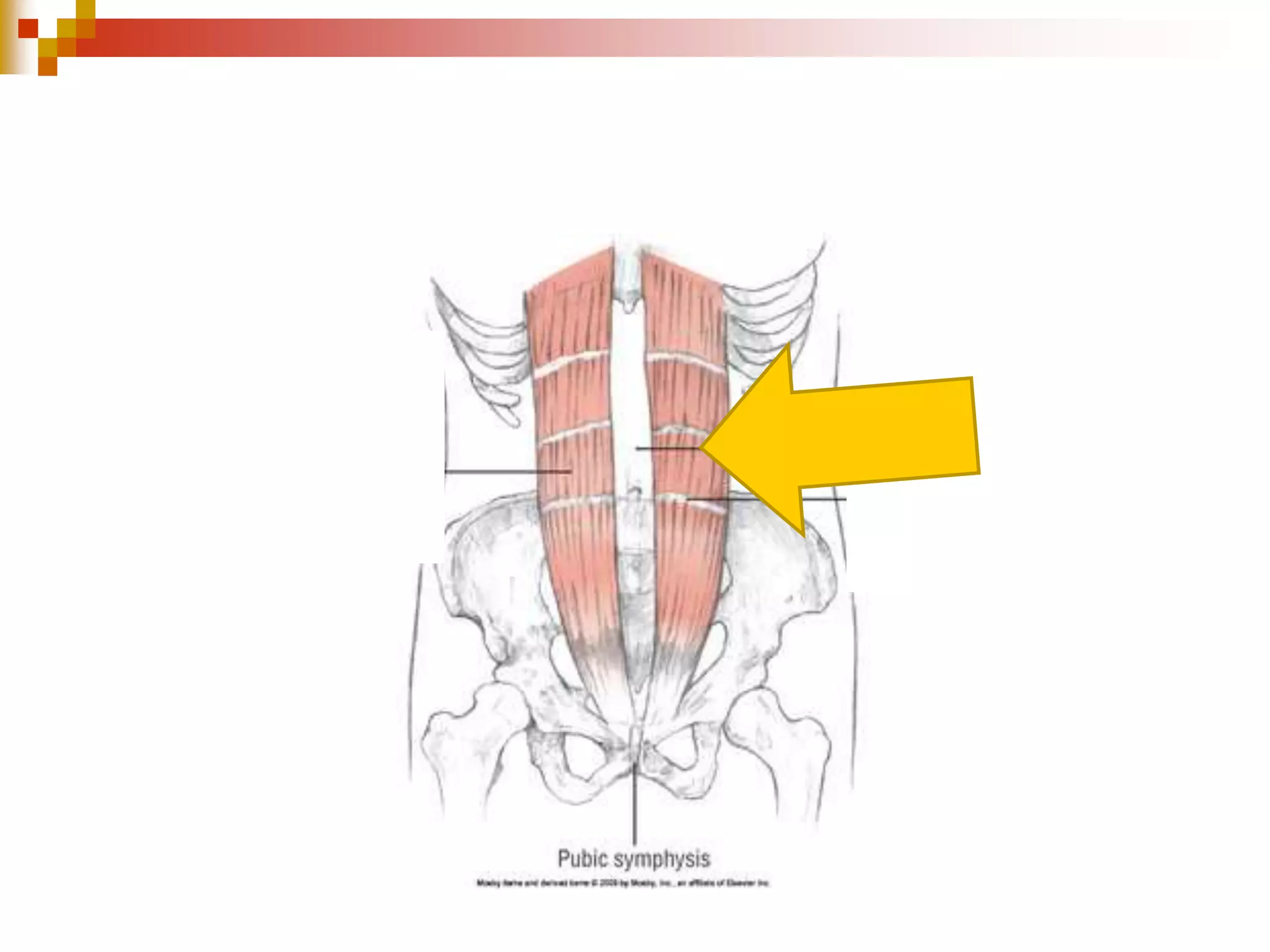
The document provides information about the muscular system and different types of muscles in the body. It discusses three main types of muscles: skeletal muscles, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. Skeletal muscles are voluntary and attach to bones, cardiac muscle is only found in the heart, and smooth muscle is involuntary and found in organs. The document also outlines characteristics of muscle tissue like excitability, contractility, and functions of muscles like movement, moving substances, stabilization, and generating heat. It provides details on skeletal muscle structure, origins/insertions, and antagonistic muscle pairs.