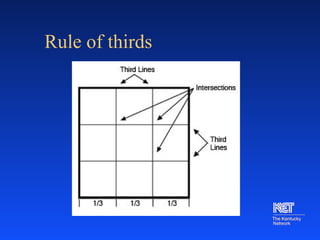
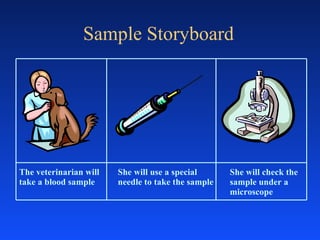
The document provides an overview of basic video production concepts and techniques. It discusses the three phases of production as pre-production, production, and post-production. It also outlines different types of camera shots including close-ups, wide shots, and medium shots. Common mistakes like too much headroom and shaky cameras are also mentioned.




















































![Missi Baker [email_address] 606.836.0474 KET conducts workshops in video production for Kentucky teachers and students.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mbvp-1209580227680708-9/85/Basic-Video-Production-55-320.jpg)