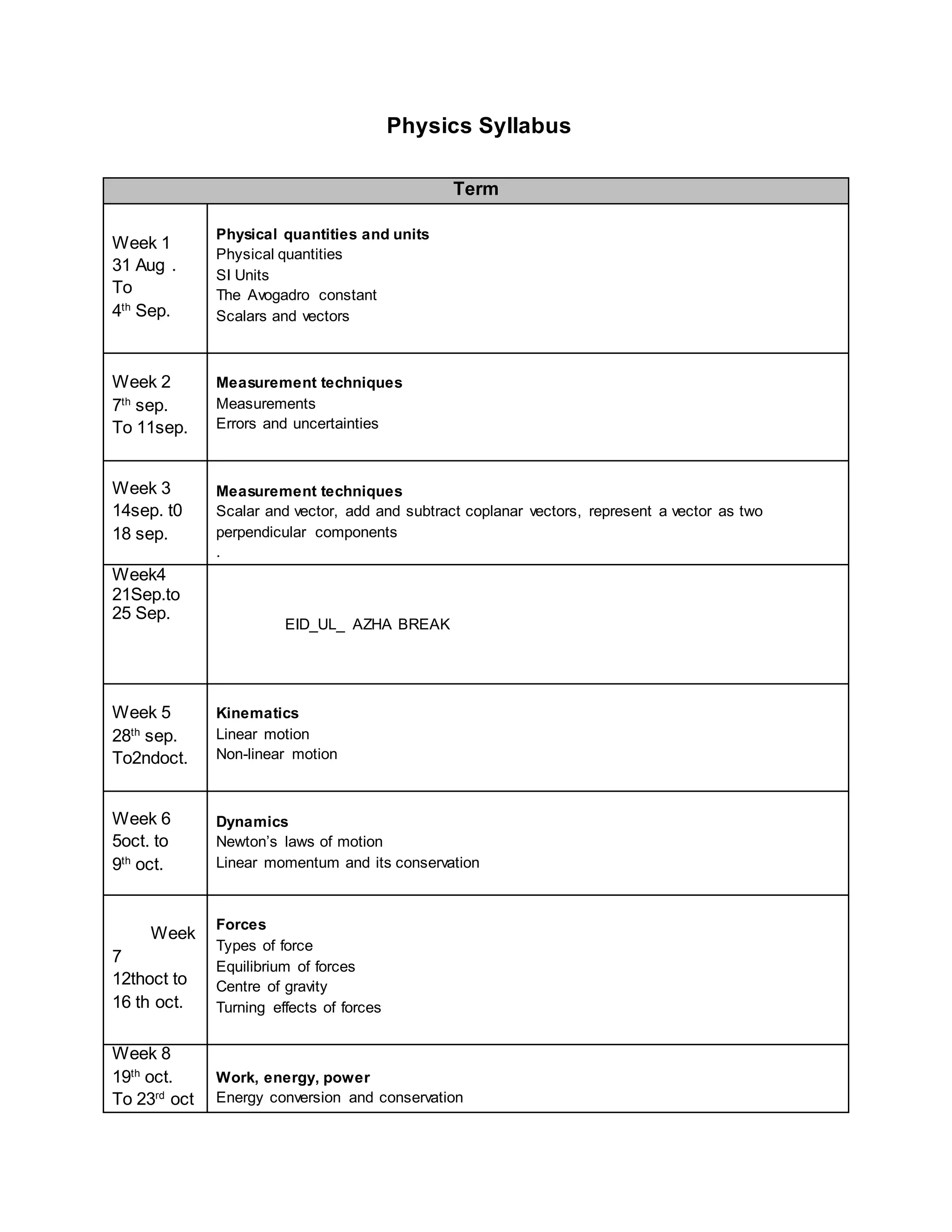
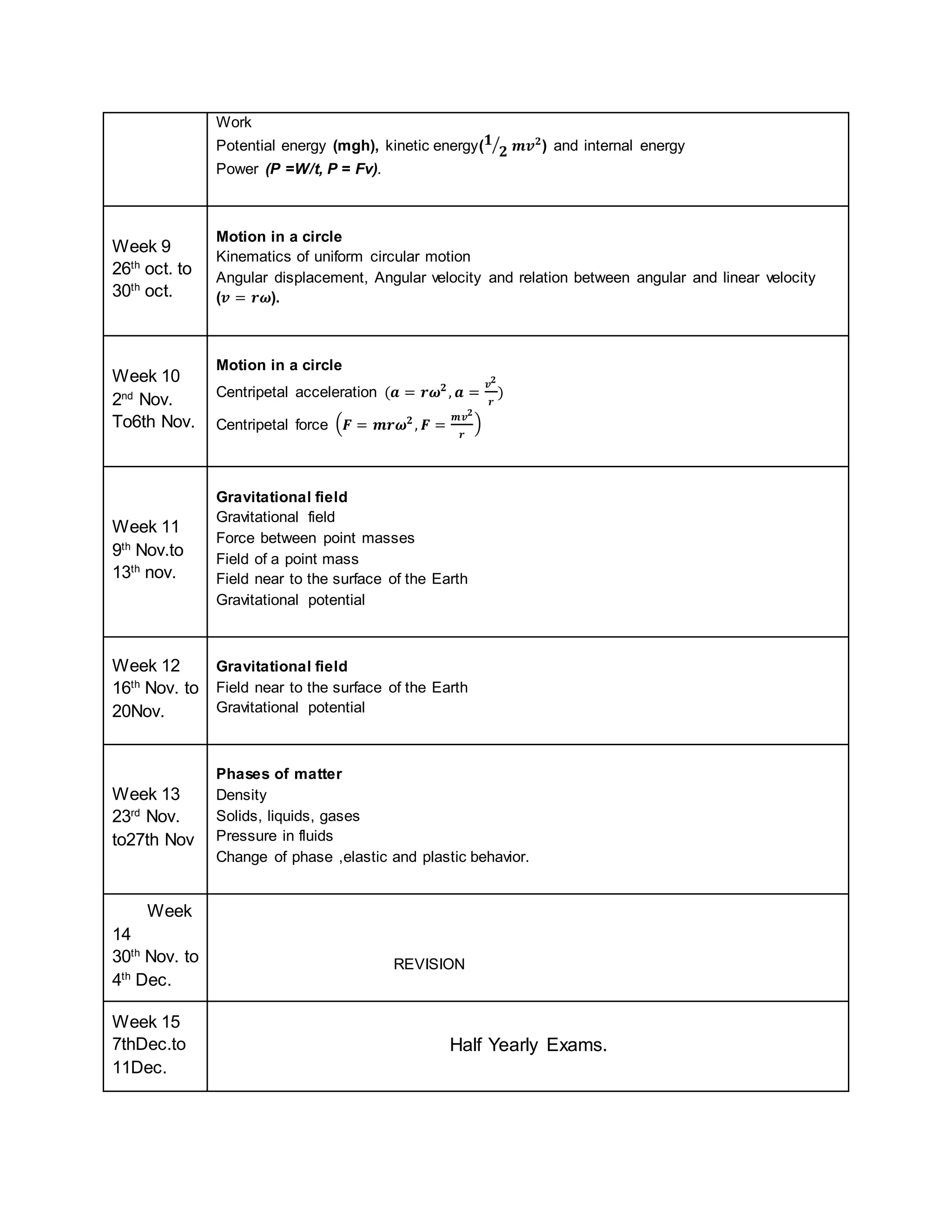
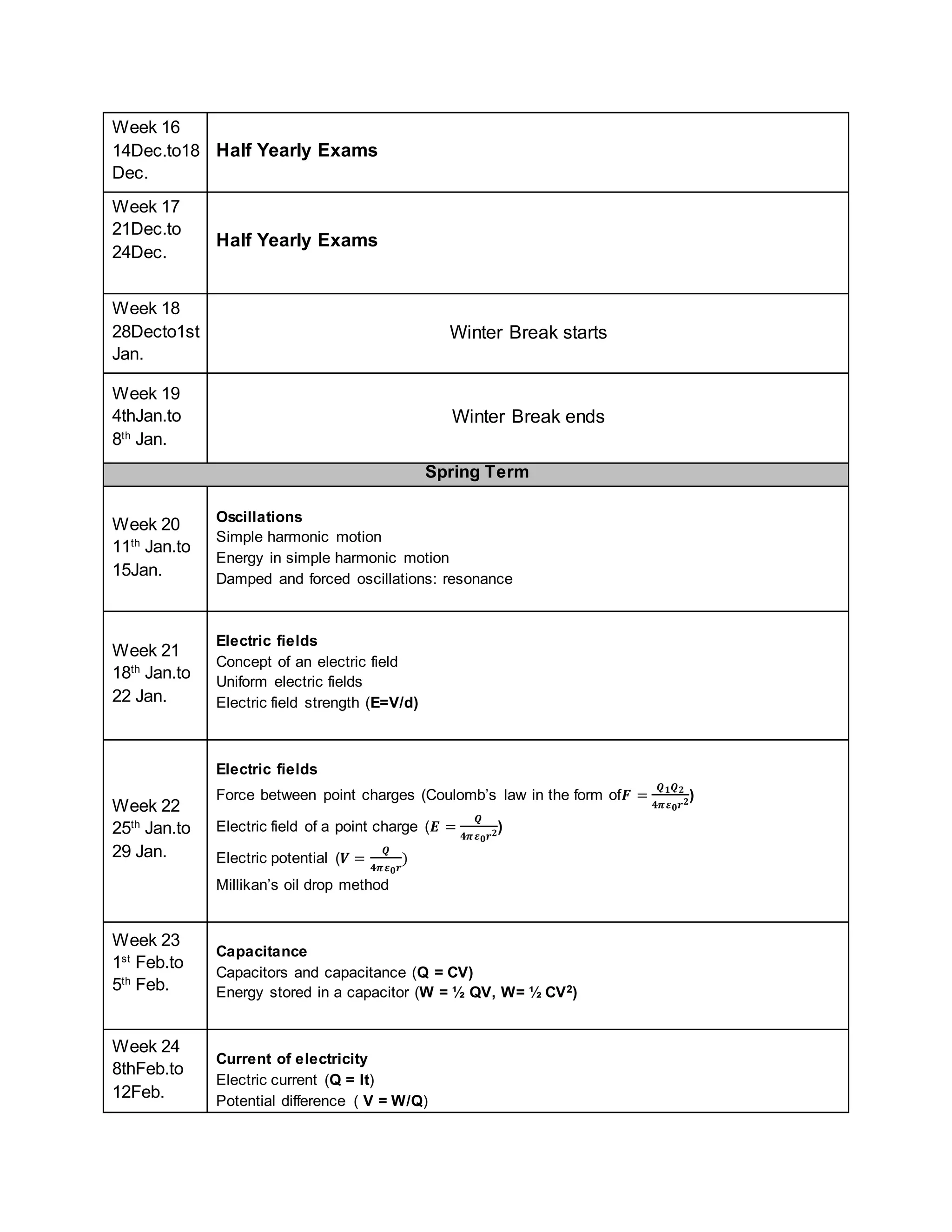
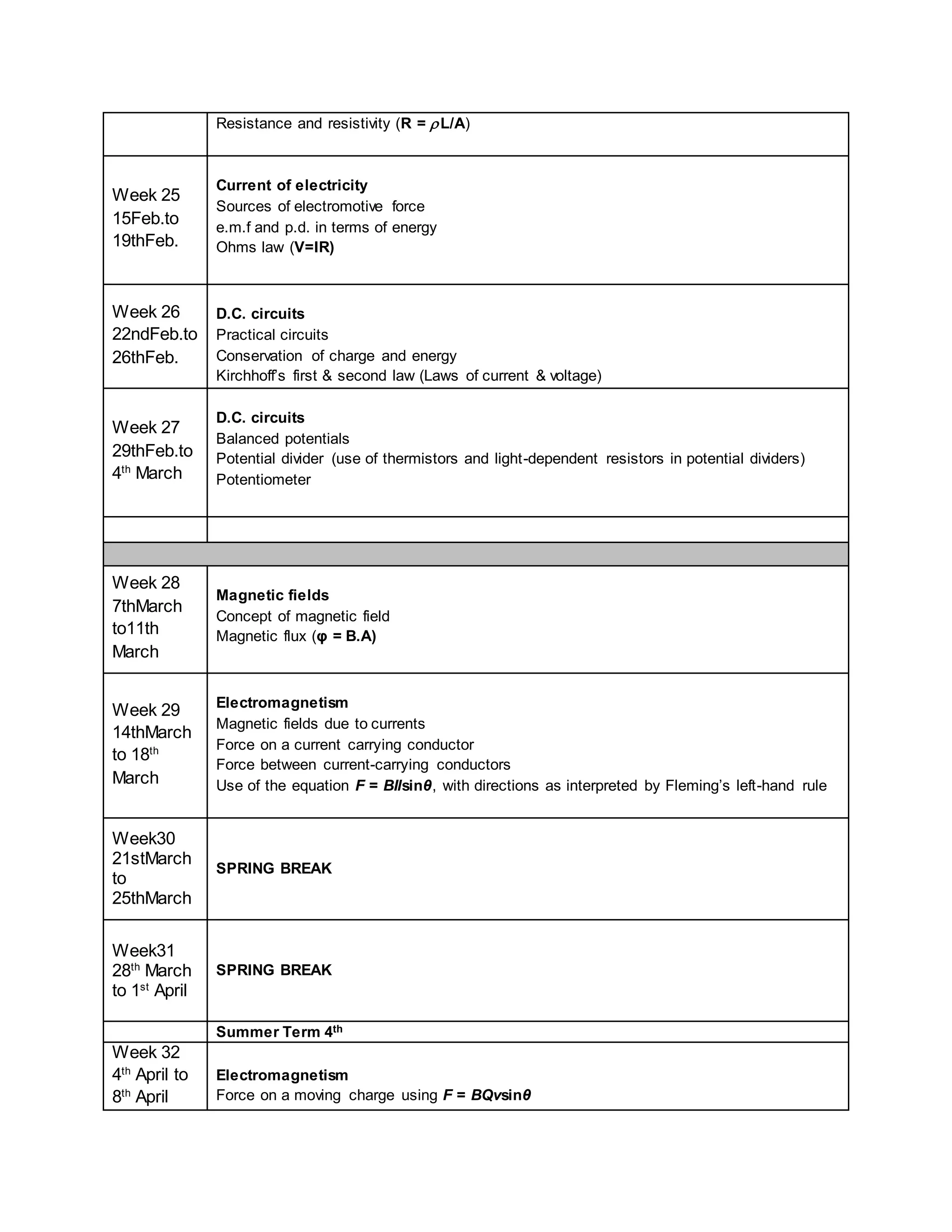
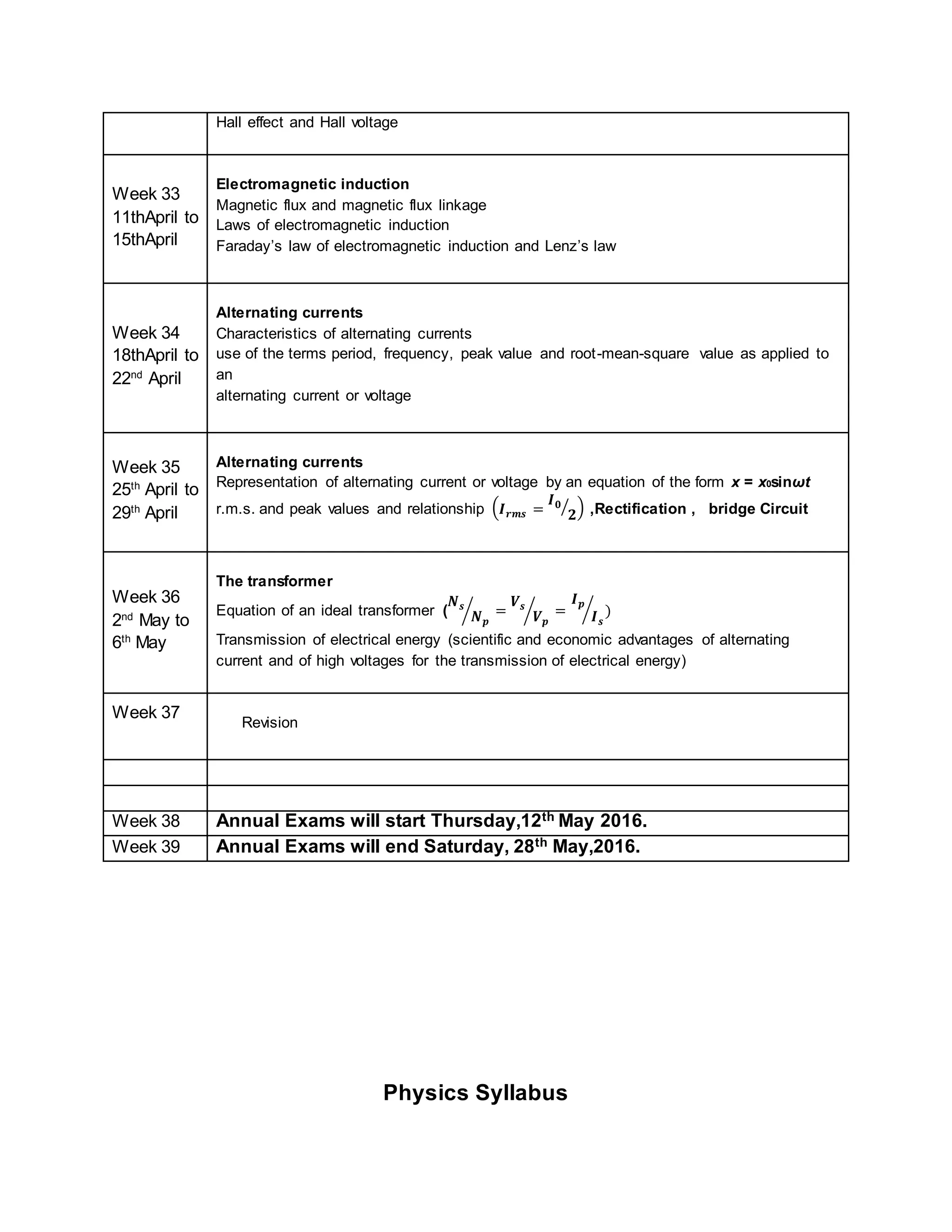
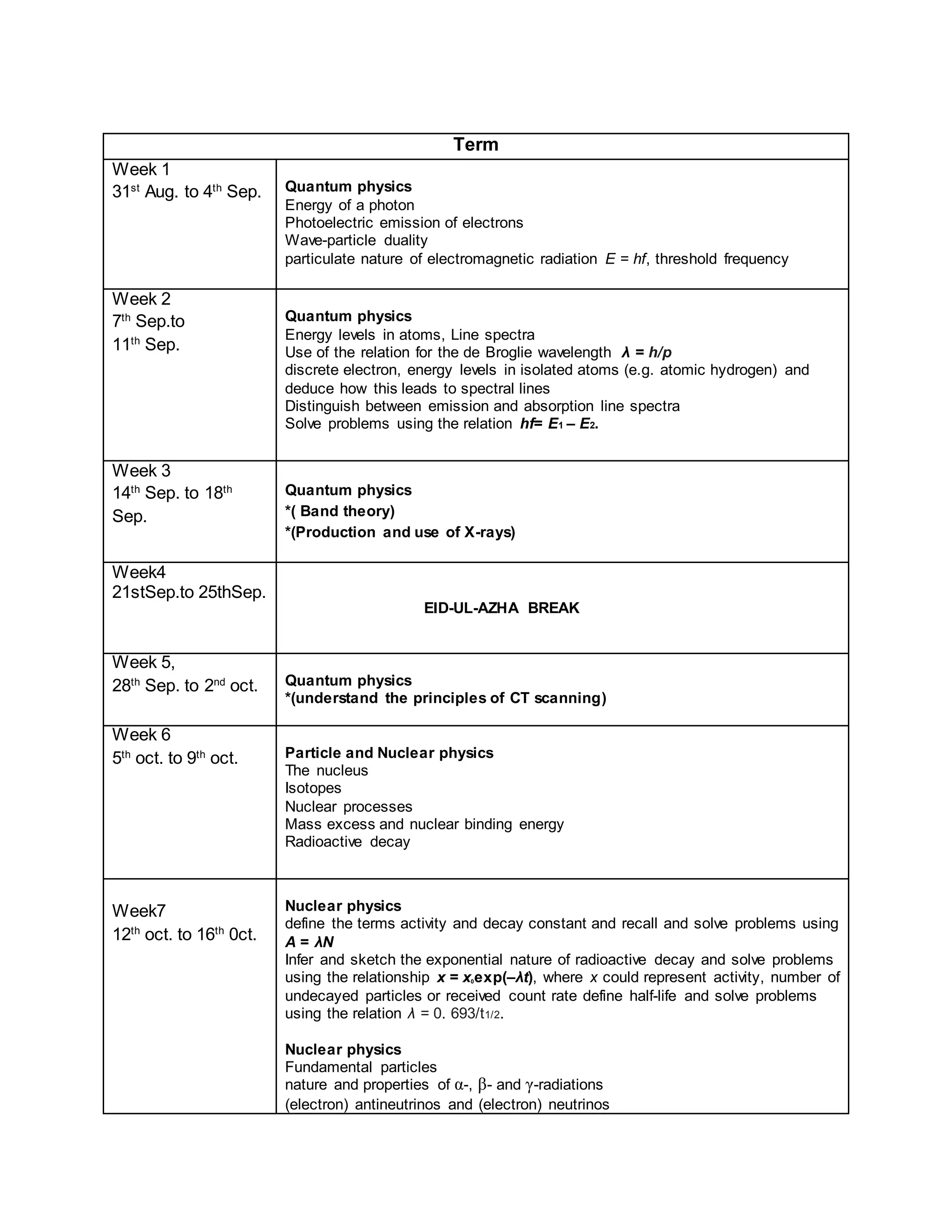
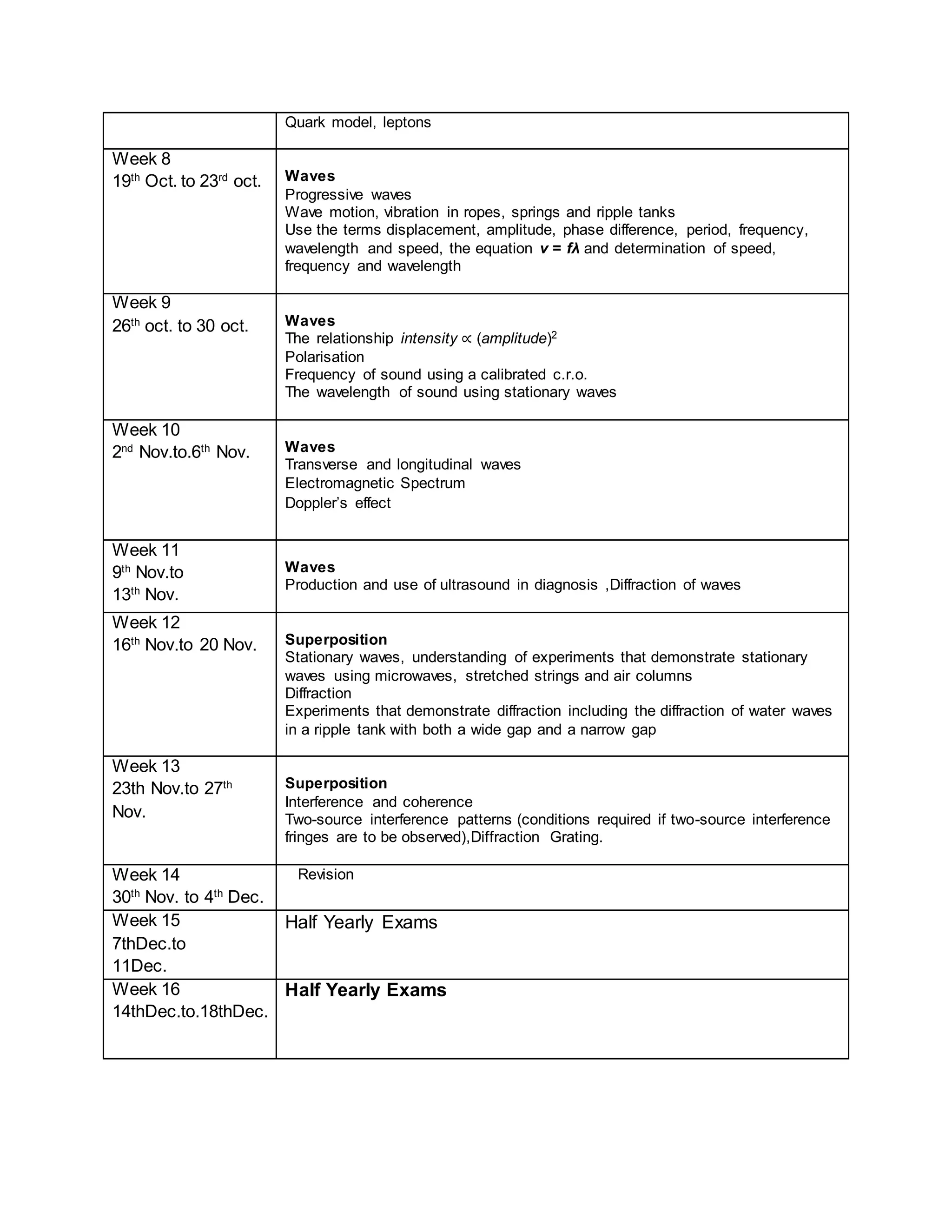
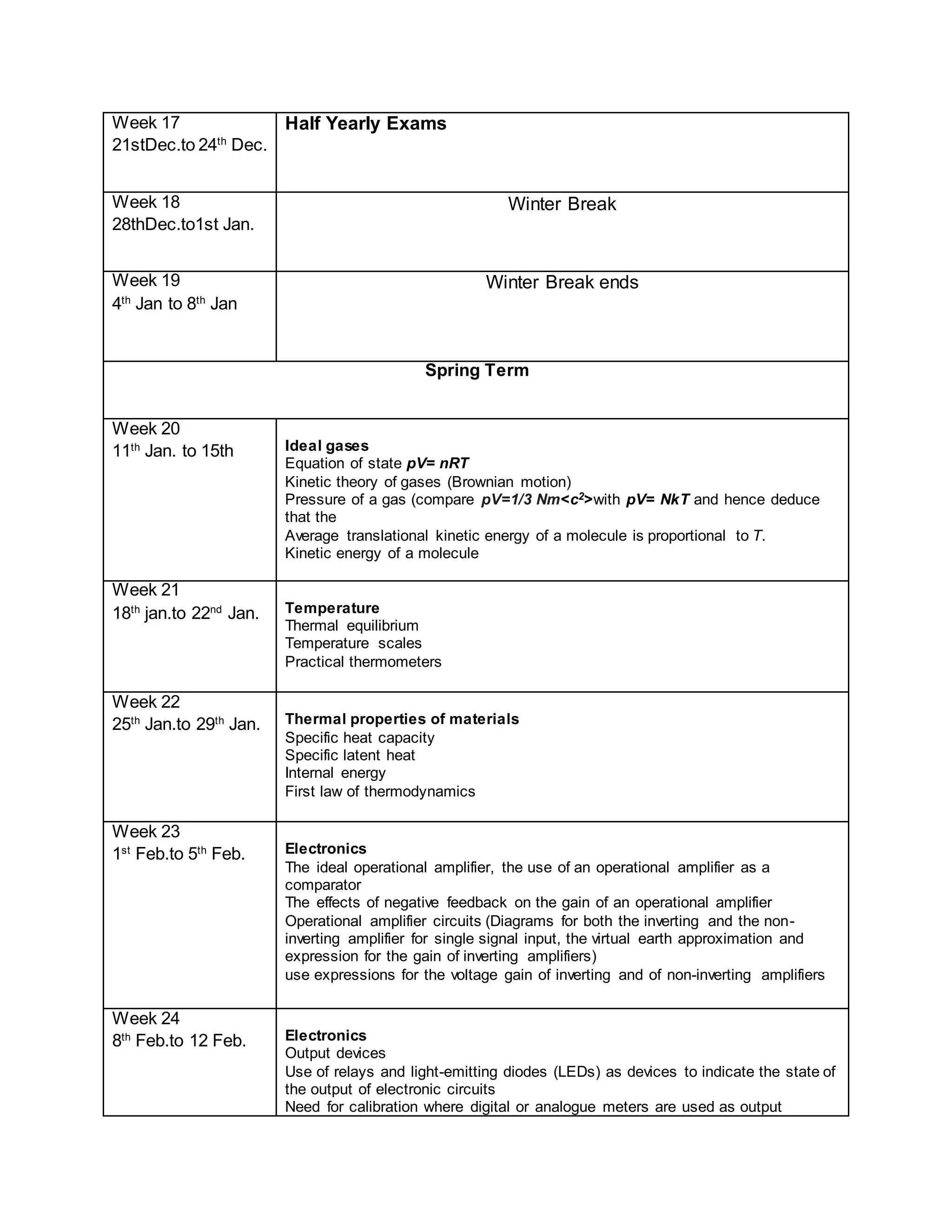
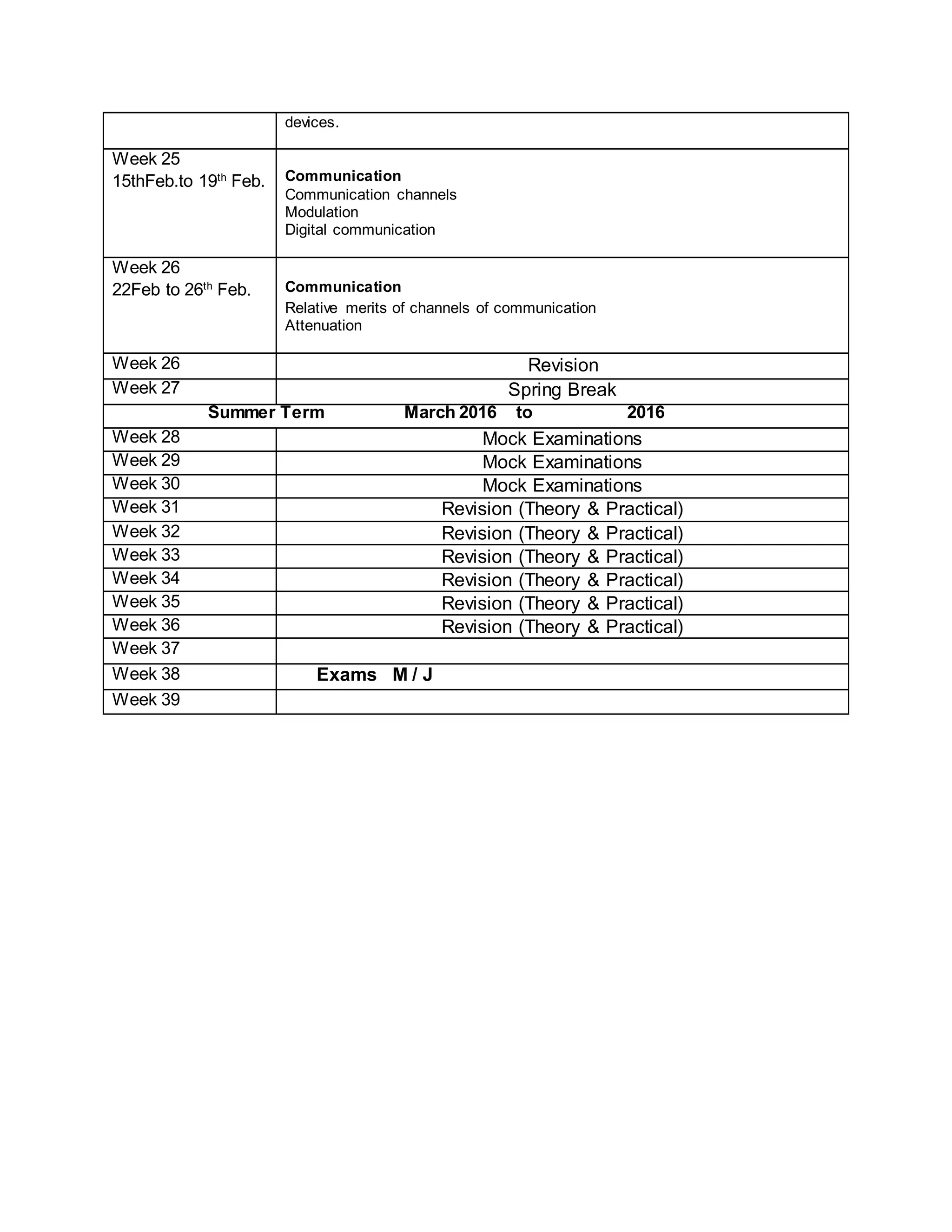
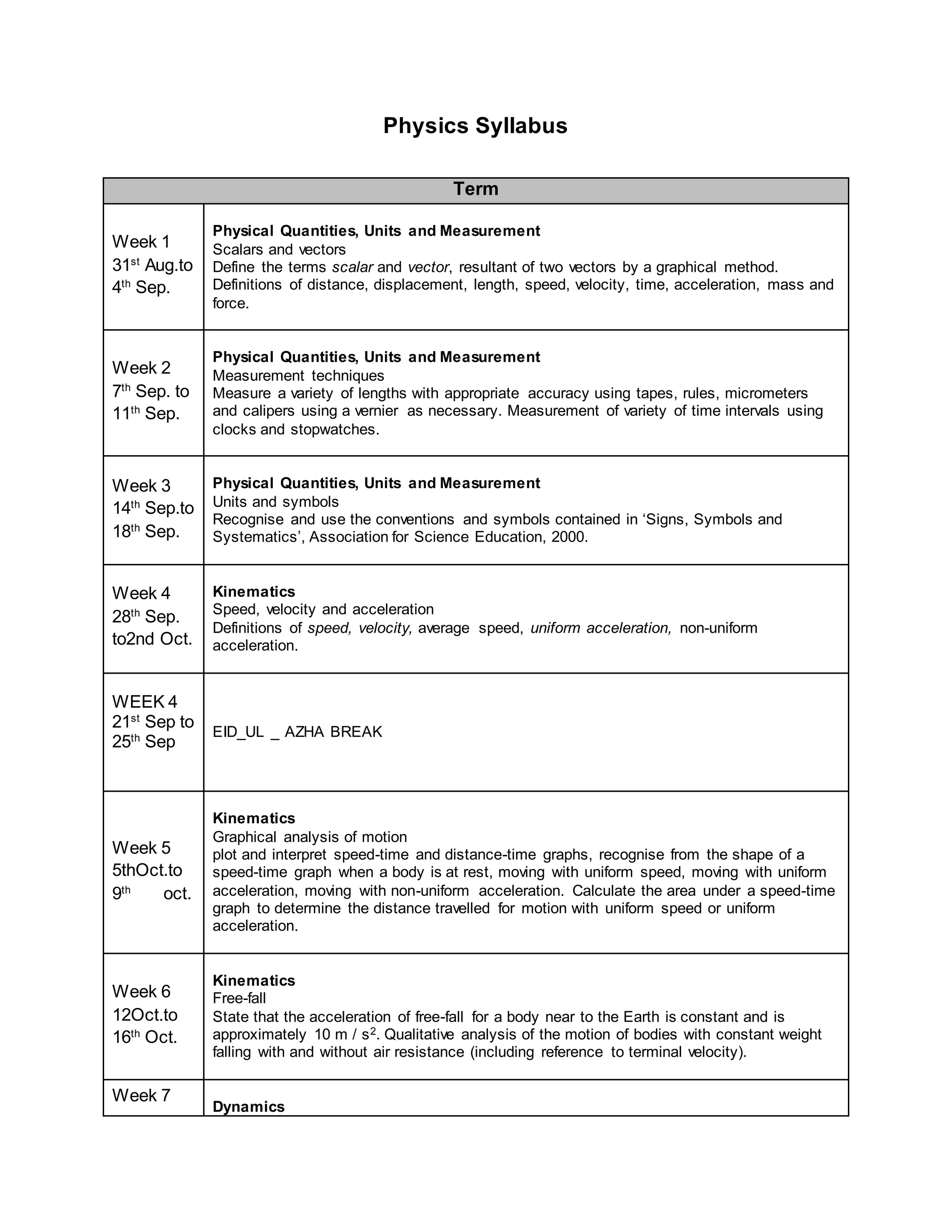
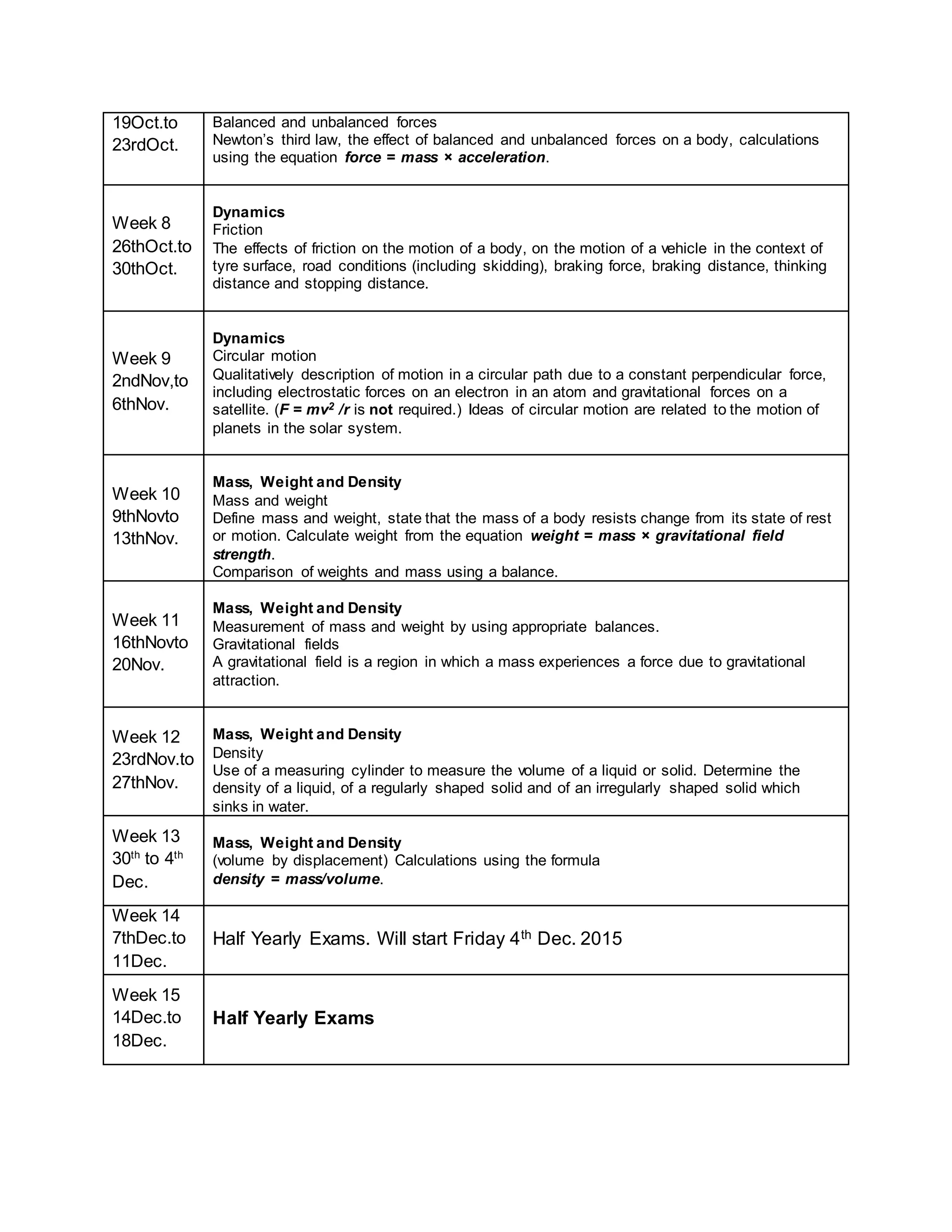
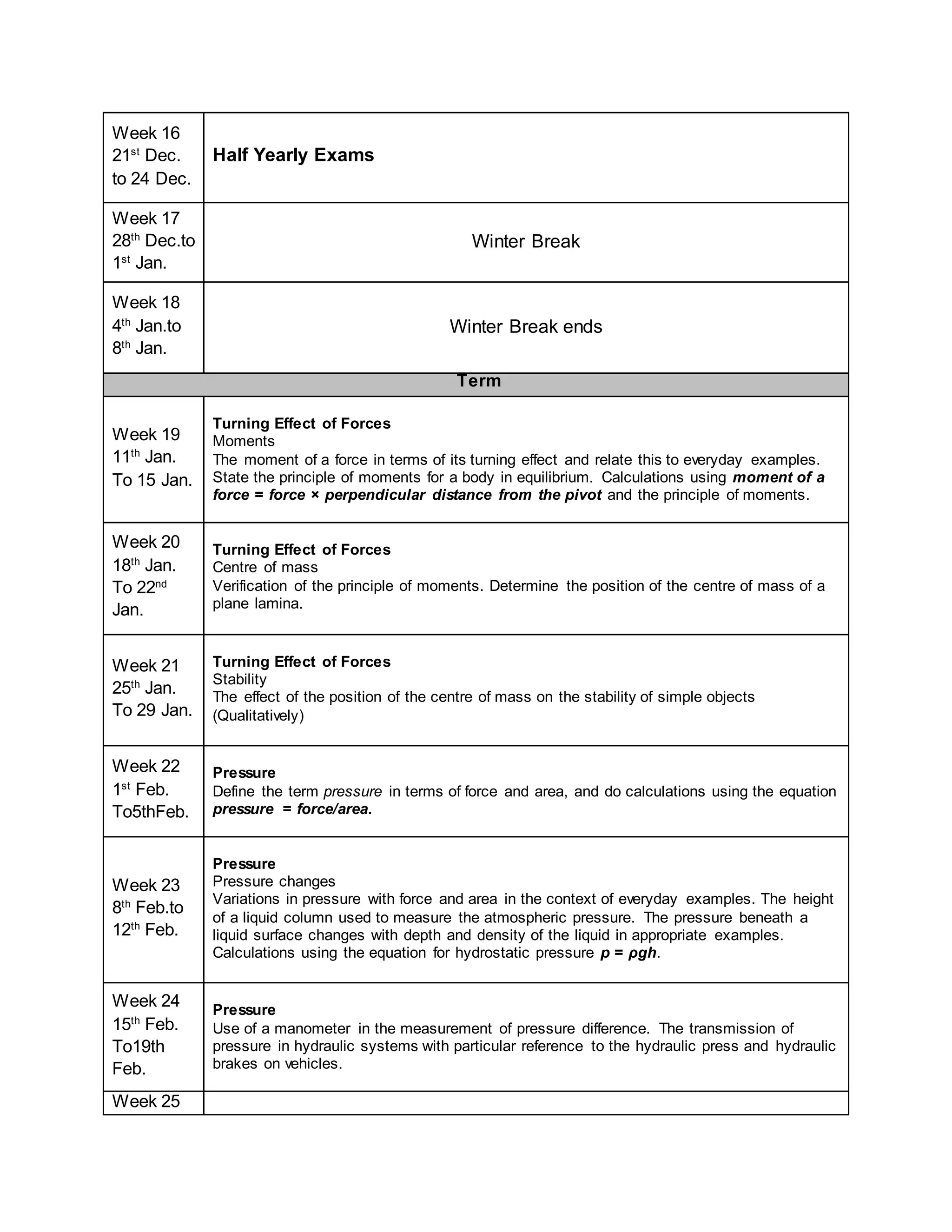
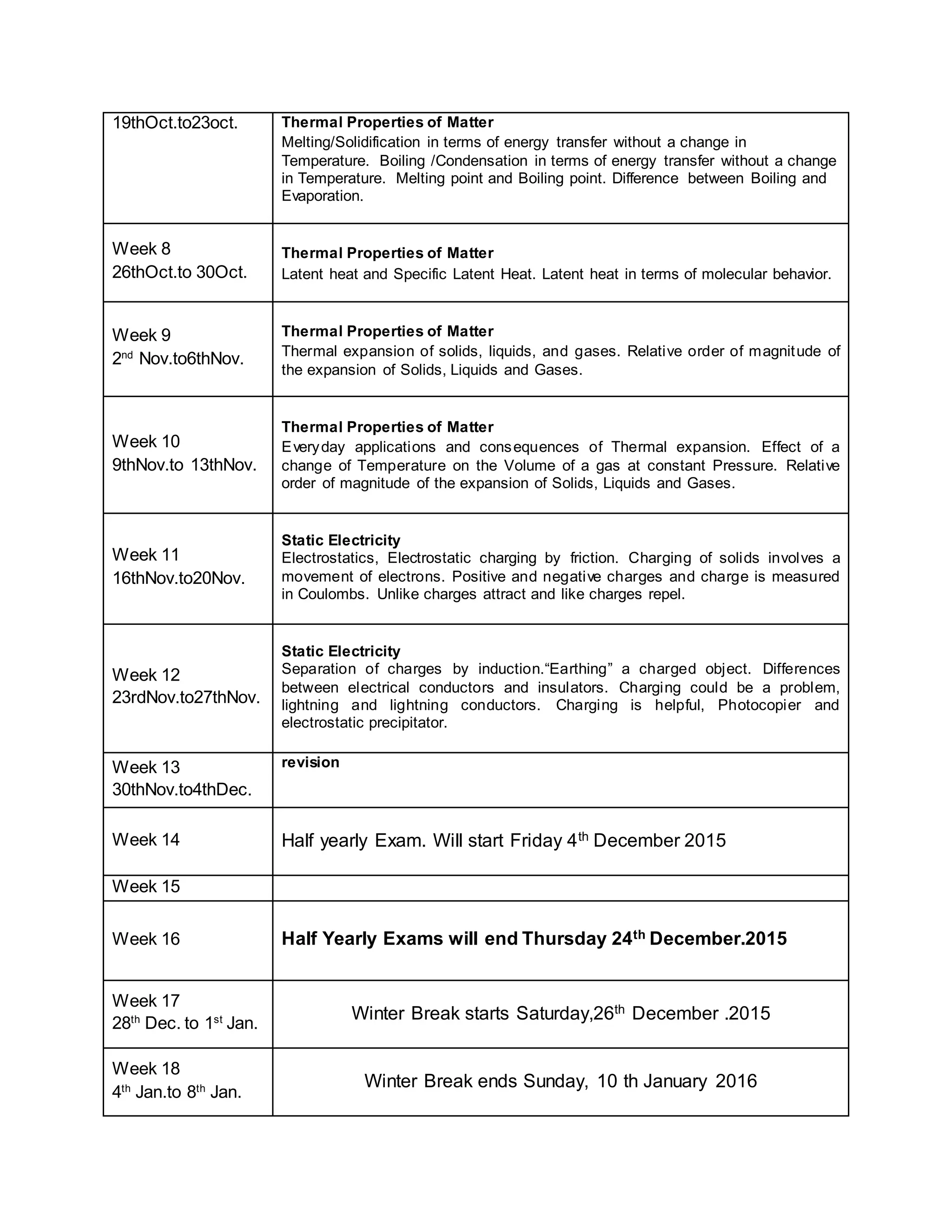
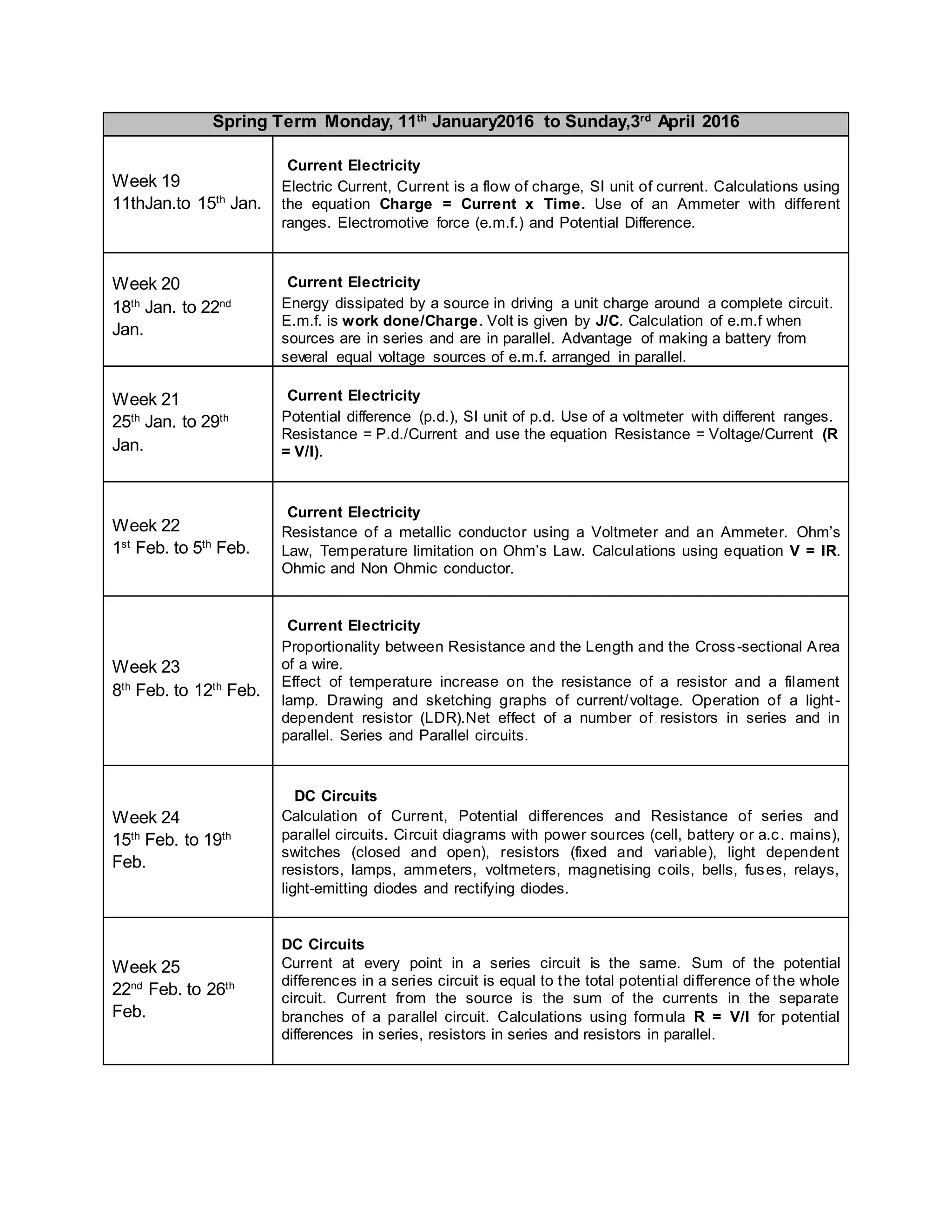
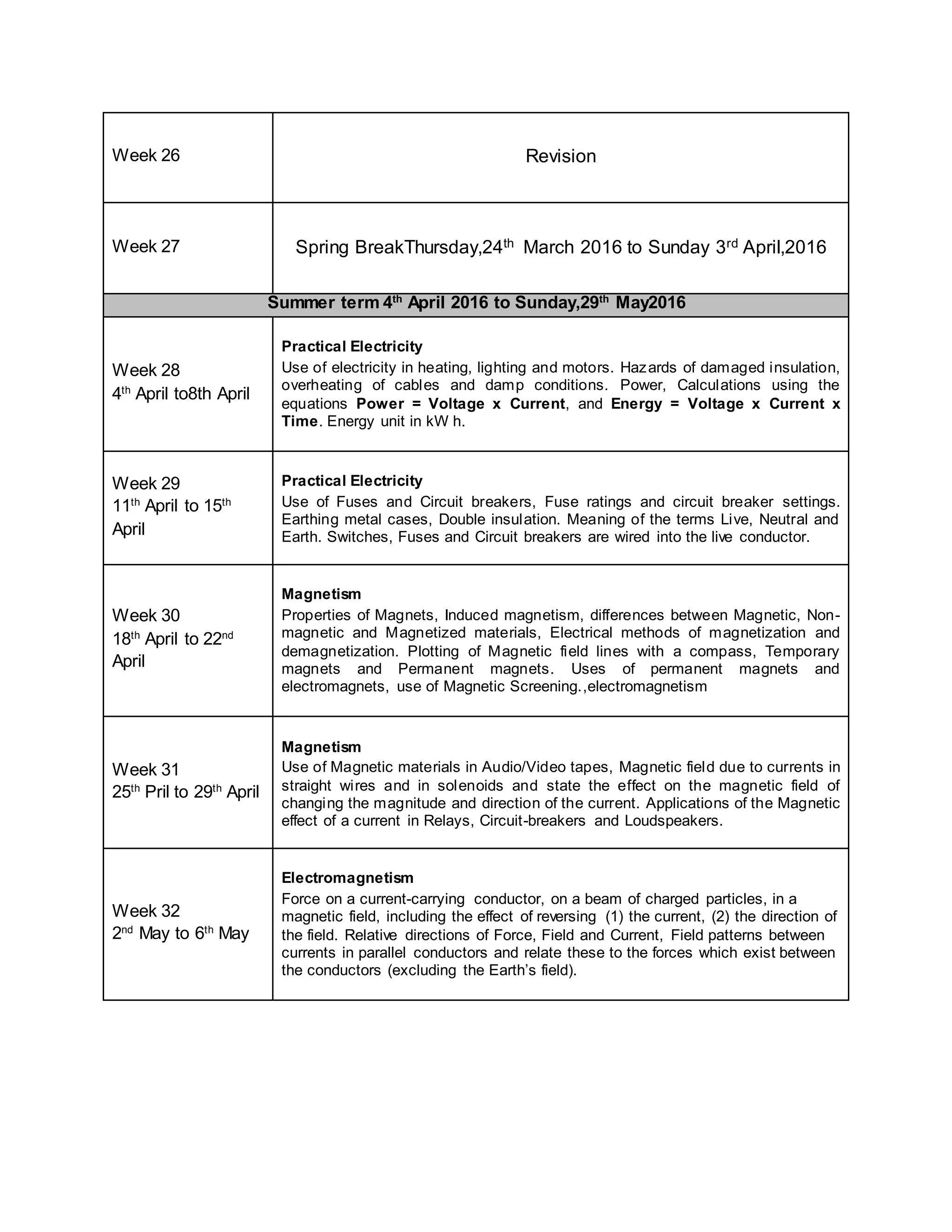
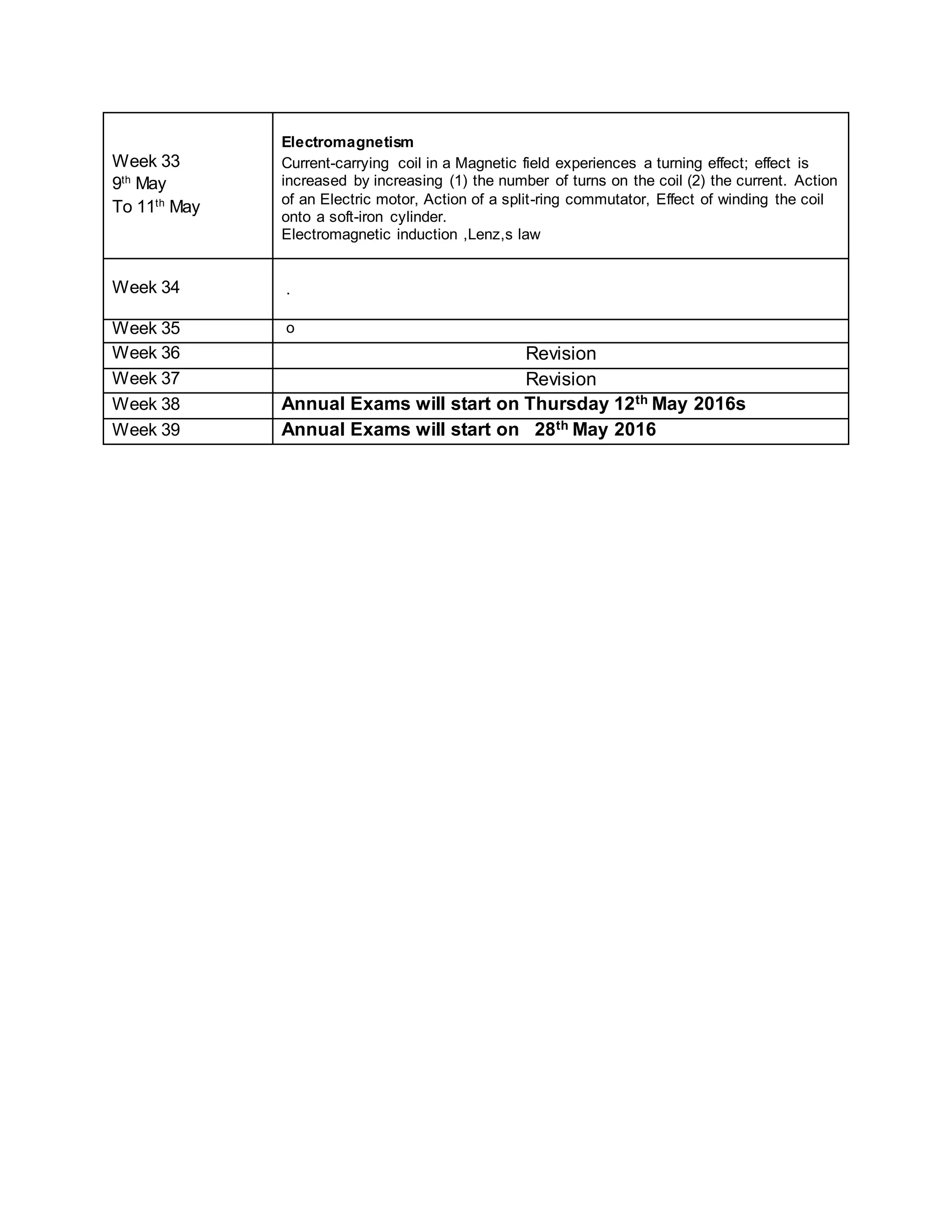
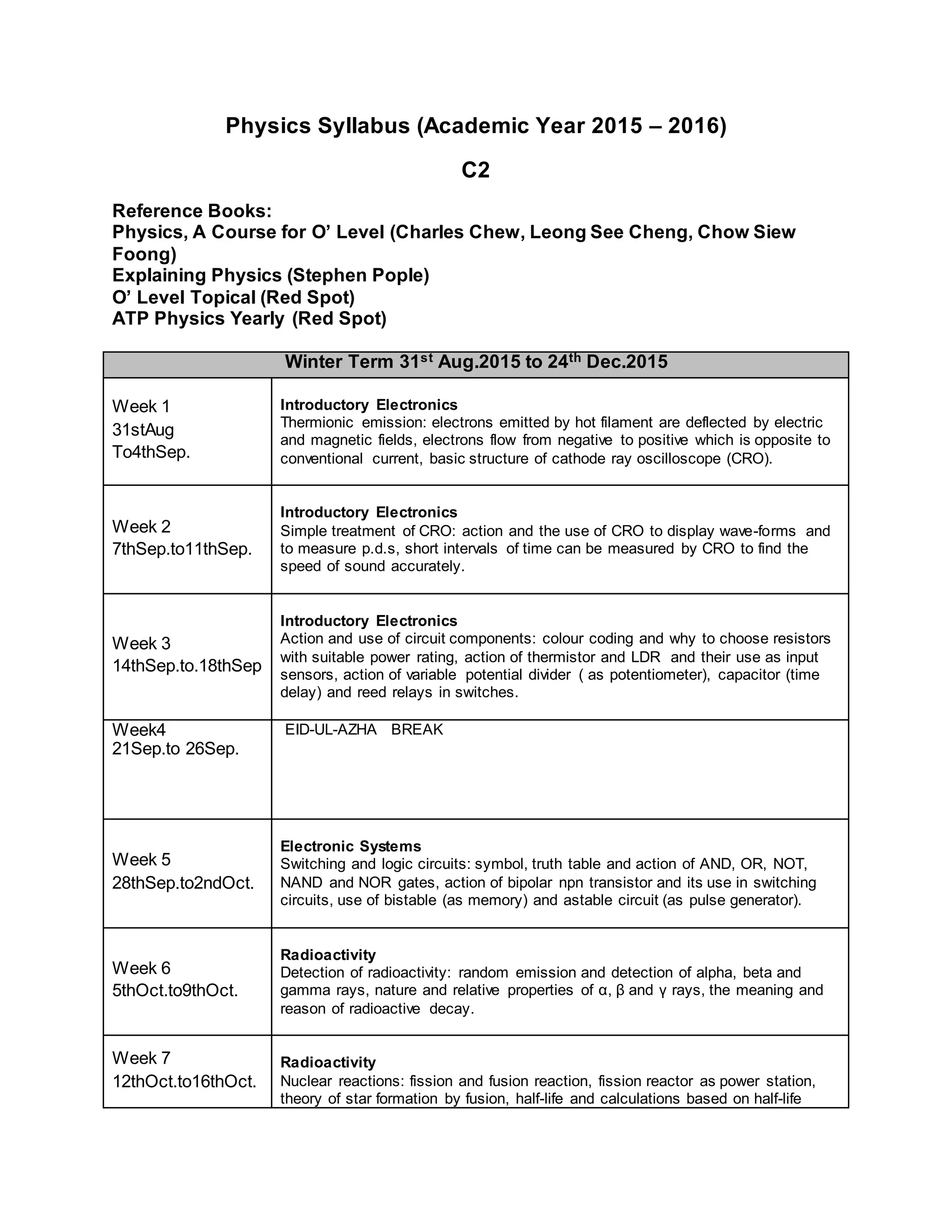
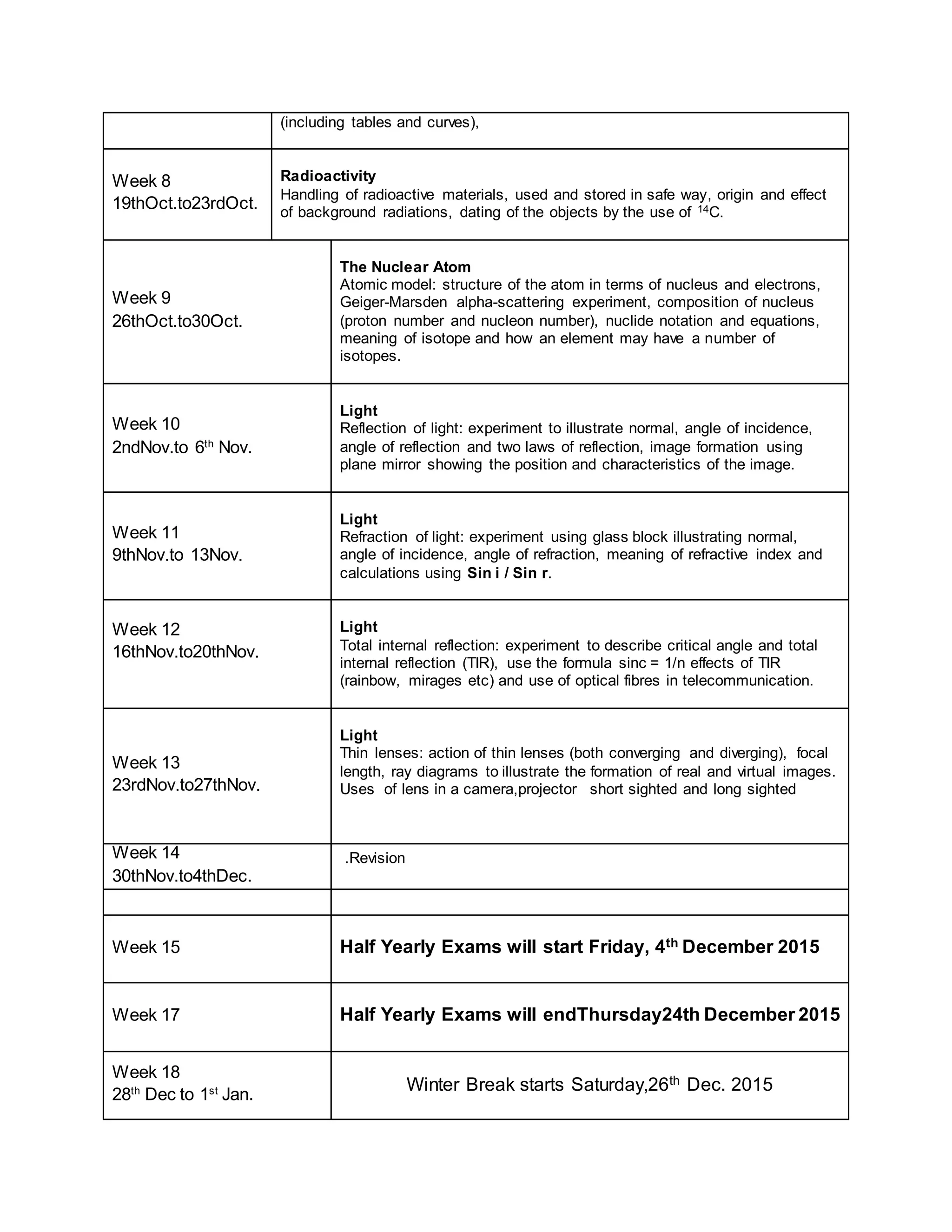
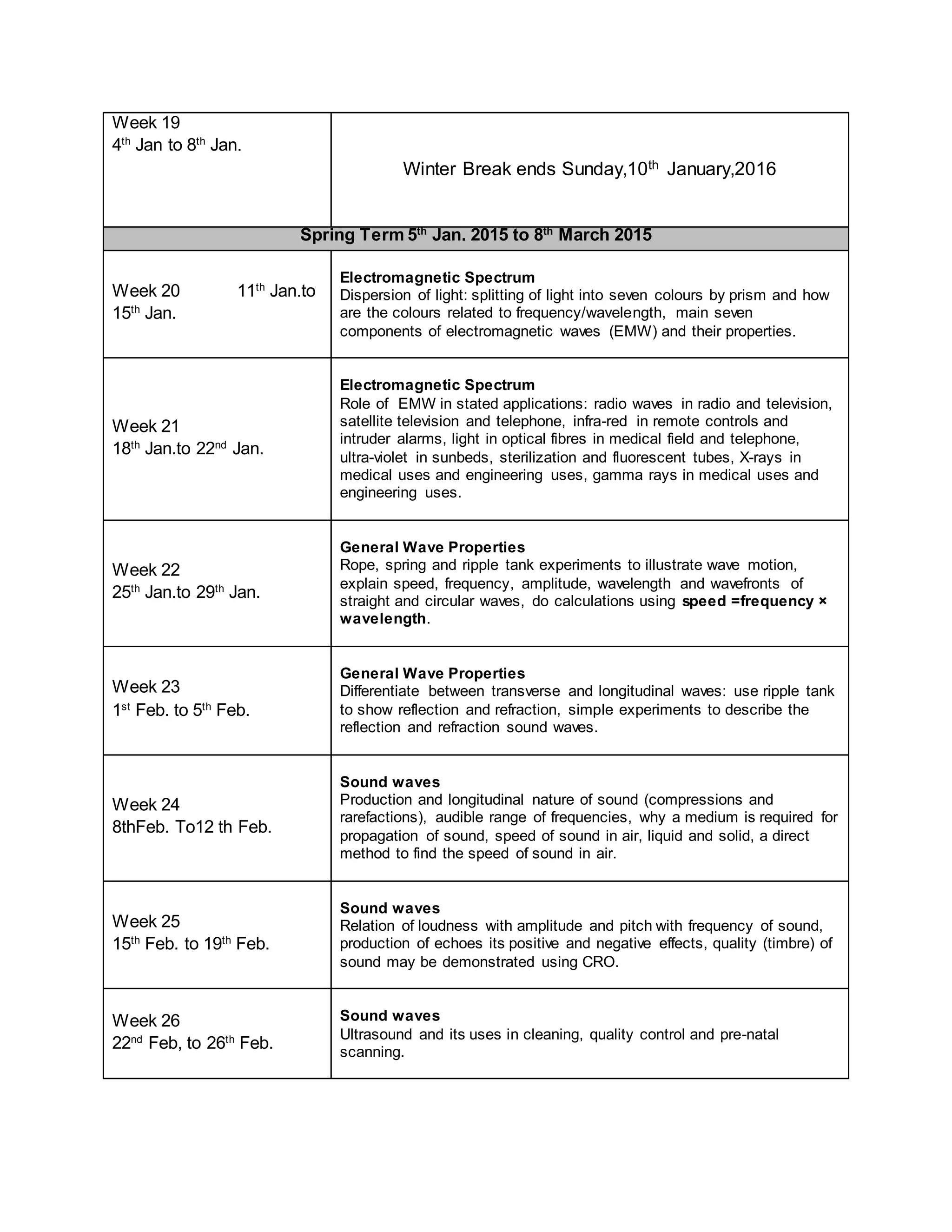
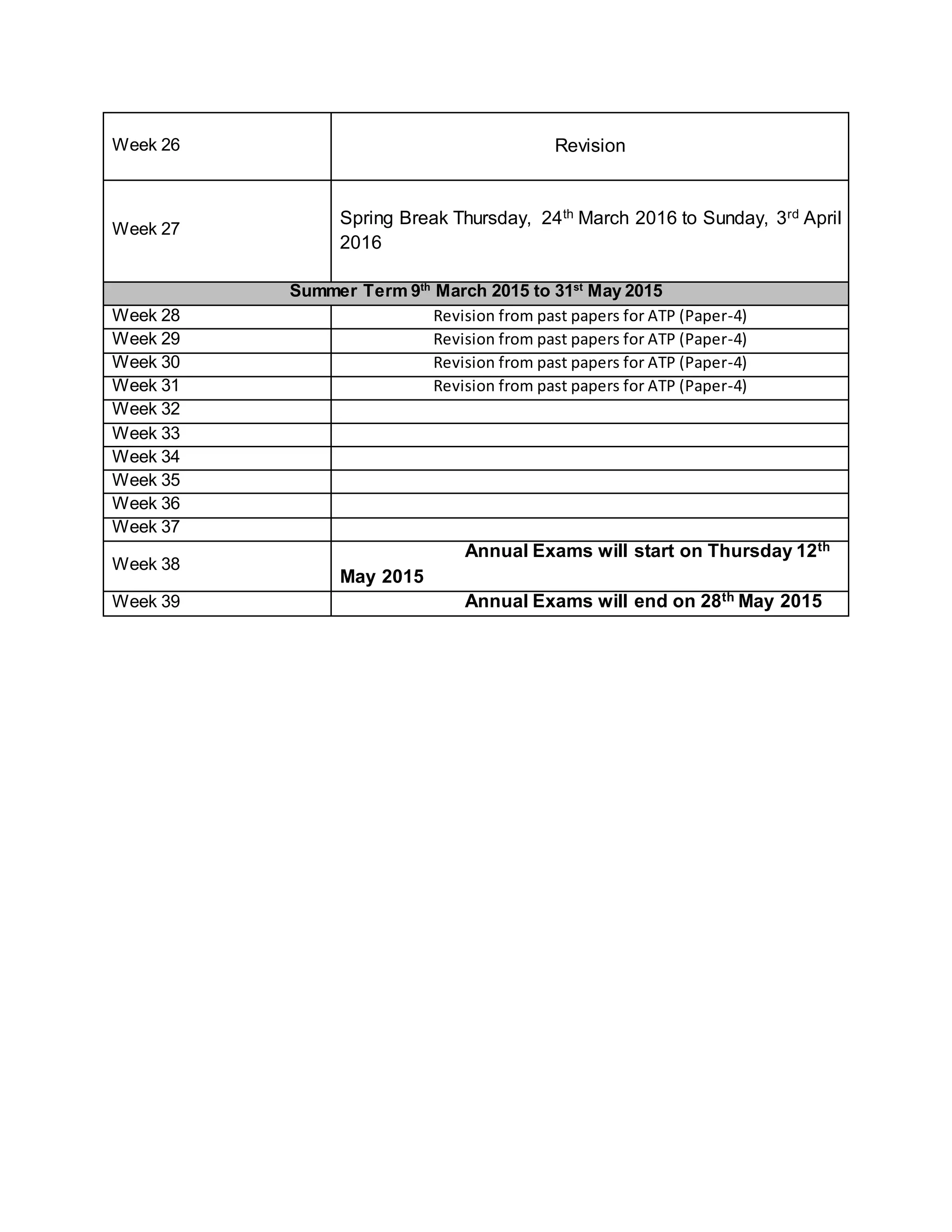
This physics syllabus outlines the topics to be covered over 38 weeks. In week 1-3, topics include physical quantities, units, measurement techniques, scalars, and vectors. Weeks 4-10 cover kinematics, dynamics, forces, work, energy, power, and motion in a circle. Weeks 11-12 discuss gravitational fields and forces. Weeks 13-17 cover phases of matter, oscillations, electric fields, capacitance, and current electricity. Weeks 18-28 discuss circuits, magnetism, electromagnetism, electromagnetic induction, and alternating currents. Weeks 29-37 cover transformers, quantum physics, particles, nuclear physics, waves, and thermodynamics. The final weeks are spent on revision