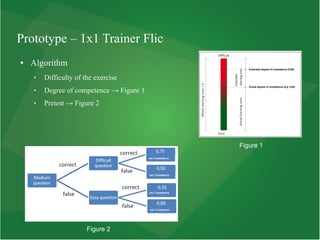
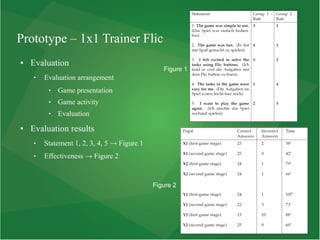
This document summarizes a masters thesis that explores using mobile applications and external Bluetooth devices for educational games. The thesis outlines research on digital game-based learning and how it can be effective using innovative technologies. It then describes a prototype called the 1x1 Trainer Flic mobile application that was created and evaluated with a third grade class. The application uses an algorithm to select math questions tailored to each student's level of competence and provides feedback to guide their learning. An evaluation of the students found the application was generally effective at improving their math skills.