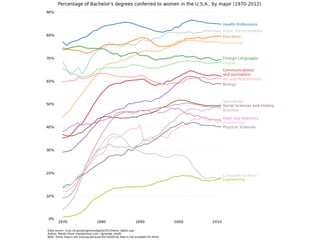
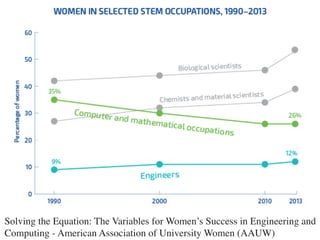
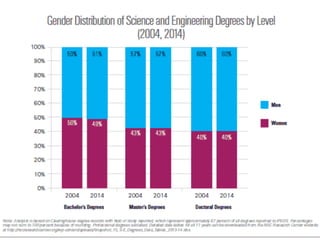
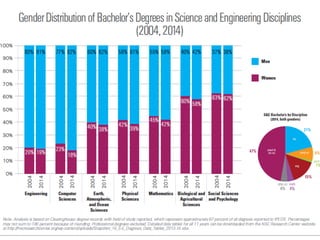
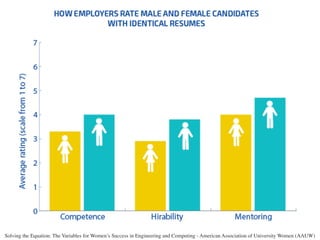
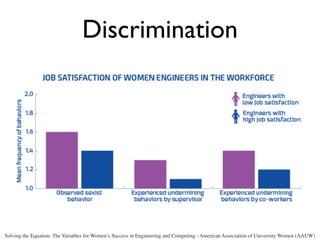
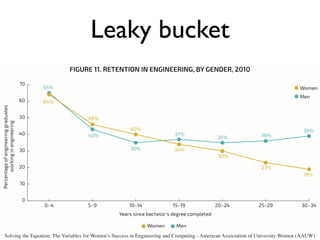
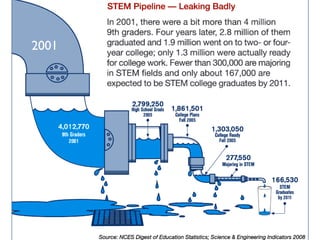
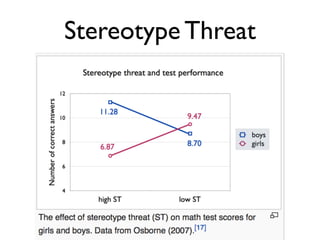
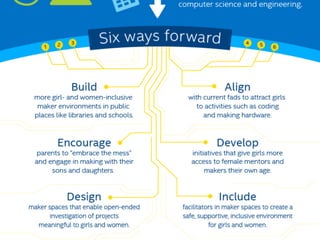
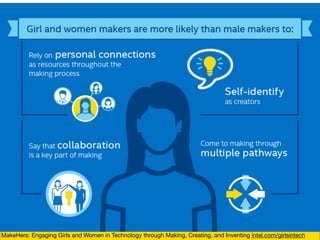
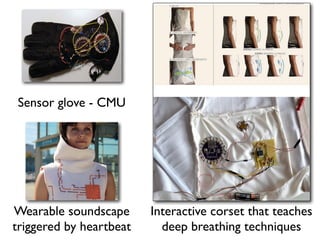
The document discusses the challenges girls face in STEM fields, highlighting issues such as gender bias, teacher influences, and societal stereotypes that contribute to the underrepresentation of women in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics. It emphasizes the importance of creating inclusive learning environments and strategies to encourage girls' engagement in these areas through hands-on making and tinkering. Additionally, the document suggests actionable steps for educators and advocates to support girls in overcoming barriers and succeeding in STEM careers.