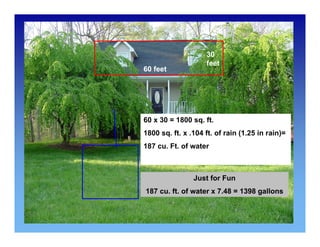
Residential rain gardens are low areas planted with native vegetation that intercept stormwater runoff and allow it to infiltrate the soil. They reduce runoff by 30% more than lawns by promoting more infiltration. Rain gardens increase groundwater recharge, help protect against flooding and pollution, and provide wildlife habitat. When designing a rain garden, consider the size based on the drainage area and type of soil. Native plants that tolerate wet and dry periods are recommended. Proper installation and mulching helps rain gardens become self-sustaining landscaping features.