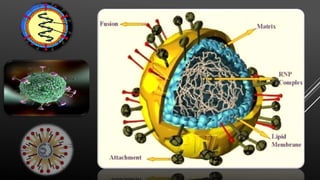
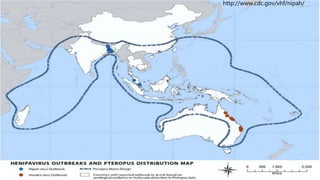
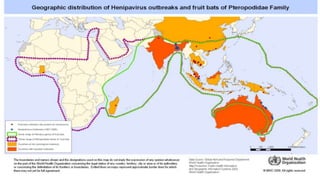
Nipah virus is a zoonotic virus that causes disease in both animals and humans. It was initially identified during an outbreak among pig farmers in Malaysia and Singapore in 1999. Bats are the natural reservoir of the virus. Transmission occurs through contact with infected bats, pigs, or infected humans. Symptoms in humans range from asymptomatic infection to acute respiratory illness and fatal encephalitis. Outbreaks have occurred in Bangladesh and India through consumption of date palm sap or close contact with bats. There is no vaccine, so prevention focuses on reducing exposure to bats and infected individuals.



![ Its name originated from Sungai Nipah, a
village in the Malaysian Peninsula where
pig farmers became ill with encephalitis.
Given the relatedness of NiV to Hendra
virus, bat species were quickly singled
out for investigation & flying foxes of
the genus Pteropus were subsequently
identified as the reservoir for NiV.
[REF: http://www.cdc.gov/vhf/nipah/]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nipahvirus1-160302044609/85/Nipah-virus-6-320.jpg)
![PROBLEM STATEMENT:
In the 1999 outbreak, Nipah virus caused
a relatively mild disease in pigs, but
nearly 300 human cases with over 100
deaths were reported.
In order to stop the outbreak, more than a
million pigs were euthanized, causing
tremendous trade loss for Malaysia.
Since this outbreak, no subsequent cases
(in neither swine nor human) have been
reported in either Malaysia or Singapore.
[REF: MMWR, Outbreak of Hendra-like virus—Malaysia and Singapore,
1998-1999. Apr 9, 1999;48(3):265-9.]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nipahvirus1-160302044609/85/Nipah-virus-10-320.jpg)
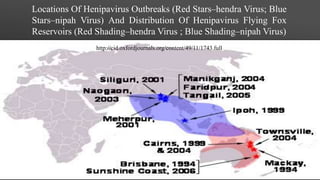
![ In 2001, NiV was again identified as the
causative agent in an outbreak of human
disease occurring in Bangladesh.
Genetic sequencing confirmed this virus as
Nipah virus, but a strain different from the one
identified in 1999.
In the same year, another outbreak was
identified retrospectively in Siliguri, India with
reports of person-to-person transmission in
hospital settings.
Outbreaks occur almost annually in Bangladesh
and have been reported several times in India.
[REF:Chadha MS, Comer JA, Lowe L, et al. Nipah virus-associated encephalitis
outbreak, Siliguri, India.Emerging Infectious Disease 2006;12(2):235-40].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nipahvirus1-160302044609/85/Nipah-virus-11-320.jpg)
![[REF: HT Chong et al. (2009) Nipah virus and bats. Neurology Asia; 14: 73–76]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nipahvirus1-160302044609/85/Nipah-virus-12-320.jpg)


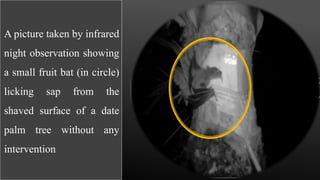
![ Conversely, person – to – person
transmission of Nipah virus in
Bangladesh and India is regularly
reported.
Direct exposure to infected bats. A
common example is consumption
of raw date palm sap contaminated
with infectious bat excretions.
[REF: Field HE, Mackenzie JS, Daszak P. Henipaviruses: emerging paramyxoviruses associated with fruit
bats. Current Topics Microbiology and Immunology 2007;315:133-59.]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nipahvirus1-160302044609/85/Nipah-virus-15-320.jpg)







![ Long-term sequelae following Nipah virus infection
have been noted, including persistent convulsions
and personality changes.
Latent infections with subsequent reactivation of Nipah virus death
have also been reported months and even years after exposure.
During the Nipah virus disease outbreak in 1998-99, 265 patients
were infected with the virus. About 40% of those patients who
entered hospitals with serious nervous disease died from the illness.
[REF:Hossain MJ, Gurley ES, Montgomery JM, et al. Clinical presentation of Nipah virus infection in
Bangladesh. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2008;46(7):977-84.]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nipahvirus1-160302044609/85/Nipah-virus-26-320.jpg)
![Highly contagious
May be asymptomatic
Acute fever (>104°F)
Severe respiratory disease
Characteristic cough – harsh,
“barking”
Neurological changes
Low mortality
[REF: www.cdc.gov/ncidod/dvrd/spb/mnpages/dispages/nipah.html]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nipahvirus1-160302044609/85/Nipah-virus-27-320.jpg)
![DISEASE IN ANIMALS
Dog
1. Distemper-like signs
2. Fever, respiratory distress
3. Ocular and nasal discharge
Cat
1. Fever, depression
2. Severe respiratory signs
Horses
1. Encephalitis
[REF: Center for Food Security and Public Health Iowa State University – 2005]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nipahvirus1-160302044609/85/Nipah-virus-28-320.jpg)
![DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS:
Differentials for NIPAH:
I. Classical swine fever,
II. Porcine Reproductive & Respiratory Syndrome (PRRS),
III. Pseudorabies,
IV.Swine enzootic pneumoniae,
V. Porcine pleuropneumonia
[REF: http://www.who.int/csr/don/archive/disease/nipah_virus/en/]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nipahvirus1-160302044609/85/Nipah-virus-29-320.jpg)


![A subunit vaccine, using the Hendra G protein, produces cross-
protective antibodies against HEN V. and NIP V. has been
recently used in Australia to protect horses against Hendra virus.
VACCINATION:
[REF:National Center for Emerging and Zoonotic Infectious Diseases (NCEZID)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nipahvirus1-160302044609/85/Nipah-virus-32-320.jpg)

![DIAGNOSIS
Laboratory diagnosis is made during the acute and convalescent
phases of the disease by using a combination of tests.
Virus isolation attempts and real time polymerase
chain reaction (RT-PCR) from throat and nasal
swabs, CSF, urine & blood should be performed
in the early stages of disease.
Antibody detection by ELISA can be used later on.
In fatal cases, immunohistochemistry on tissues
collected during autopsy may be the only way to confirm diagnosis.
[REF: Lim CCT, Lee KE, Lee WL, et al. Nipah virus encephalitis: Serial MR study of an emerging
disease.Radiology 2002;222(1):219-26].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nipahvirus1-160302044609/85/Nipah-virus-34-320.jpg)
![TREATMENT:
Treatment is limited to supportive care.
Standard infection control practices and proper barrier nursing
techniques are important in preventing nosocomial transmission.
The drug ribavirin has been shown to be effective against the
viruses in vitro, but human investigations to date have been
inconclusive & the clinical usefulness of ribavirin remains
uncertain.
Passive immunization using a human monoclonal antibody
targeting the Nipah G glycoprotein has been evaluated in the post-
exposure therapy in the ferret model & found to be of benefit.
[REF: Mounts AW, Kaur H, Parashar UD, et al. A cohort study of health care workers to assess nosocomial transmissibility of Nipah
virus, Malaysia, 1999. Journal of Inf. Disease 2001;183(5):810-3.]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nipahvirus1-160302044609/85/Nipah-virus-35-320.jpg)
![NIPAH AS A BIOLOGICAL WEAPON
CDC Category C Bioterrorism Agent
Emerging pathogen
Potentially high morbidity and mortality
Major health impact
Aerosolization potential
Economic impact
Social disruption (fear, panic)
[REF:Wong KT, Shieh WJ, Kumar S, et al. Nipah virus infection. Pathology and pathogenesis of an emerging paramyxoviral zoonosis.
American Journal of Pathology 2002;161(6):2153-67.]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nipahvirus1-160302044609/85/Nipah-virus-36-320.jpg)
![1. Why is respiratory disease and person-to-person transmission
more common among human NiV infection in Bangladesh
compared to Malaysia?
2. How stable is the genome of Nipah?
3. Is there a substantial risk of mutation that would improve the
efficiency of person-to-person transmission of the virus?
4. How common is unrecognized, including subclinical, infection
with NiV?
[REF: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK114486/]
UNANSWERED QUESTIONS
? ? ?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nipahvirus1-160302044609/85/Nipah-virus-37-320.jpg)
