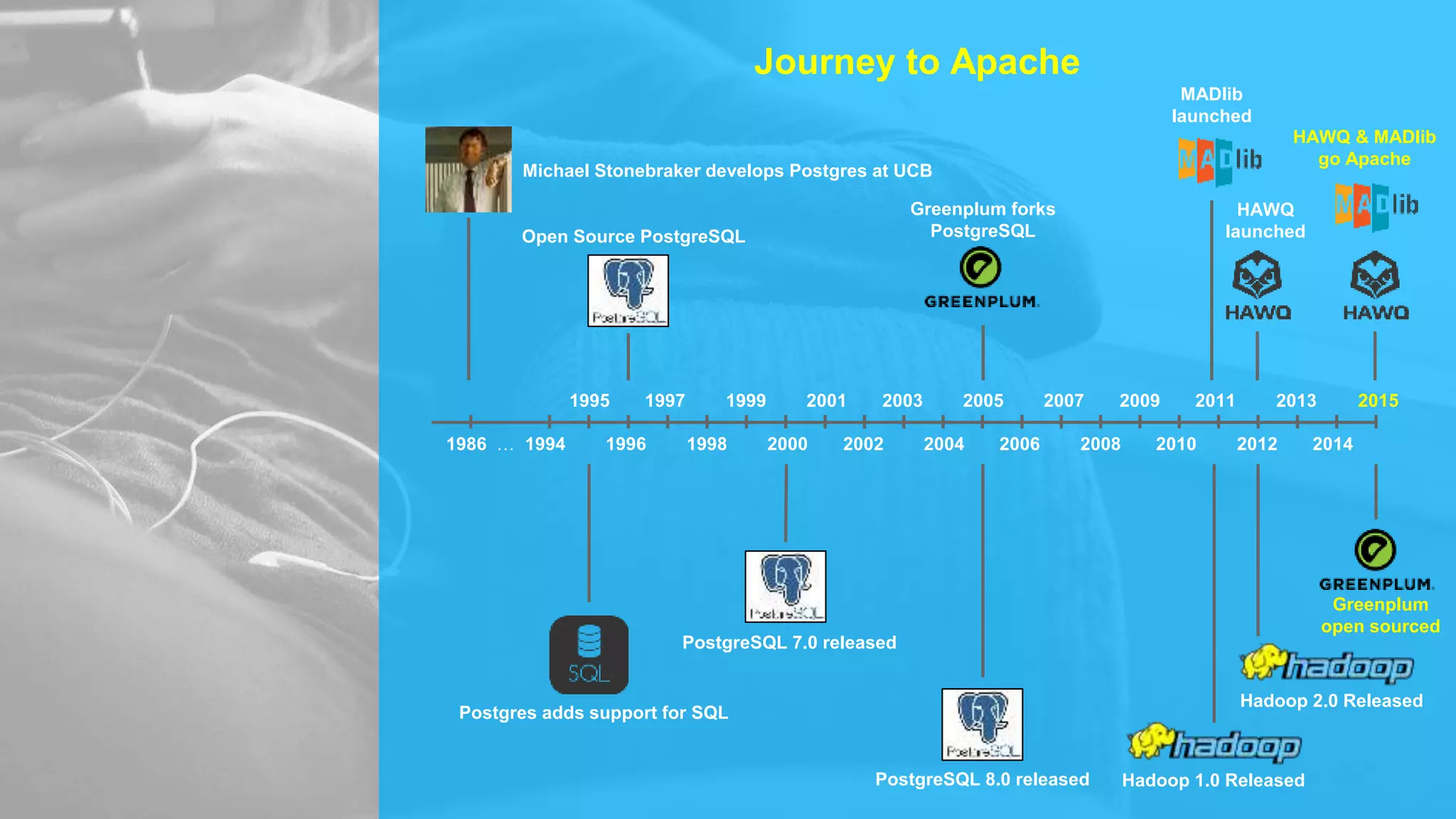
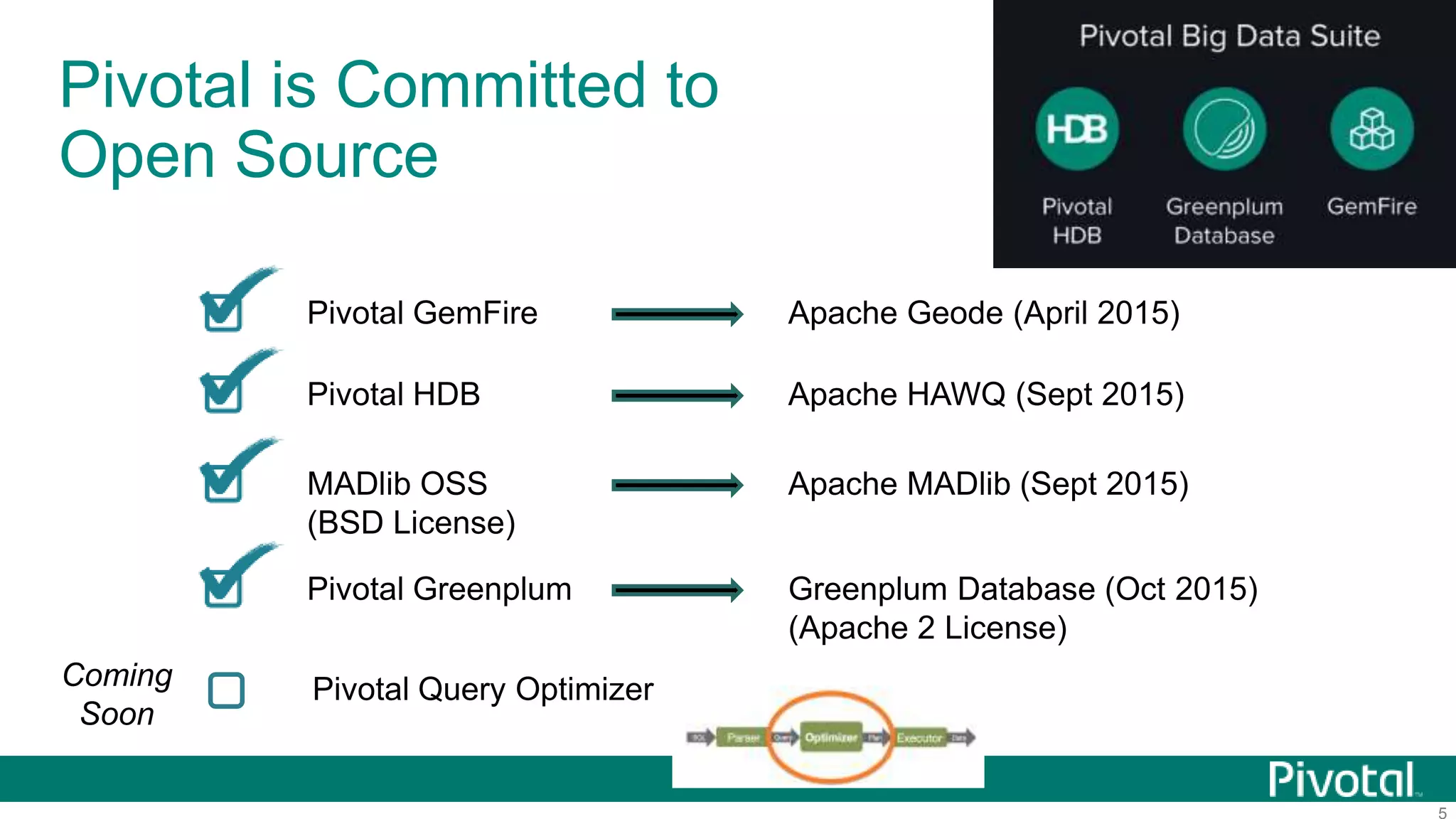
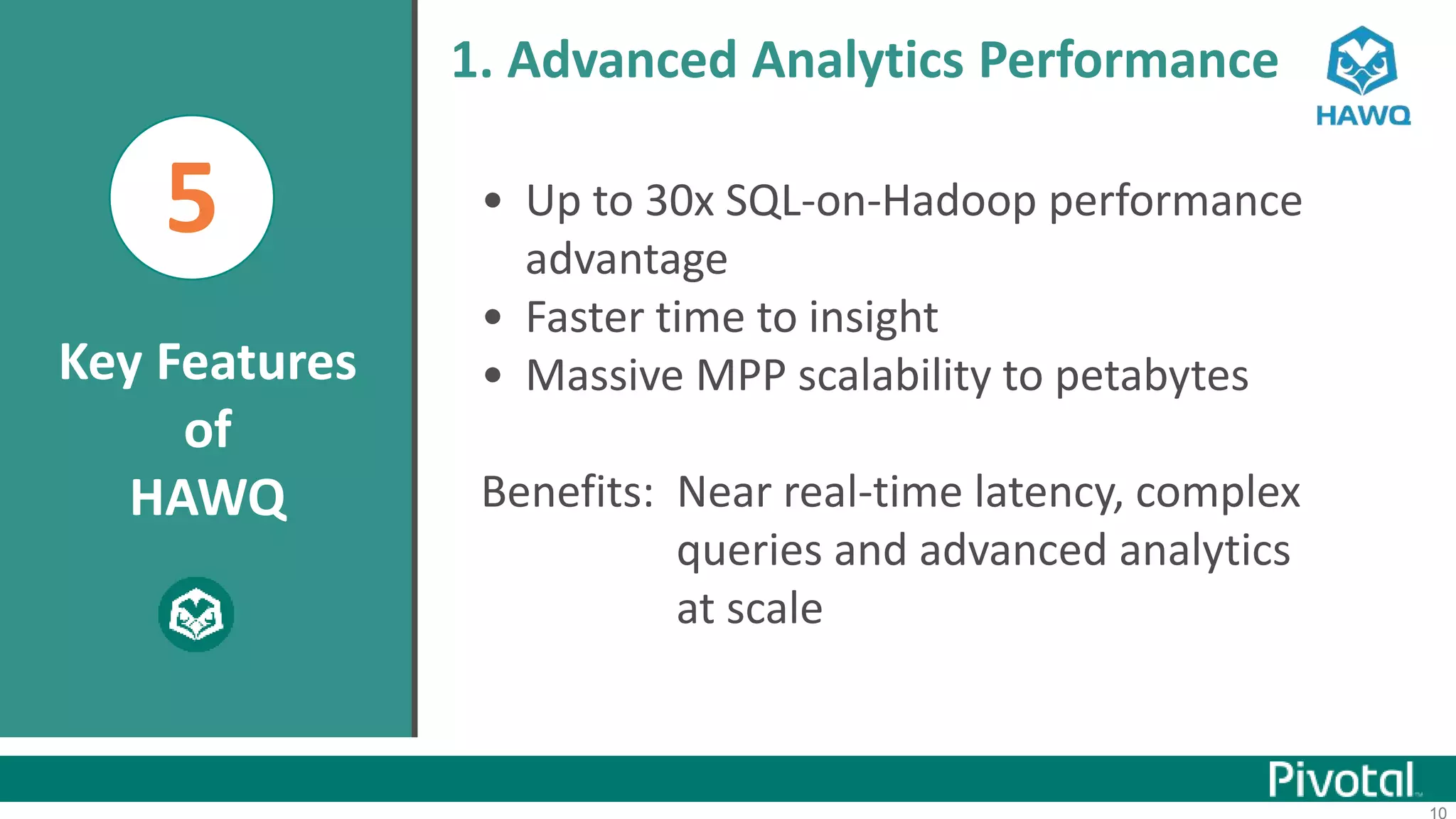
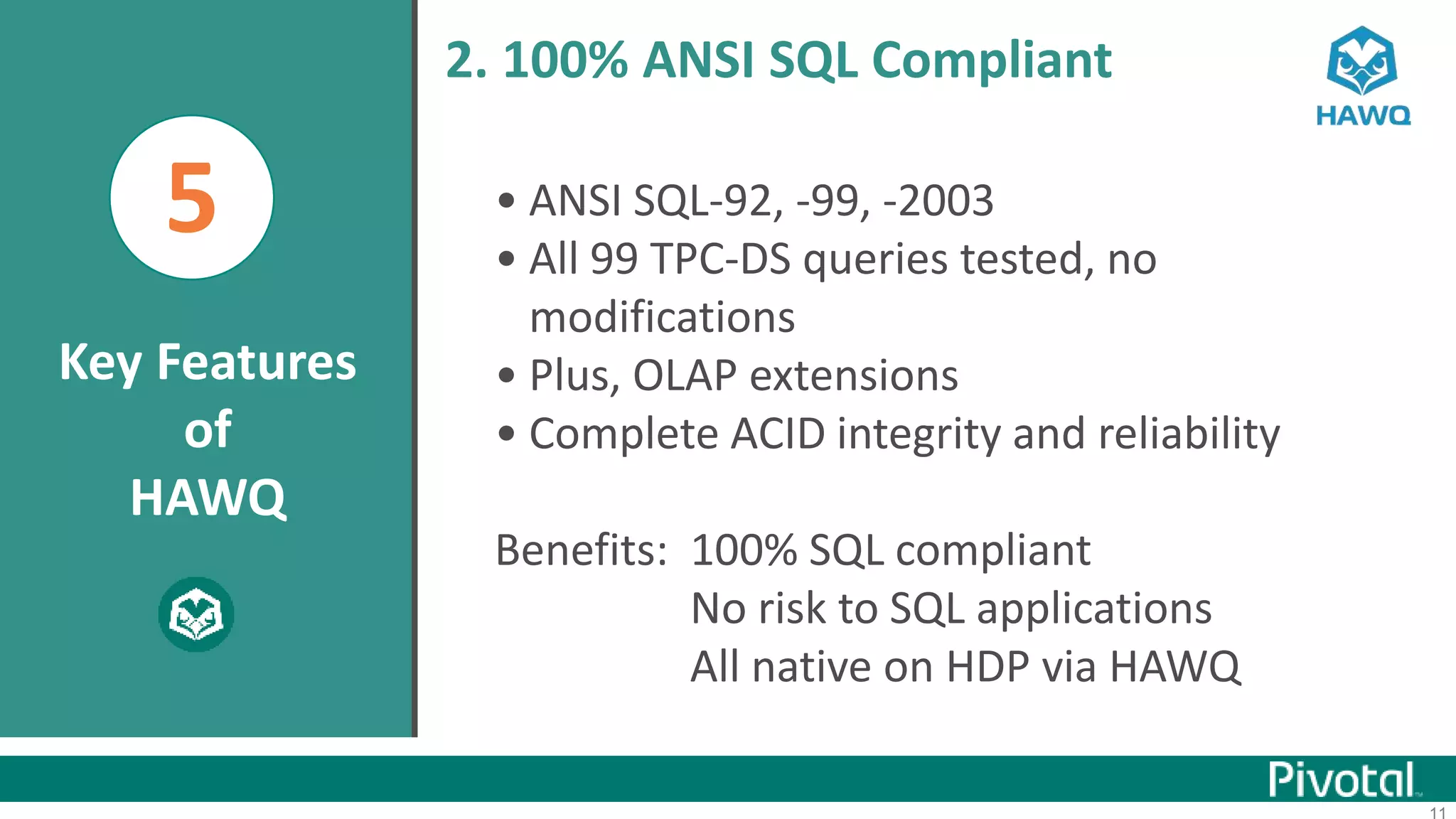
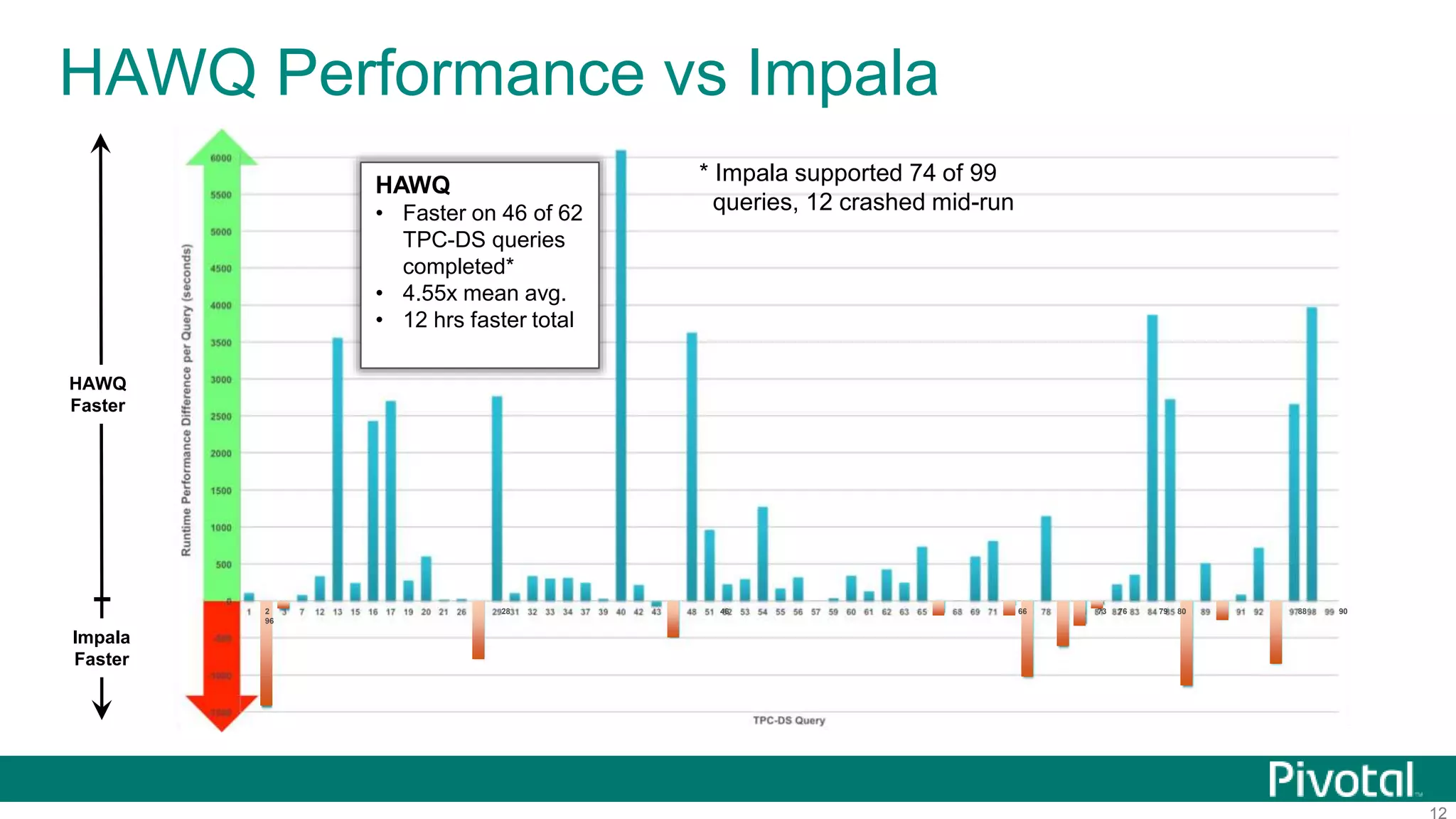
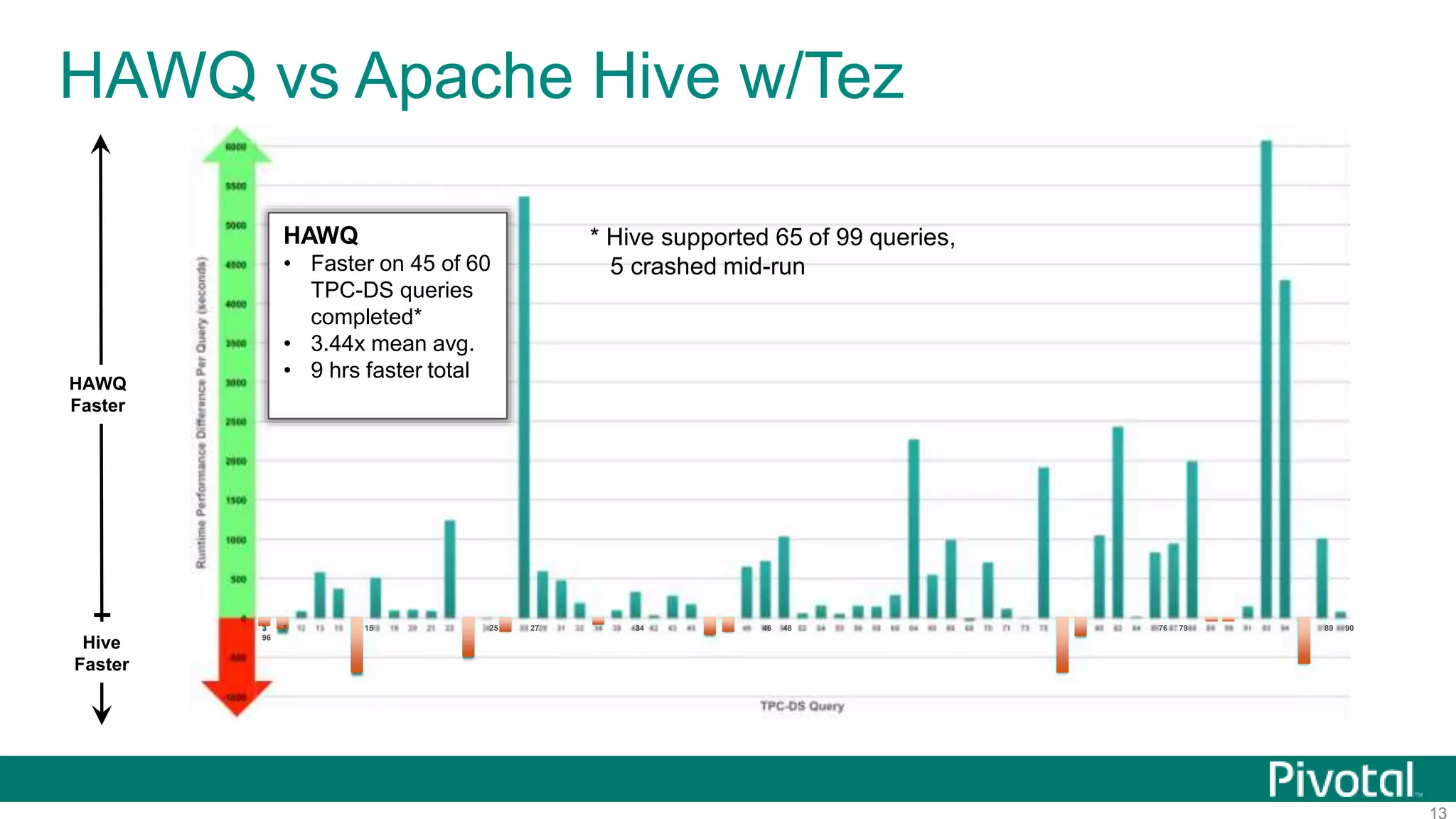
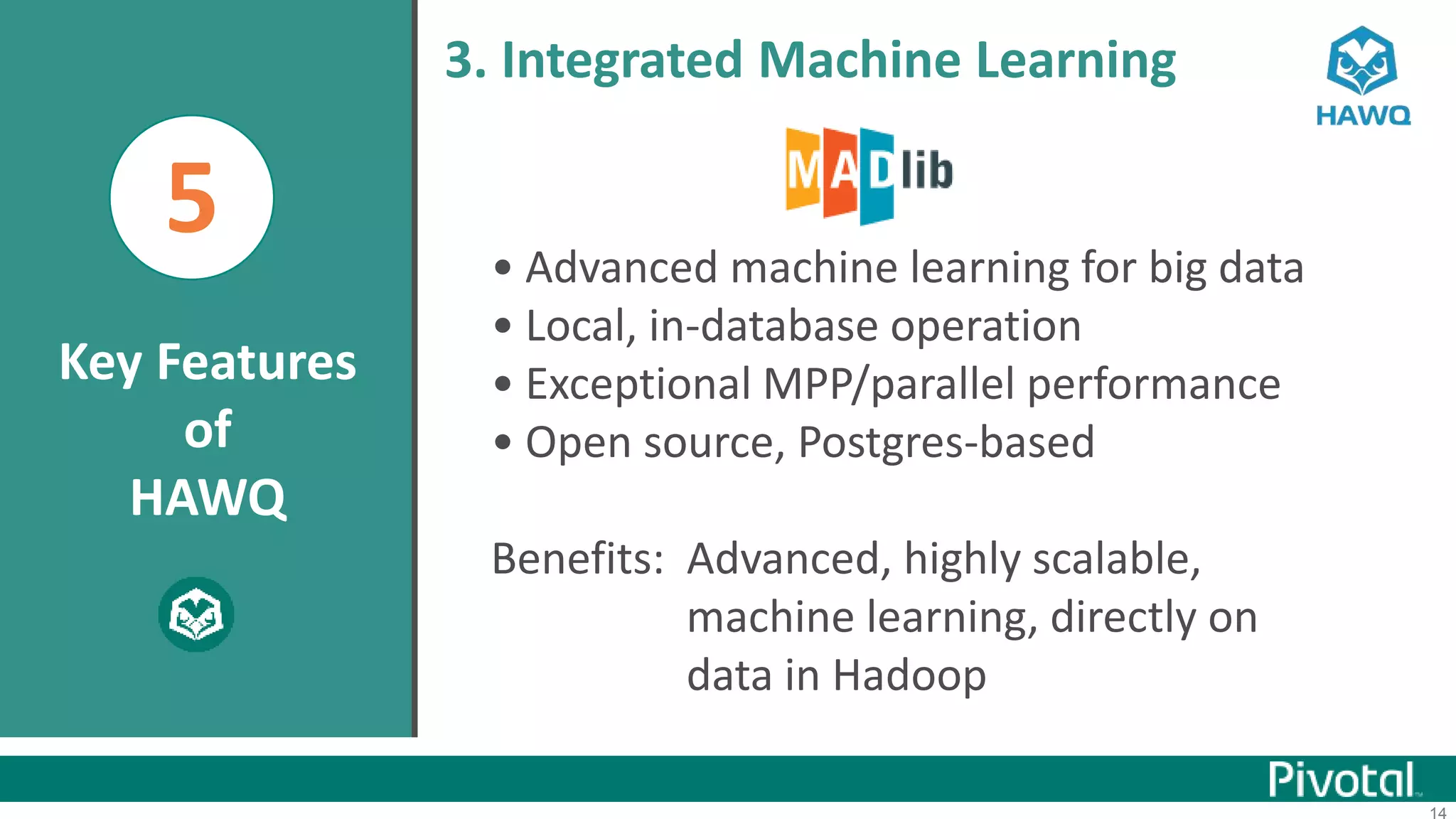
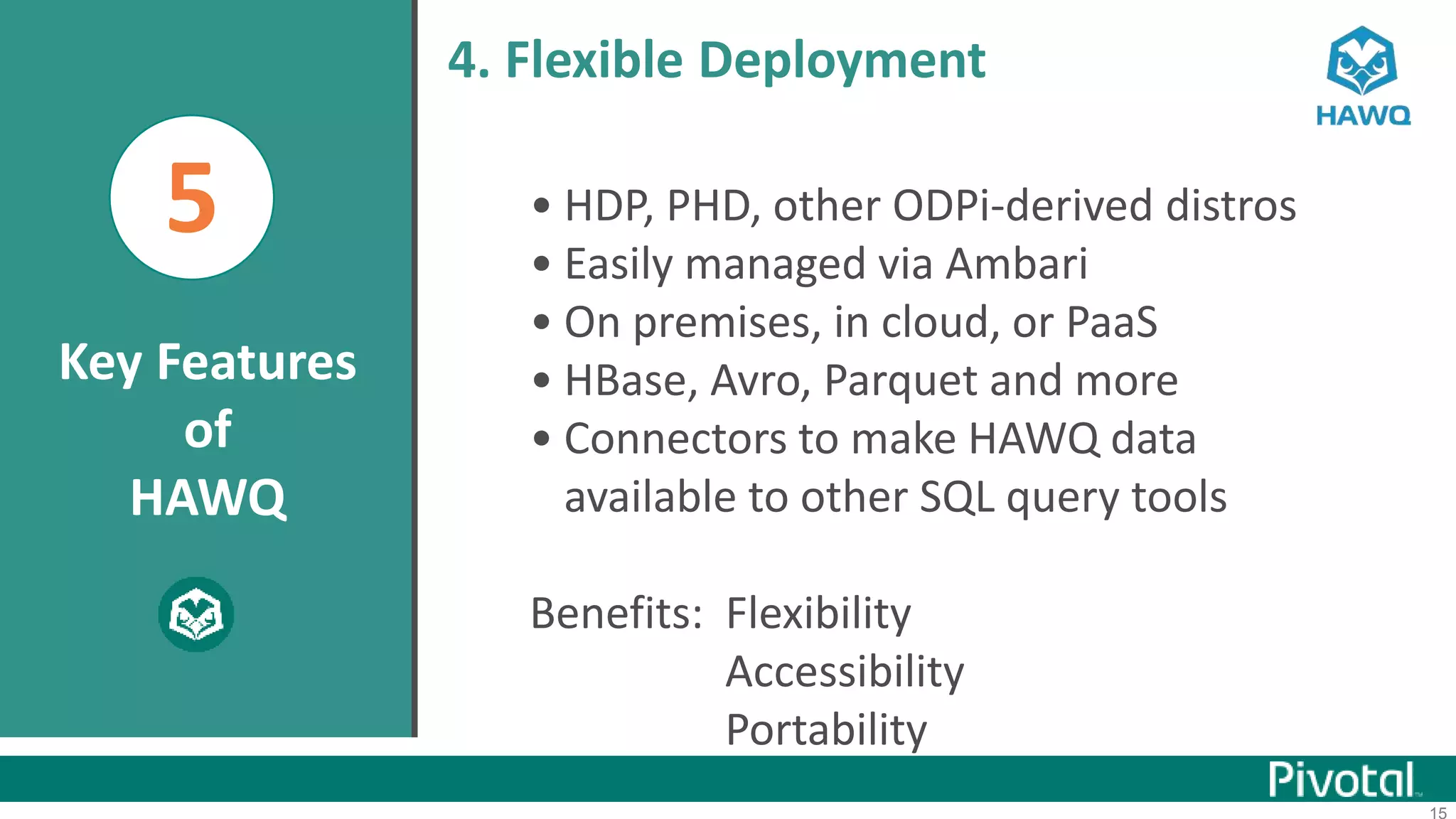
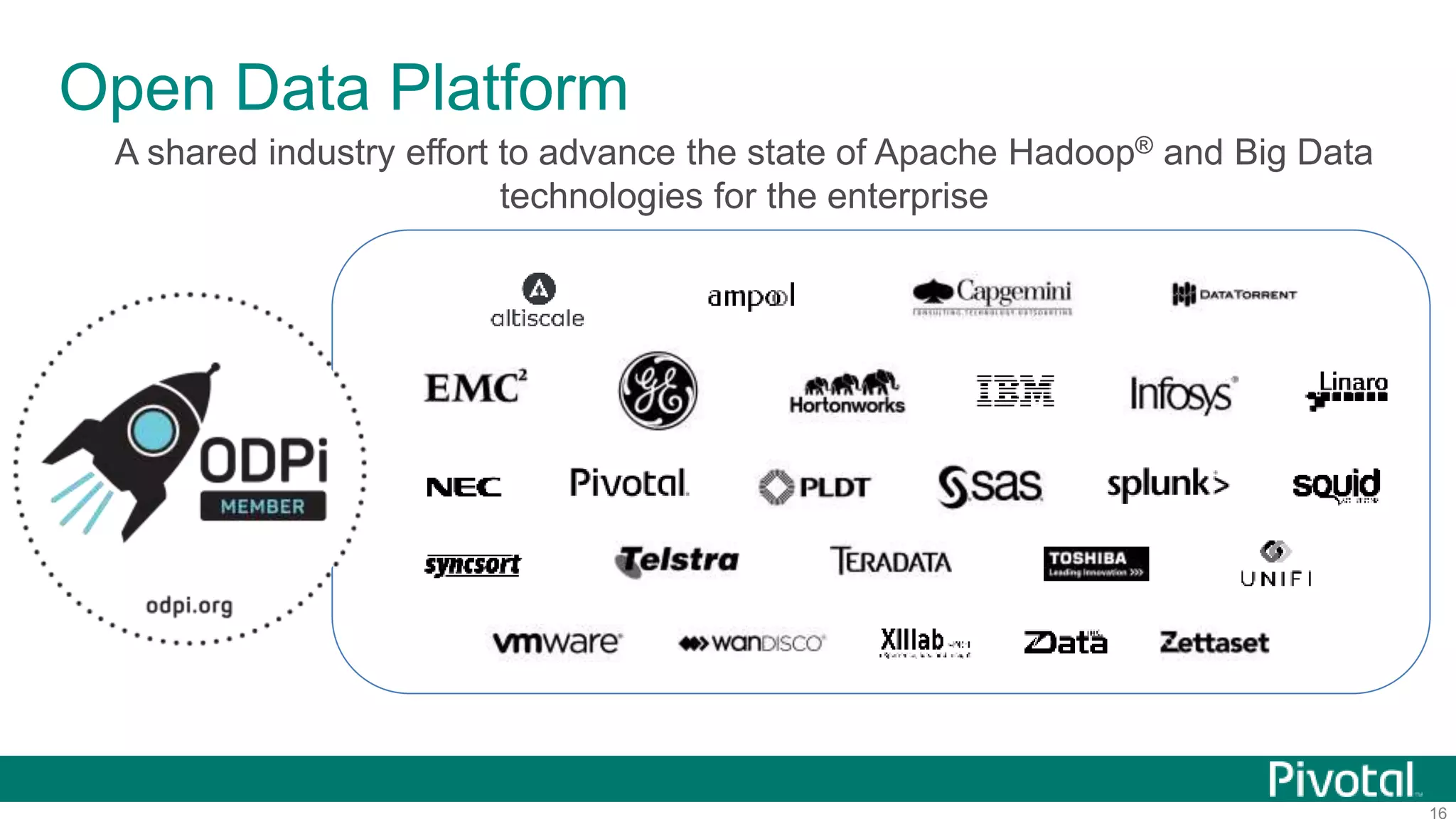
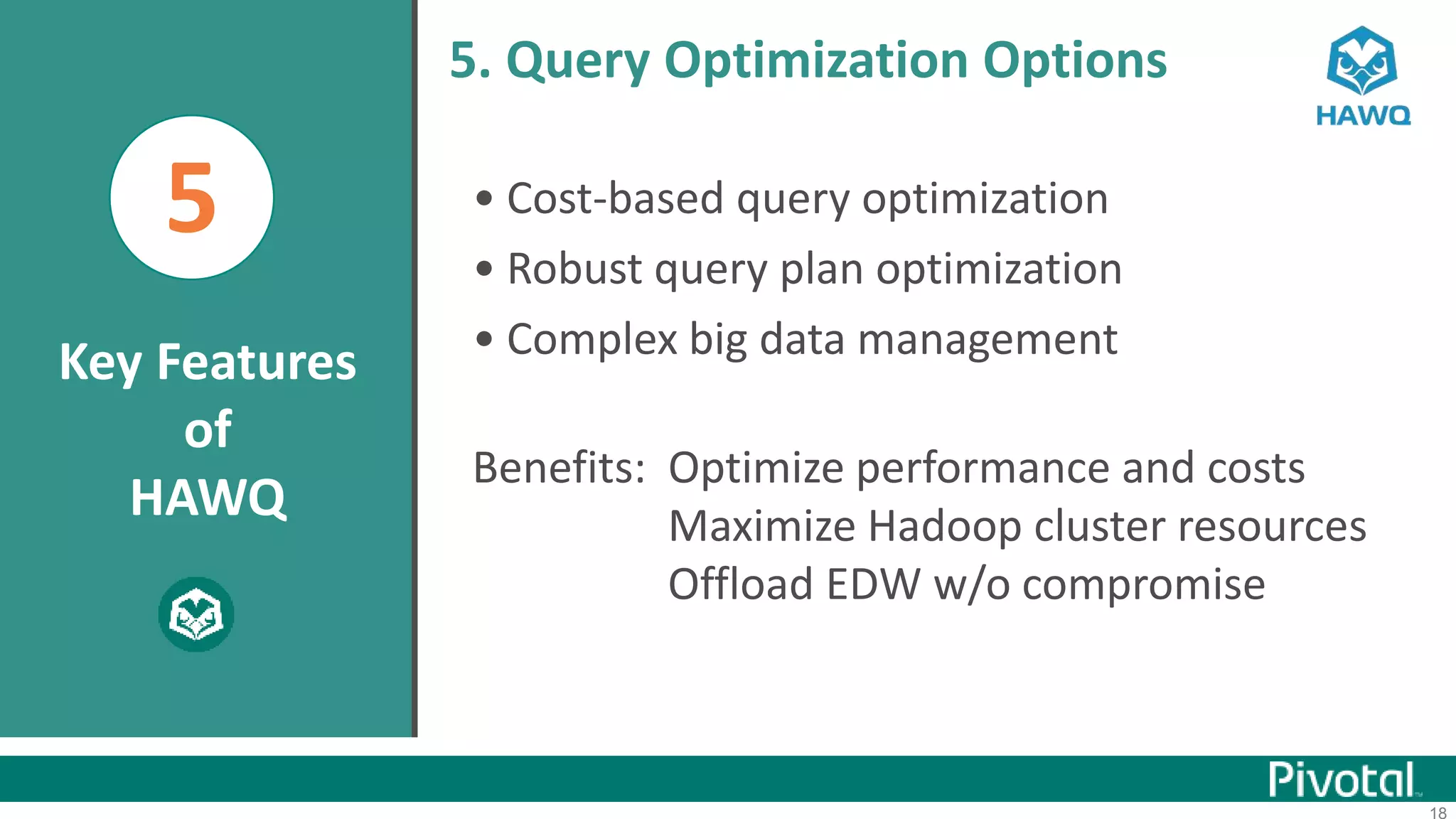
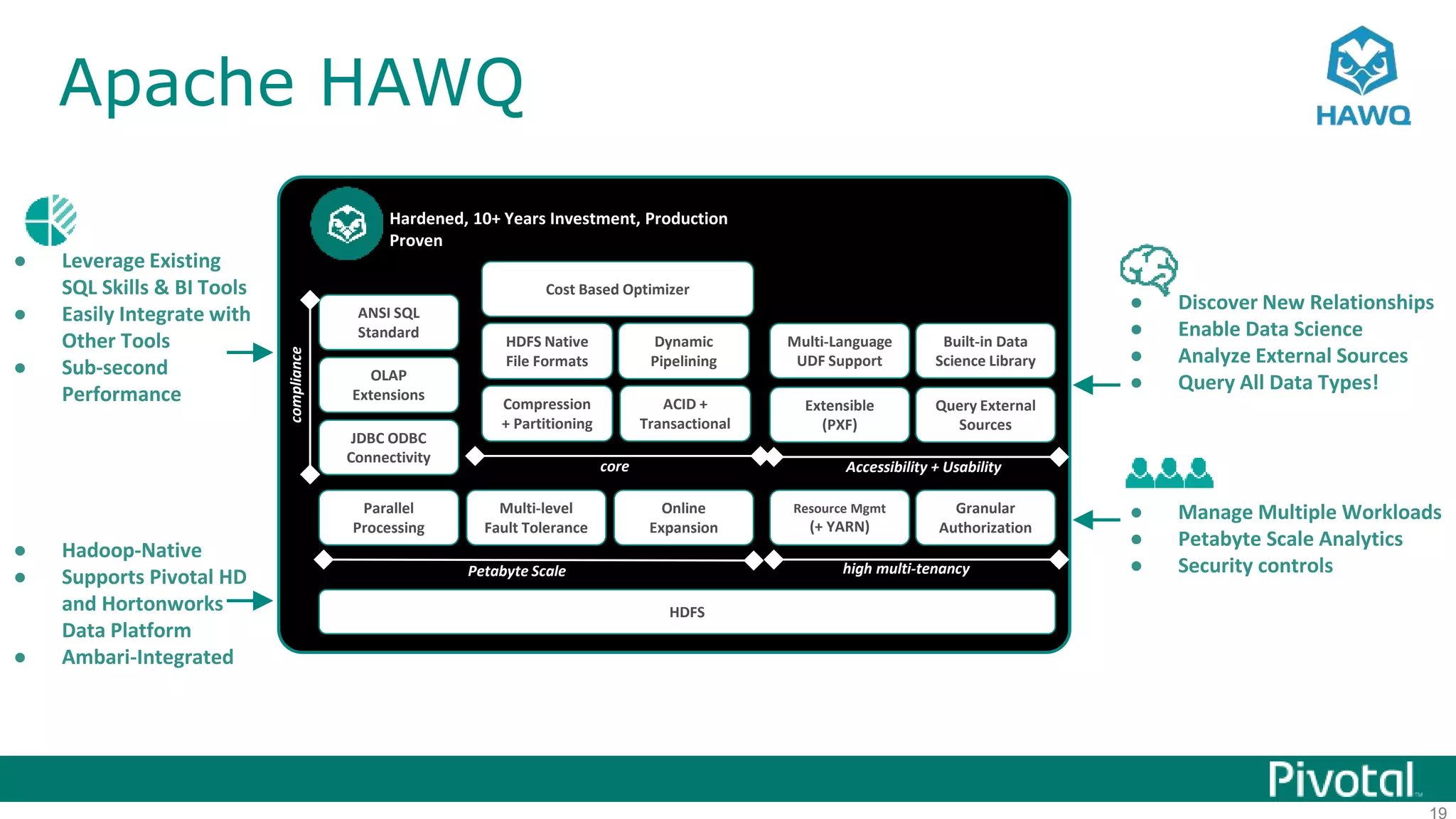
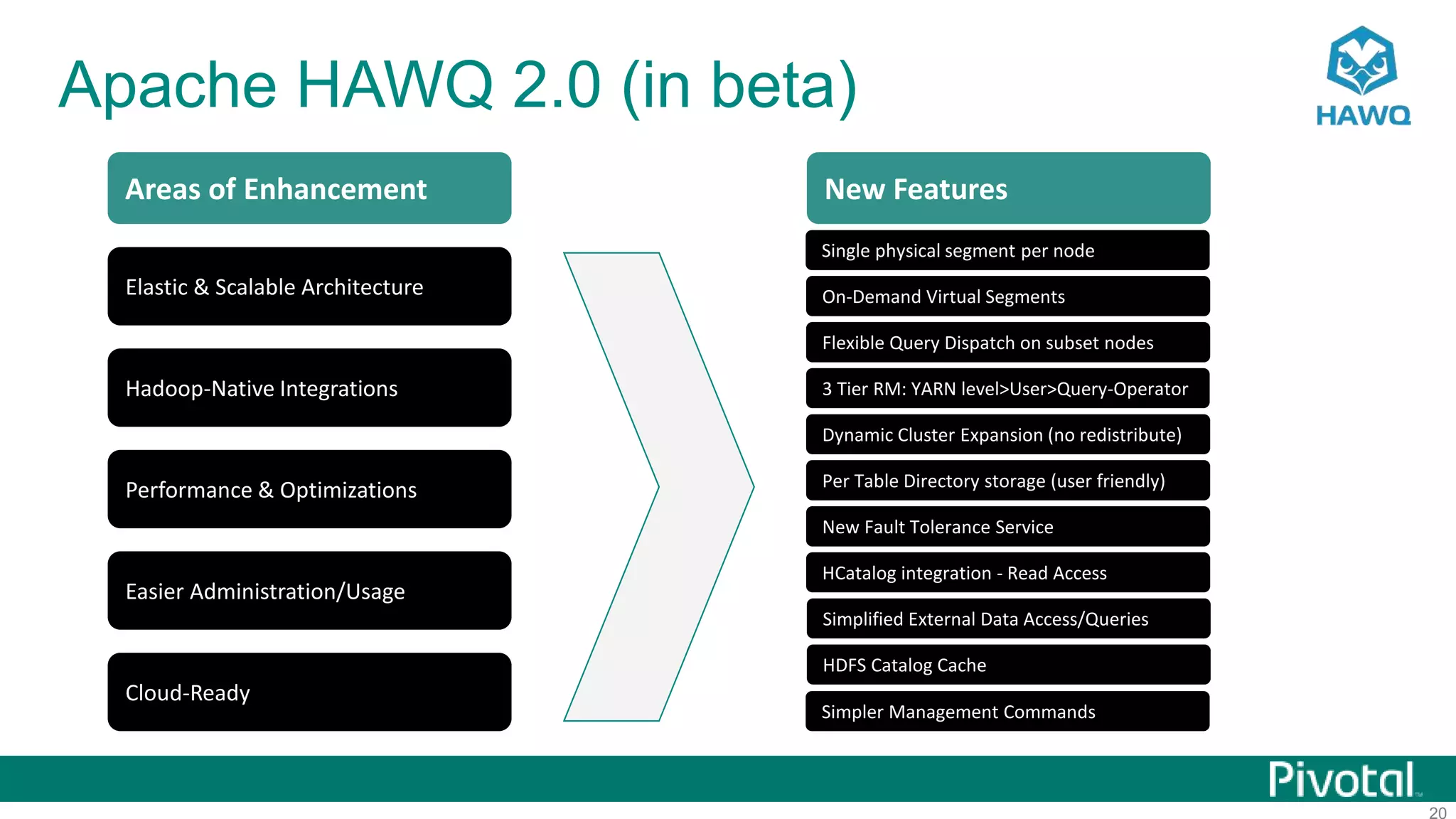
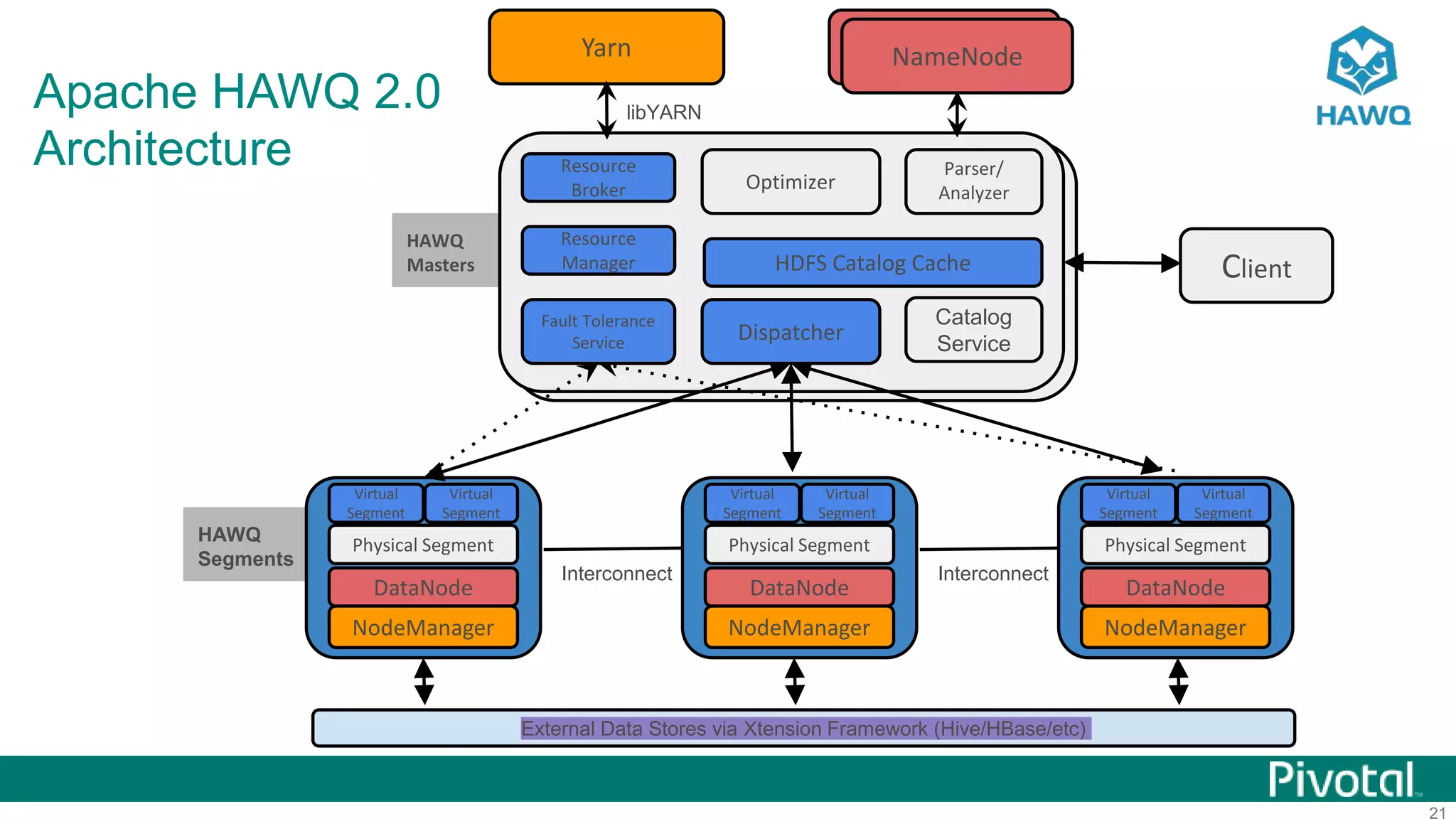
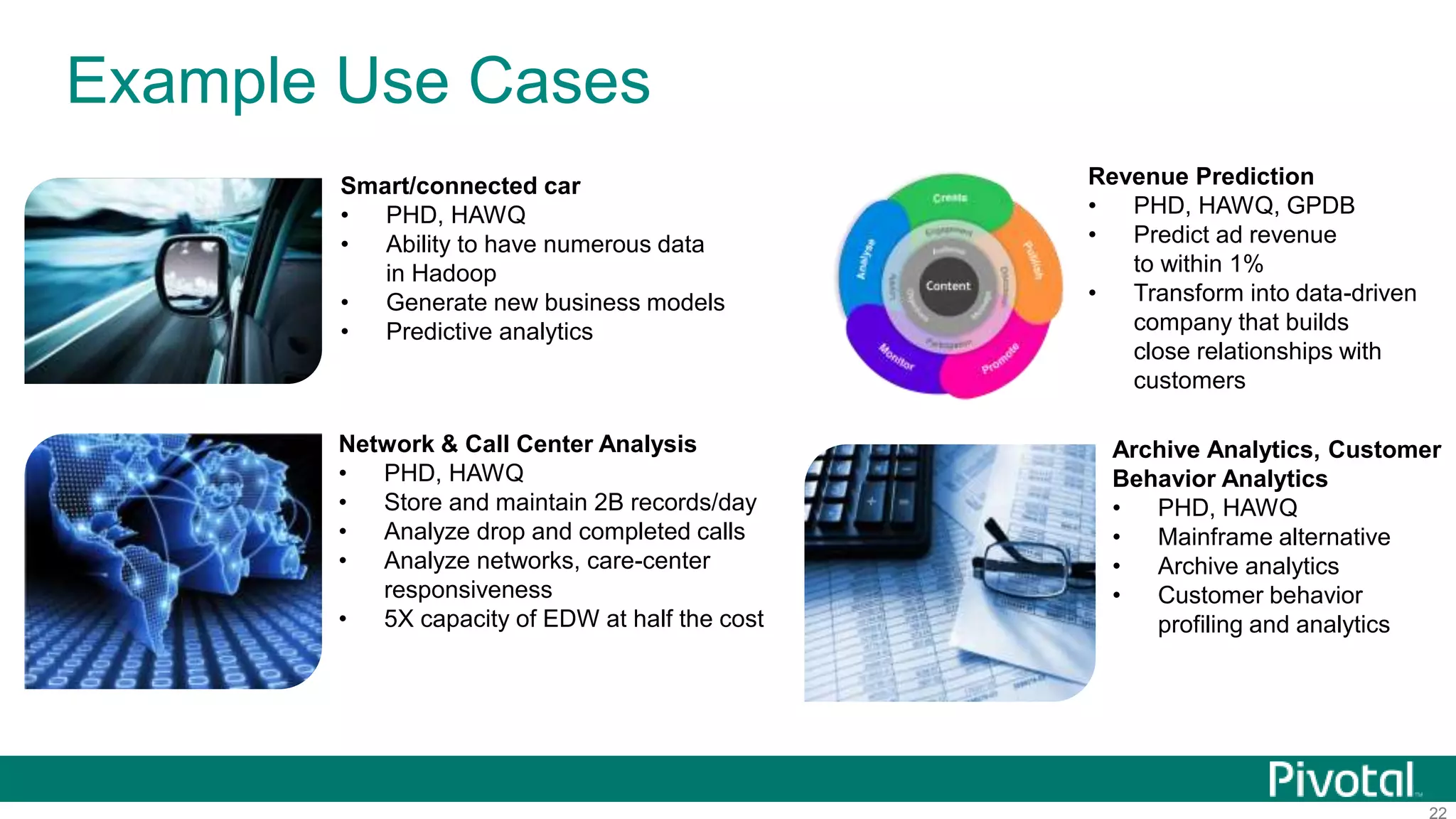
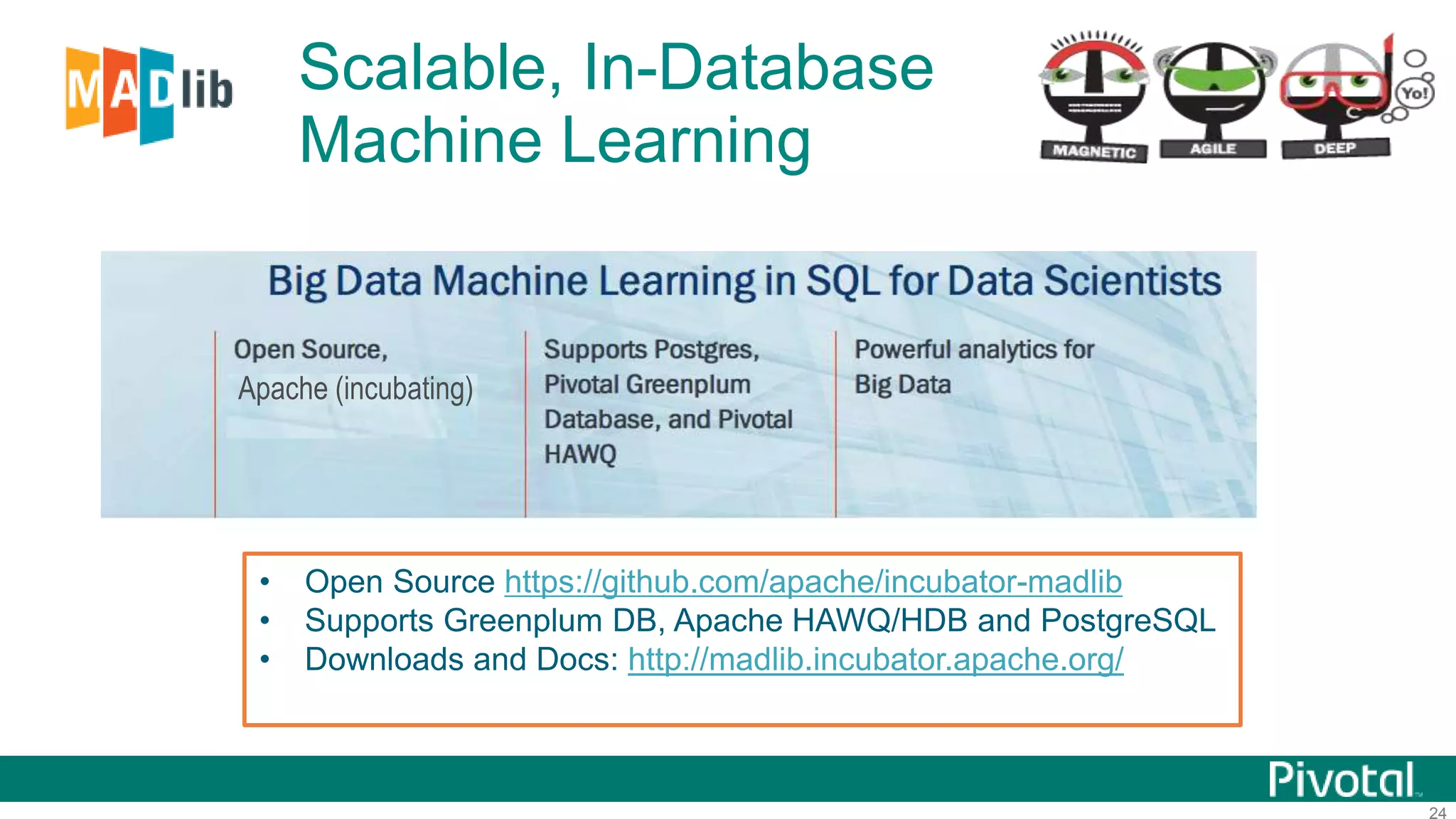
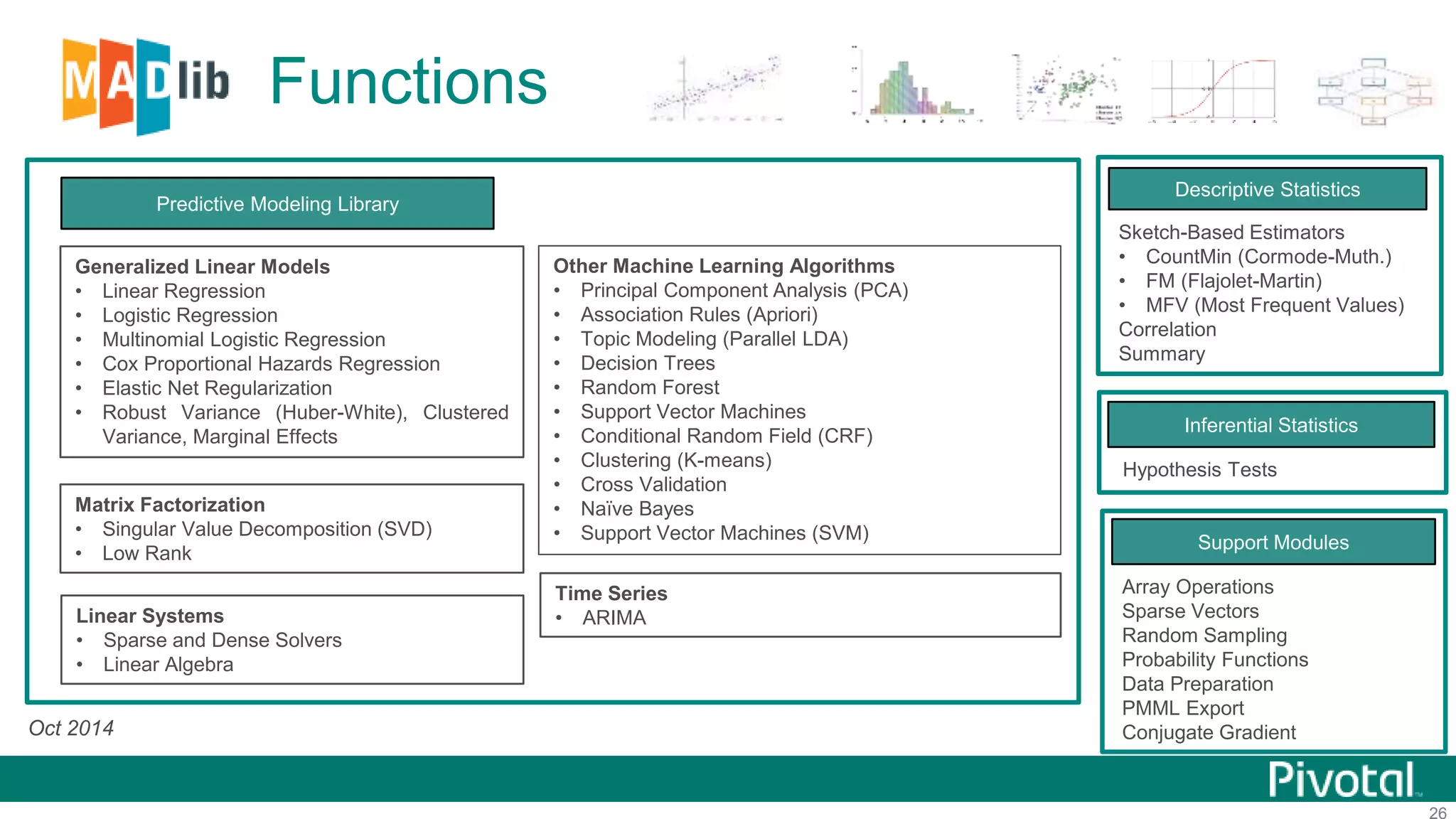
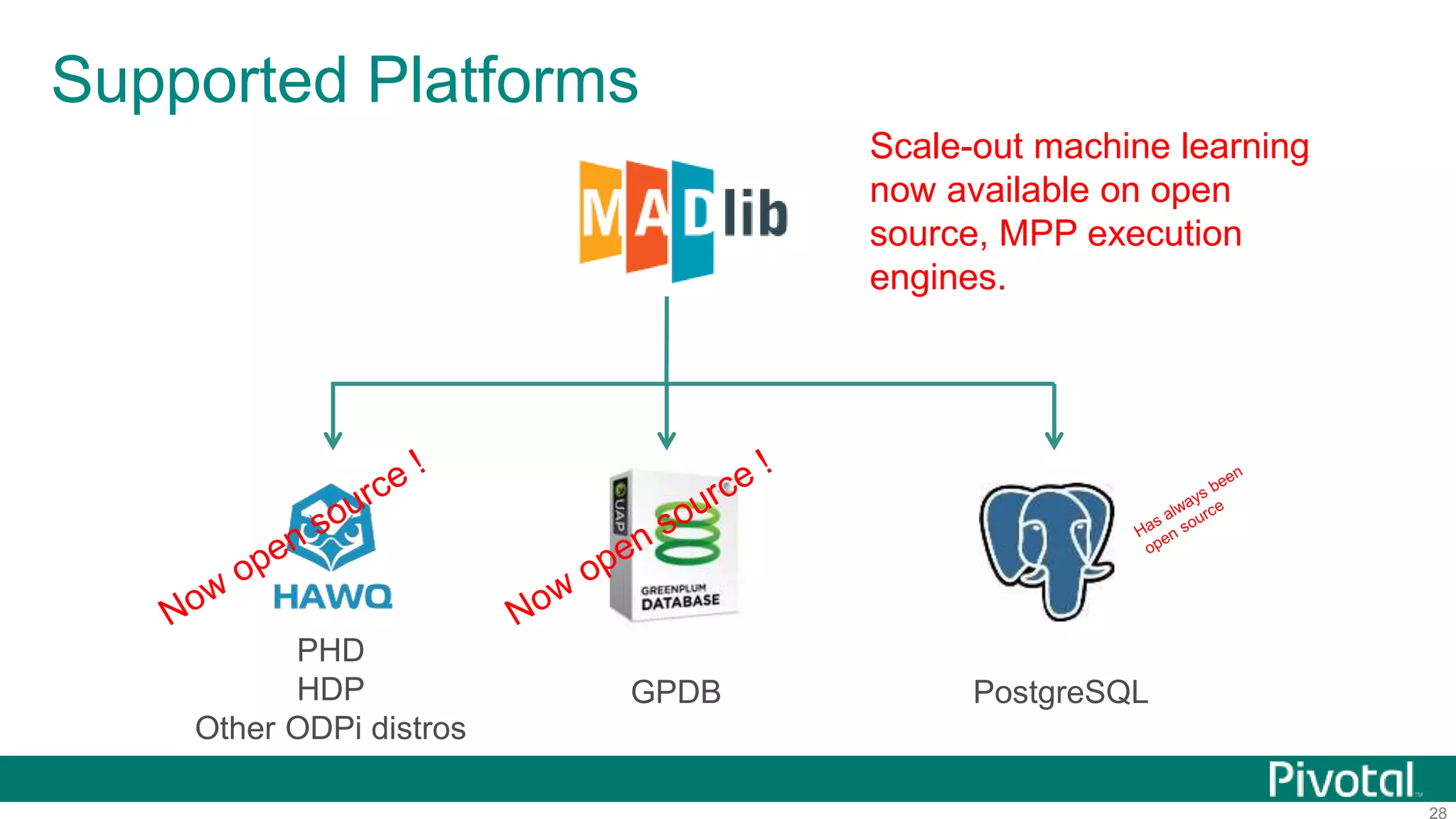
The document summarizes the journey of HAWQ and MADlib from being proprietary Pivotal technologies to becoming Apache open source projects. It provides an overview of HAWQ, including its key features like SQL compliance, performance advantages over other SQL-on-Hadoop systems, and flexible deployment options. It also summarizes MADlib, describing its machine learning functions and advantages of scalable in-database machine learning. Both projects are now available on open source platforms like Hadoop and aim to advance SQL and machine learning on big data through open collaboration.