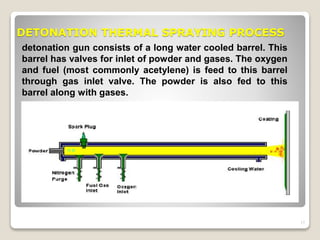
This dissertation evaluates coatings for reducing erosion wear in hydroelectric turbine blades. HVOF thermal spray coating techniques are applied to test samples of 16Cr5Ni steel. Coatings of WC-Co-Cr, Cr2C3+NiCr, and diamalloy are evaluated using a jet erosion tester with silty water. The testing finds that the WC-Co-Cr coating significantly reduces erosion wear at both low and high impact angles compared to uncoated steel. Abrasion blasting is used to prepare the steel samples for coating adhesion before HVOF coating deposition. The dissertation aims to increase hydropower plant efficiency by minimizing turbine blade erosion through optimized coatings.