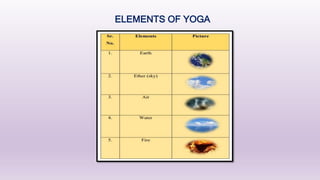
Yoga, originating in ancient India, encompasses a variety of physical, mental, and spiritual practices aimed at achieving peace and self-realization. It involves moral principles (Yama), observances (Niyama), physical postures (Asana), breath control (Pranayama), and meditation (Dhyana), among other elements. Benefits of yoga include improved physical health, reduced stress, and enhanced spiritual awareness.