This document proposes a decentralized approach to reducing malnutrition in India through meal production units. Key points:
- Malnutrition rates in India are extremely high, with over 20 million children going to bed hungry every night.
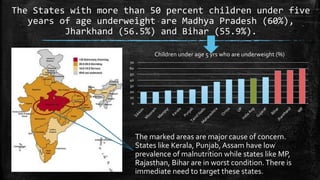
- A centralized system of meal production units located in towns would cook, package and distribute meals to schools in surrounding villages. Targeted "red zones" have over 60% of children underweight.
- Each unit would be automated and distribute around 40,000 meals per month. Total estimated monthly cost is Rs. 500 per child.
- Challenges include monitoring the network, managing costs, ensuring equitable distribution and controlling leakage.