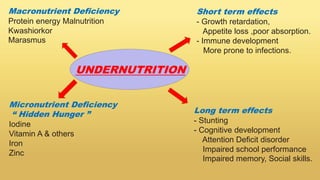
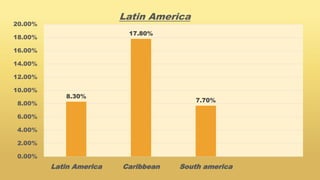
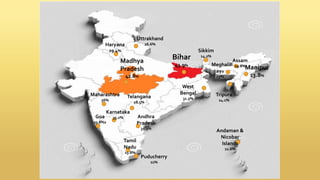
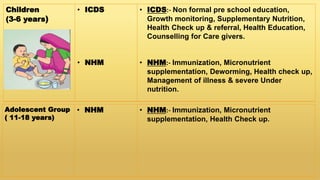
Undernutrition among children under 5 years old remains a major global public health problem. In India, approximately one third of children are underweight. The Integrated Child Development Services program aims to address undernutrition through nutrition supplementation, health services, and preschool education, though it has had limited effectiveness. Improving implementation by increasing focus on the first 1000 days of life, strengthening nutrition education, improving coordination between frontline workers, and enhancing community participation could help reduce undernutrition. Addressing its multidimensional causes requires commitment across health, nutrition, education, agriculture, and social welfare programs.