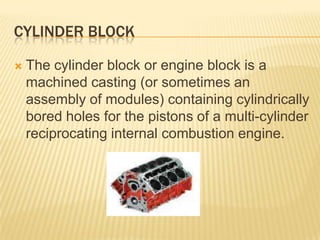
This document provides an overview of Yamaha's manufacturing plant. It details Yamaha's founding date and president, as well as its major product lines which include motorcycles, boats, engines, and other vehicles and machinery. The plant layout includes administrative areas, shops for casting, treatment, machine work, and plating. It also explains key engine parts like the cylinder head, spark plug, rocker arm, cylinder liner, cylinder block, piston, connecting rod, crankshaft, flywheel, and sump tank. Heat engines are defined as converting heat from fuel combustion into mechanical work.