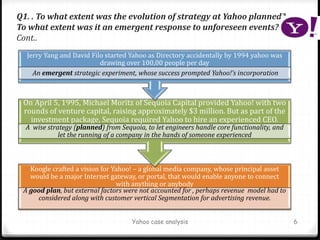
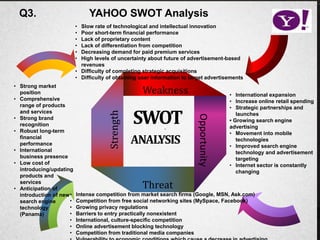
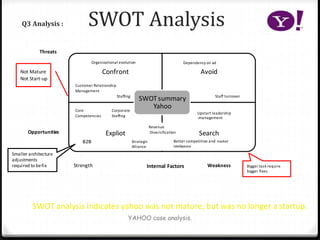
Yahoo was founded in 1994 by two Stanford students and grew rapidly, going public in 1996. Between 1994 and 2000, Yahoo's strategy evolved as planned with the goal of becoming a major internet portal, however the company struggled to adapt to unforeseen events like the dot-com bubble bursting in 2001. Facing declining advertising revenue, the then-CEO Timothy Koogle resigned in 2001, demonstrating for a public company the CEO often takes responsibility for performance issues beyond their control.