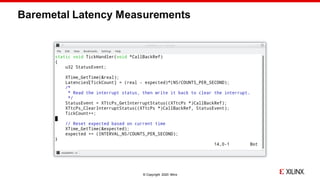
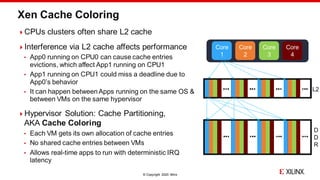
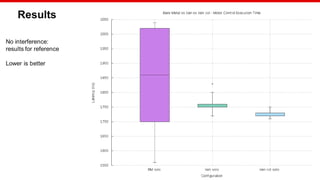
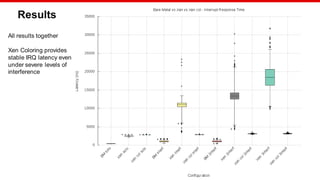
The document discusses Xilinx's implementation of cache coloring in the Xen hypervisor to mitigate cache interference in real-time applications. It outlines the benefits of cache partitioning, such as improved execution times and reduced IRQ latency, even under stress conditions. Additionally, it provides benchmarking results demonstrating the effectiveness of this cache coloring approach on the Xilinx MPSoC hardware.






![© Copyright 2020 Xilinx
Coloring Configuration
Xen command line
Dom0-less DomUs
xl domU config files
way_size=65536 xen_colors=0 dom0_colors=1-6
fdt set /chosen/domU0 colors <0x0 0x80>
colors=["10-11"]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cachecoloringelcna-200630220407/85/Xen-Cache-Coloring-Interference-Free-Real-Time-System-13-320.jpg)
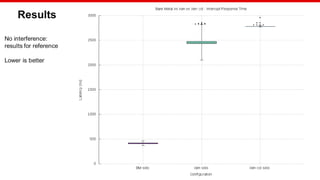
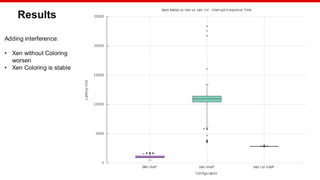
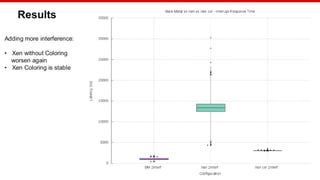
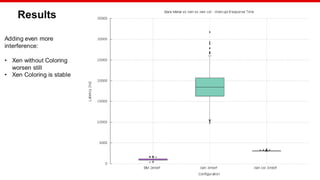
![© Copyright 2020 Xilinx
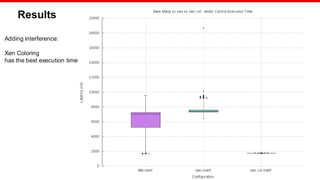
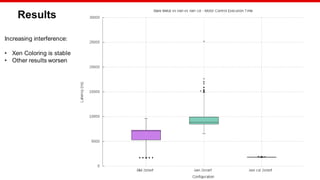
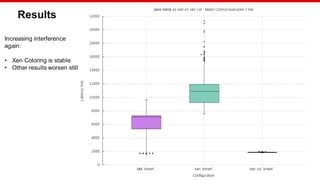
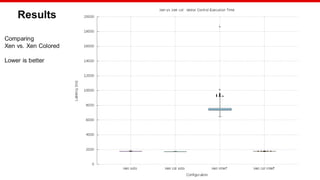
Benchmarking
Hardware: Xilinx MPSoC
Workload: Bare Metal application
Stress: Bare Metal application
Test configuration:
Measured load: 1500 sums
Internal load: 8000 sums every 250us
Interrupt triggered every 8ms
Samples:1000
Colored configuration:
Xen: ["0,1"]
Motor Control DomU: ["4,7"]
Stress DomU: ["8,11"]
Stress2 DomU:["12,15"]
Linux stress:["2,3"]
Linux stress command: stress -m 1 --vm-bytes 8M --vm-stride 64 --vm-keep -t 3600 &](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cachecoloringelcna-200630220407/85/Xen-Cache-Coloring-Interference-Free-Real-Time-System-14-320.jpg)





![© Copyright 2020 Xilinx
Xen Cache Coloring: Demo
Xen
[0]
Baremetal
Latency
Measurements
[7]
Baremetal Memory
Stress
[10 11]
Dom0
[1 2 3 4 5 6]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cachecoloringelcna-200630220407/85/Xen-Cache-Coloring-Interference-Free-Real-Time-System-30-320.jpg)