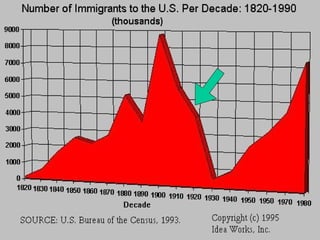
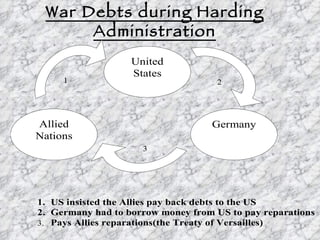
The 1920s were a period of conflict in the United States. Xenophobia against immigrants was widespread after World War 1 as returning soldiers struggled with competition for jobs. The Red Scare led to raids against communists and prejudice against many immigrant groups. Prohibition went into effect in 1919 due to pressure from temperance groups, but led to increased crime and corruption as underground alcohol markets emerged. Women gained the right to vote with the passage of the 19th amendment in 1920. The 1920s also saw economic growth under pro-business administrations.