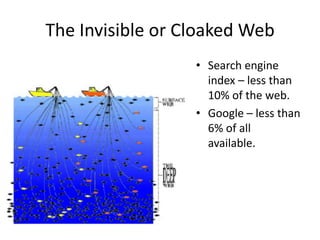
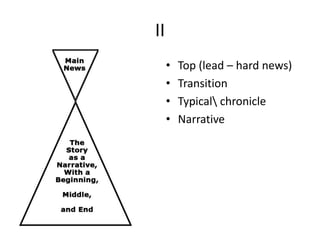
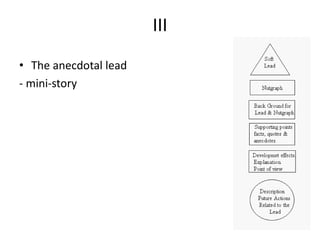
This document provides guidance on writing stories for the web. It outlines seven deadly sins to avoid such as pride, apathy, and ignorance. It also describes steps for story-building such as listening to find the story, determining where it's likely to be found, and specifying the field. The document discusses the invisible web that search engines don't index and recommends using primary search engines to locate databases and then search within those databases. It also covers different types of stories, structures, leads, and endings to use when writing for the web.