The document contains code examples that demonstrate different data types in C#, including writing to the console, reading user input, numeric formatting, overflow handling, floating point numbers, enumerations, and arrays. Specifically, it shows how to:
1) Write and read from the console using Console.Write and Console.ReadLine methods.
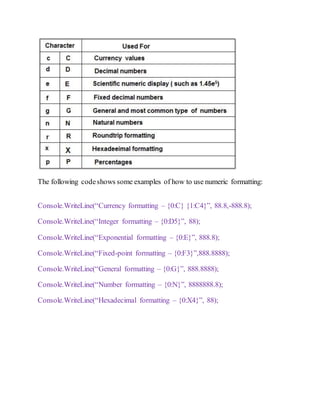
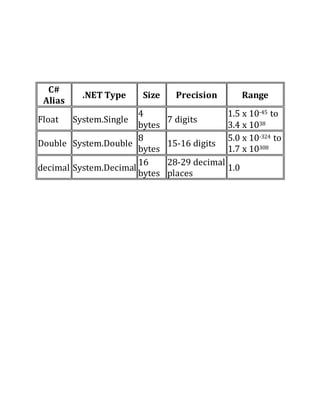
2) Format numeric output using formats like currency, integer, exponential, etc.
3) Demonstrate overflow for byte data type values beyond its range.
4) Define and use enumerations to represent day names.
5) Initialize and access elements of an integer array.
![Write and WriteLine Methods
// Namespace Declaration
using System;
// Program start class
class InteractiveWelcome
{
// Main begins program execution.
public static void Main()
{
// Write to console/get input
Console.Write("What is your name?: ");
Console.Write("Hello, {0}! ", Console.ReadLine());
Console.WriteLine("Welcome to the C# Station Tutorial!");
}
}
Output:
>What is your Name? <type your name here> [Enter Key]
>Hello, <your name here>! Welcome to the C# Station Tutorial!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/writeandwritelinemethods-160811042352/85/Write-and-write-line-methods-1-320.jpg)












![ARRAYS
using System;
class ArrayExample
{
static void Main()
{
int[] numbers = new int[5];
numbers[0] = 3;
numbers[1] = 2;
numbers[2] = 1;
numbers[3] = 5;
numbers[4] = 6;
int len = numbers.Length;
for (int i=0; i<len; i++)
{](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/writeandwritelinemethods-160811042352/85/Write-and-write-line-methods-16-320.jpg)
![Console.WriteLine(numbers[i]);
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/writeandwritelinemethods-160811042352/85/Write-and-write-line-methods-17-320.jpg)