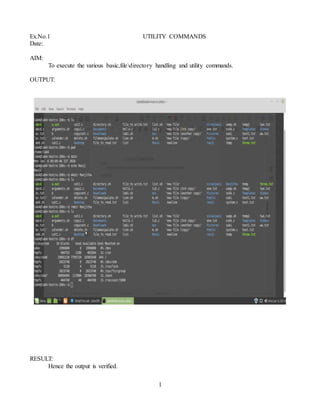
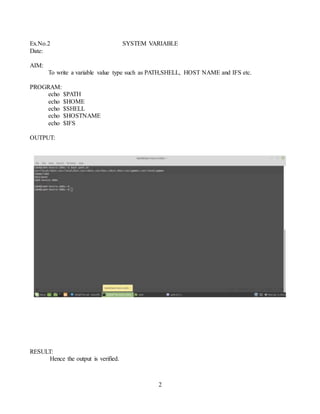
The document contains summaries of various Unix/Linux commands and programs executed by a student. It includes 15 examples covering topics like utility commands, system variables, administrative commands, displaying users, file permissions, deleting files, displaying code from a file, deleting lines containing a word, checking file/directory type, arithmetic/logical calculations, factorials, string operations, checking for vowels, and file operations. For each example, it lists the aim, program/commands used, outputs, and verifies the results.


![5
Ex.No.5 DISPLAY THE LIST OF USERS
Date
AIM:
To write a shell script that displays a list of all files in the current directory to which the user has
read ,write and execute permissions.
PROGRAM:
echo "enter the directory name"
read dir
if [ -d $dir ]
then
cd $dir
ls > f
exec < f
while read line
do
if [ -f $line ]
then
if [ -r $line -a -w $line -a -x $line ]
then
echo "$line has all permissions"
else
echo "files not having all permissions"
fi
fi
done
fi
OUTPUT:
RESULT :
Hence the output is verified.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linuxlabmanual-220923053636-9ce5a321/85/Linux-Lab-Manual-doc-5-320.jpg)


![8
Ex.No.8 DELETE A LINE CONTAINING SPECIFIED WORD
Date
AIM:
To write a shell script that deletes all lines containing a specified word in one or more files
supplied as arguments to it.
PROCEDURE:
1. Start.
2. Get the file names as command line arguments.
3. Write “enter the word to search and delete”.
4. Read word.
5. For each argument repeat step 6 to step 8.
6. if it is file then go to next step else display “error in file”.
7. Search the lines not contain specified “word”.
8. Write the above result into same file.
9. Stop.
PROGRAM:
if [ $# -eq 0 ]
then
echo NO ARUGUMENTS
else
pattern=$1
shift
for fname in $*
do
if [ -f $fname ]
then
echo DELETING $pattern FROM $fname
sed '/'$pattern'/d' $fname
else
echo $fname NOT FOUND
fi
done
fi](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linuxlabmanual-220923053636-9ce5a321/85/Linux-Lab-Manual-doc-8-320.jpg)

![10
Ex.No.9 FILES OR DIRECTORY DOCUMENTS.
Date
AIM:
To write a shell script that receives any number of file names as its arguments, check if every
argument supplied is a file or a directory and reports accordingly. Whenever the argument is a file, the
number of lines on its to be reported.
PROCEDURE:
1. Start.
2. Get the file names and command line arguments.
3. Check the file is directory or file.
4. Display the number of lines in the file.
5. stop.
PROGRAM:
for x in $*
do
if [ -f $x ]
then
echo "$x is a file"
echo "no of lines in the files are"
wc -l $x
elif [ -d $x ]
then
echo "$x is a directory"
else
echo "enter valid filename or directory name"
fi
done](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linuxlabmanual-220923053636-9ce5a321/85/Linux-Lab-Manual-doc-10-320.jpg)

![12
PROGRAM:
#!/bin/sh
a=10
b=10
val=`expr $a + $b`
echo "a + b : $val"
val=`expr $a - $b`
echo "a - b : $val"
val=`expr $a * $b`
echo "a * b : $val"
val=`expr $b / $a`
echo "b / a : $val"
val=`expr $b % $a`
echo "b % a : $val"
if [ $a == $b ]
then
echo "a is equal to b"
fi
if [ $a != $b ]
then
echo "a is not equal to b"
fi
OUTPUT:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linuxlabmanual-220923053636-9ce5a321/85/Linux-Lab-Manual-doc-12-320.jpg)
![13
RESULT:
Hence the output is verified.
Ex .No. 11.FACTORIAL OF THE GIVEN NUMBER
Date:
AIM:
To write a shell script to find the factorial of a given number.
PROCEDURE:
1. start
2. get the number as “num”
3. calculate the factorial number
4. display the number
5. stop
SHELL COMMAND:
echo "enter a number"
read num
fact=1
while [ $num -gt 1 ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linuxlabmanual-220923053636-9ce5a321/85/Linux-Lab-Manual-doc-13-320.jpg)

![15
Ex. No.12. STRING OPERATIONS
Date:
AIM:
To write a shell script to perform various operations on given string.
PROCEDURE:
1. start
2. get two strings
3. to perform the string operation such as string compare, string length, reverse the string,
combine the string etc.
4. display the result string
5. stop
SHELL COMMAND:
clear
choice=y
while [ "$choice" = "y" ]
do
echo "____________________________________________"
echo "1. COMPARE TWO STRINGS"
echo "2. JOIN TWO STRINGS"
echo "3. FIND THE LENGTH OF A GIVEN STRING"
echo "4. OCCURRENCE OF CHARACTER AND WORDS"
echo "5. REVERSE THE STRING"
echo "6. EXIT"
echo "____________________________________________"
echo "Enter Choice: "
read ch
echo "____________________________________________"
case $ch in
1)
echo "Enter String1: "
read str1
echo "Enter String2: "
read str2
if [ $str1 = $str2 ]
then
echo "String is equal"
else
echo "String is not equal"
fi
;;
2)
echo "Enter String1: "
read str1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linuxlabmanual-220923053636-9ce5a321/85/Linux-Lab-Manual-doc-15-320.jpg)
![16
echo "Enter String2: "
read str2
str3=$str1$str2
echo "Join String: " $str3
;;
3)
len=0
echo "Enter String1: "
read str1
len=$(echo "$str1" | wc -c)
len=`expr $len - 1`
echo "Length: " $len
;;
4)
echo "Enter String: "
read str
echo "Enter Word to find : "
read word
echo $str | cat > str1.txt
grep -o $word str1.txt | cat > str2.txt
count=`grep -c $word str2.txt`
echo "Count: "$count
;;
5)
echo "Enter String1: "
read str
len=`expr $str | wc -c`
len=`expr $len - 1`
while [ $len -gt 0 ]
do
rev=`expr $str | cut -c $len`
ans=$ans$rev
len=`expr $len - 1`
done
echo "Reverse String: "$ans
;;
6) exit ;;
*) echo "Invalid Choice ....." ;;
esac
echo "Do u want to continue.....? [y/n]"
read choice](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linuxlabmanual-220923053636-9ce5a321/85/Linux-Lab-Manual-doc-16-320.jpg)

![18
Ex. No.13 VOWELS CHECKING
Date:
AIM:
To write an awk script to find the number of lines in a file that do not contain vowels I (or) o
PROCEDURE:
1. start the program
2. to create the text file containing text with vowels and non vowels
3. read the file name (that is text)
4. check the words in the file not containing vowels
5. display the number of lines not containing vowels
6. stop
PROGRAM:
#!/bin/bash
echo "Enter file name"
read file
awk '$0!~/[aeiou]/{ count++ }
END{print "The number of lines that does not contain vowels are: ",count}' $file
OUTPUT:
new](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linuxlabmanual-220923053636-9ce5a321/85/Linux-Lab-Manual-doc-18-320.jpg)



![22
Ex No.15 .BINARY SEARCH
Date:
AIM:
To write a shell script to search an element from an array using binary search
PROCEDURE:
1. Start
2. get the size of an array
3. get the elements one by one
4. get the target value
5. start with the middle element. If the target value is equal to the middle element of the array, then
return the index of the middle element. If not compare the middle with other value
6. when a match is found, print successful search
7. if no match is found, print unsuccessful search
8. stop the program
PROGRAM:
echo Enter array limit
read limit
echo Enter elements
n=1
while [ $n -le $limit ]
do
read num
eval arr$n=$num
n=`expr $n + 1`
done
echo Enter key element
read key
low=1
high=$n
found=0
while [ $found -eq 0 -a $high -gt $low ]
do
mid=`expr ( $low + $high ) / 2`
eval t=$arr$mid
if [ $key -eq $t ]
then
found=1
elif [ $key -lt $t ]
then
high=`expr $mid - 1`
else
low=`expr $mid + 1`
fi
done](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linuxlabmanual-220923053636-9ce5a321/85/Linux-Lab-Manual-doc-22-320.jpg)
![23
if [ $found -eq 0 ]
then
echo Unsuccessfull search
else
echo Successfull search
fi
OUTPUT:
RESULT:
Hence the output is verified](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linuxlabmanual-220923053636-9ce5a321/85/Linux-Lab-Manual-doc-23-320.jpg)
![24
Ex. No.16. FILE OPERATIONS
Date:
AIM:
To write a c program that takes one or more file/directory names as command line input and
reports the following information on the file.
A) file type
B) number of links
C)take of last access
D)read,write and execute permissions
PROCEDURE:
1. get the file name in the command line.
2. Display the node number
3. report the file or directory
4. display the number of link
5. display the time of last access
6. display the modification time
7. display the last change time
8. display the read,write and execute permissions
9. stop
PROGRAM:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
#include<sys/stat.h>
#include<time.h>
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
char *at,*mt,*ct; struct stat buf; stat(argv[1],&buf);
printf("the inode no is : %dn",buf.st_ino); if(S_ISDIR(buf.st_mode))
printf("it is a directory"); if(S_ISREG(buf.st_mode)) printf("it is regurlar filen");
printf("the no of links is %dn",buf.st_nlink); at=ctime(&buf.st_atime);
printf("the time of last access is %sn",at); mt=ctime(&buf.st_mtime);
printf("the modification time is :%sn",mt); ct=ctime(&buf.st_ctime);
printf("time of last change is : %sn",ct); if((buf.st_mode&S_IRUSR)==S_IRUSR)
printf("user has read permissionn"); if((buf.st_mode &S_IWUSR)==S_IWUSR)
printf("user has write permisssionn"); if((buf.st_mode &S_IXUSR)==S_IXUSR)
printf("user has execute permissionn"); if((buf.st_mode & S_IRGRP)==S_IRGRP)
printf("group has read permissionn"); if((buf.st_mode &S_IWGRP)==S_IWGRP)
printf("group has write permissionn"); if((buf.st_mode & S_IXGRP)==S_IXGRP)
printf("group has execute permissionn"); if((buf.st_mode &S_IROTH)==S_IROTH)
printf("others has read permissionn"); if((buf.st_mode &S_IWOTH)==S_IWOTH)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linuxlabmanual-220923053636-9ce5a321/85/Linux-Lab-Manual-doc-24-320.jpg)


