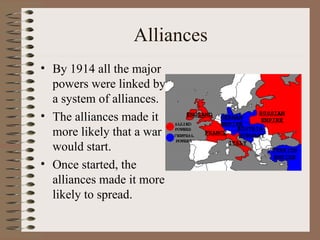
The document discusses several key causes of World War 1: militarism led European powers like Germany and Russia to rapidly build up their armed forces in the early 20th century; a system of alliances tied the major European powers to one another militarily; imperialism and nationalism increased tensions in areas like the Balkans; and assertive leaders like Kaiser Wilhelm II pursued aggressive foreign policies. The assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand by Serbian nationalists in 1914 triggered a series of escalating diplomatic and military actions by European powers due to these underlying factors, ultimately resulting in World War 1.