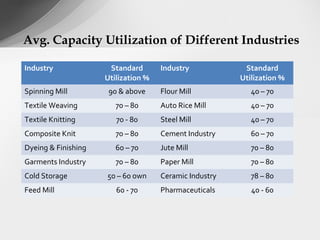
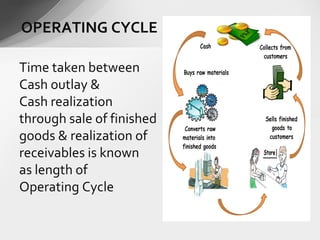
This document discusses working capital assessment methods and factors. It defines working capital as the short-term funds used in a company's day-to-day operations, calculated as current assets minus current liabilities. It identifies sources of working capital and factors that affect working capital levels, such as the nature of business, operating cycle, and competition. The document also outlines methods for assessing working capital, like the operating cycle method, and provides an example working capital analysis for an export-oriented garment business.





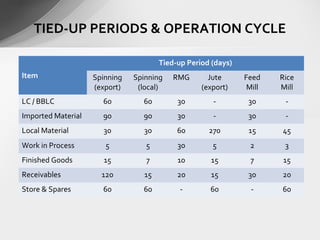
![WORKING CAPITAL ANALYSIS
[EXPORT ORIENTED RMG]
Item Tied-up
(day)
Capacity Utilization (%)
100 80 70
Raw Material (LC) 30 56.2 45.0 39.3
Raw Material (Inventory) 30 56.2 45.0 39.3
Accessories (Inventory) 60 42.1 33.7 29.5
Working in Process 30 125.7 100.6 88.0
Finished Goods 10 41.9 33.5 29.3
Receivables 20 83.8 67.0 58.7
Total 180 405.9 324.8 284.1
Less Clients equity (0%) 0 0 0
Net Requirement 406 325 284](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wc-150606171449-lva1-app6892/85/Working-Capital-Assessment-8-320.jpg)
![Assumptions:
– Knit Garments (30-line): 36,000 pcs/day
– Yarn Required (2.5 kg/dz): 7,500 kg
– Price of Yarn: US$ 3.2 per kg
– Yarn Cost (7500*3.2*78): Tk. 1.872 million/day
– Accessories (US$ 3/dz): Tk. 0.702 million/day
– Exchange Rate: Tk. 78/US$
– Wages & Salaries: Tk. 15 million/month
– Fuel & Gas: Tk. 2.00 million/month
– Knitting Charge (Tk. 15/kg) Tk. 0.112 million/day
– Dyeing Charge (US$ 1.6/kg) Tk. 0.936 million/day
– WIP= (56.2+21.06+15+2+(0.112+0.936)*30 Tk. 125.7 million/day
WORKING CAPITAL ANALYSIS
[EXPORT ORIENTED RMG]
The assessment requires to extract actual and authenticated data to calculate
WC. Remember, to assess the real requirement of the project, you will require
to reach into the heart of the business. Consider yourself wearing the shoes of
the key person of the business.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wc-150606171449-lva1-app6892/85/Working-Capital-Assessment-9-320.jpg)