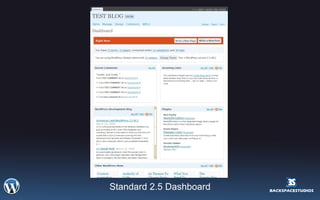
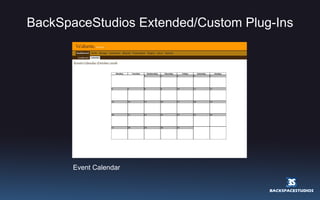
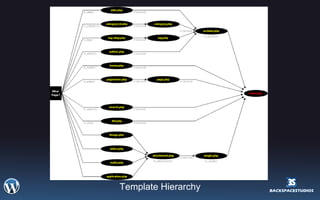
This document provides an overview and introduction to WordPress 2.5. It discusses what WordPress is, how it can be used and installed, its basic configuration and dashboard interface. It also covers templates, plugins, conditional tags, CSS integration and resources for further learning. The workshop aims to teach participants how to use WordPress for blogging, websites and more.













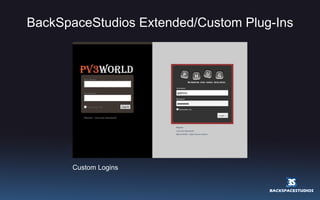
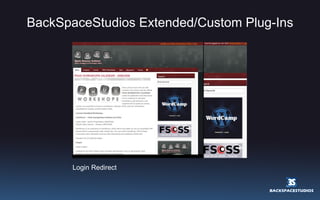


















![Bridging Two Worlds! FlashPress is an extension to WordPress, which allows Flash designers/developers to use the WordPress engine to communicate with a Flash site. The use of the WordPress CMS in Flash overcomes many obstacles involved with maintaining and updating a Flash site. The FlashPress development thread is restricted to contributors of this group. If you would like to contribute to this project please contact us at [email_address] Launching soon http://www.flashpress.ca and http://www.flashpressdevelopers.com We will be launching FlashPress at FITC Toronto 2009!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wp25-090619065941-phpapp01/85/WordPress-2-5-Overview-Rich-Media-Institute-38-320.jpg)
![FREE PHUG Workshops Current Scheduled Workshops: FlashPress – Flash management Solutions by PHUG Drupal Papervision3D - Using Papervision3D and Parallax to build environments Firefox UI Design Flash Media Server and BeatMaker Open Source in the Real World Adopting Opens Source Commercially We would like to thank some of our sponsors and affiliates: PHUG, Lifecapture Interactive Inc., BackSpaceStudios, Mozilla Firefox, WordPress.org, Drupal.org, BNOTIONS, FITC ( Flash In The Can ), RMI ( Rich Media Institute ) If you would like to present or no someone who does we are still taking applications. Please send us an email at [email_address] http://workshops.phug.ca](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wp25-090619065941-phpapp01/85/WordPress-2-5-Overview-Rich-Media-Institute-39-320.jpg)

![Thank You WordPress 2.5 Workshop at RMI Brendan Sera-Shriar, Owner BackSpaceStudios http://www.backspacestudios.com [email_address] Founder of PHUG – Open Source Culture http://www.phug.ca](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wp25-090619065941-phpapp01/85/WordPress-2-5-Overview-Rich-Media-Institute-41-320.jpg)