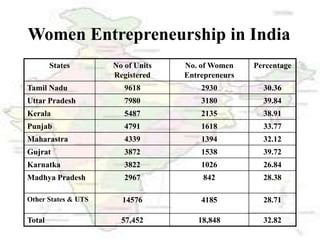
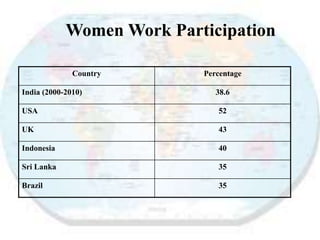
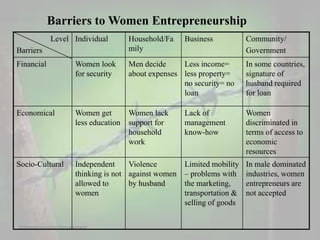
This document discusses women entrepreneurship in India. It notes that while women have traditionally been involved in activities like cooking, childcare and handicrafts, more women are now starting their own businesses in various sectors like electricity, electronics and engineering. The document outlines some of the barriers women entrepreneurs face at the individual, family, business and government levels, such as lack of access to financing and education. It proposes some ways to facilitate women's entrepreneurship, such as providing training, easier financing, and developing gender sensitivity. The document concludes by highlighting the stories of two successful Indian women entrepreneurs, Ekta Kapoor and Shahnaz Husain.