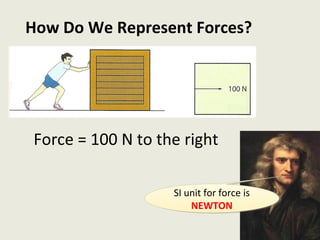
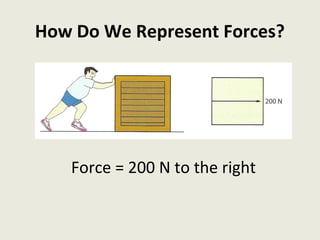
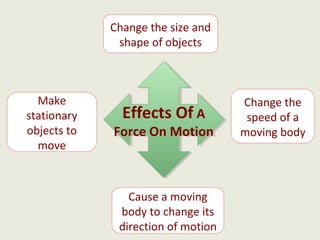
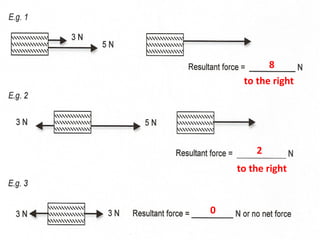
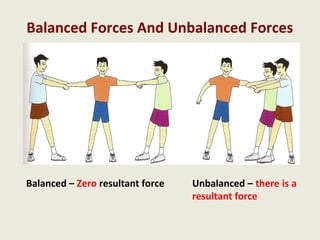
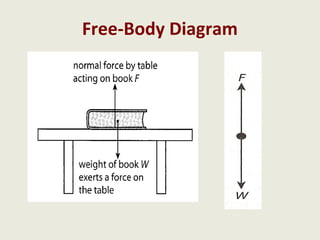
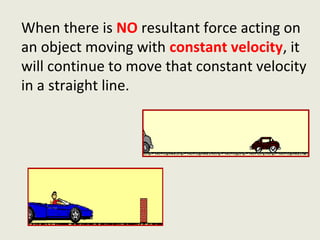
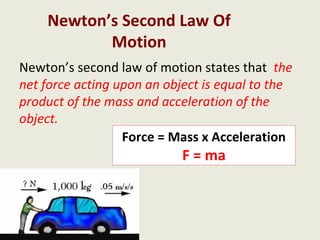
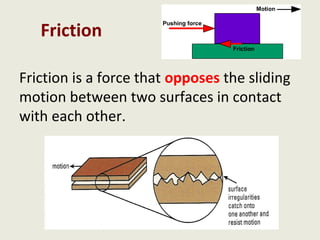
Dynamics is the study of forces and energies. A force is a push or pull that has both a direction and magnitude. Forces can be represented as vectors and measured in Newtons. Forces can change the motion of objects by changing their speed or direction according to Newton's laws. Unbalanced forces cause changes in motion while balanced forces do not. Friction opposes motion between surfaces and can have both positive and negative effects that engineers aim to reduce.