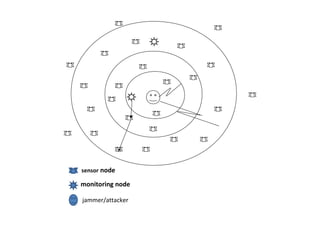
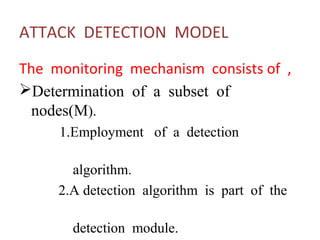
This document presents optimal jamming attack strategies in wireless sensor networks. It discusses using monitoring nodes to detect jammer attacks and putting sensor nodes in sleep mode when attacks are detected to avoid energy loss. The document outlines different types of attacks in wireless sensor networks including passive and active attacks. It proposes using a detection algorithm at monitoring nodes to analyze observations and decide if an attack is occurring. The goal is to study controllable jamming attacks that are difficult to detect and defend against.