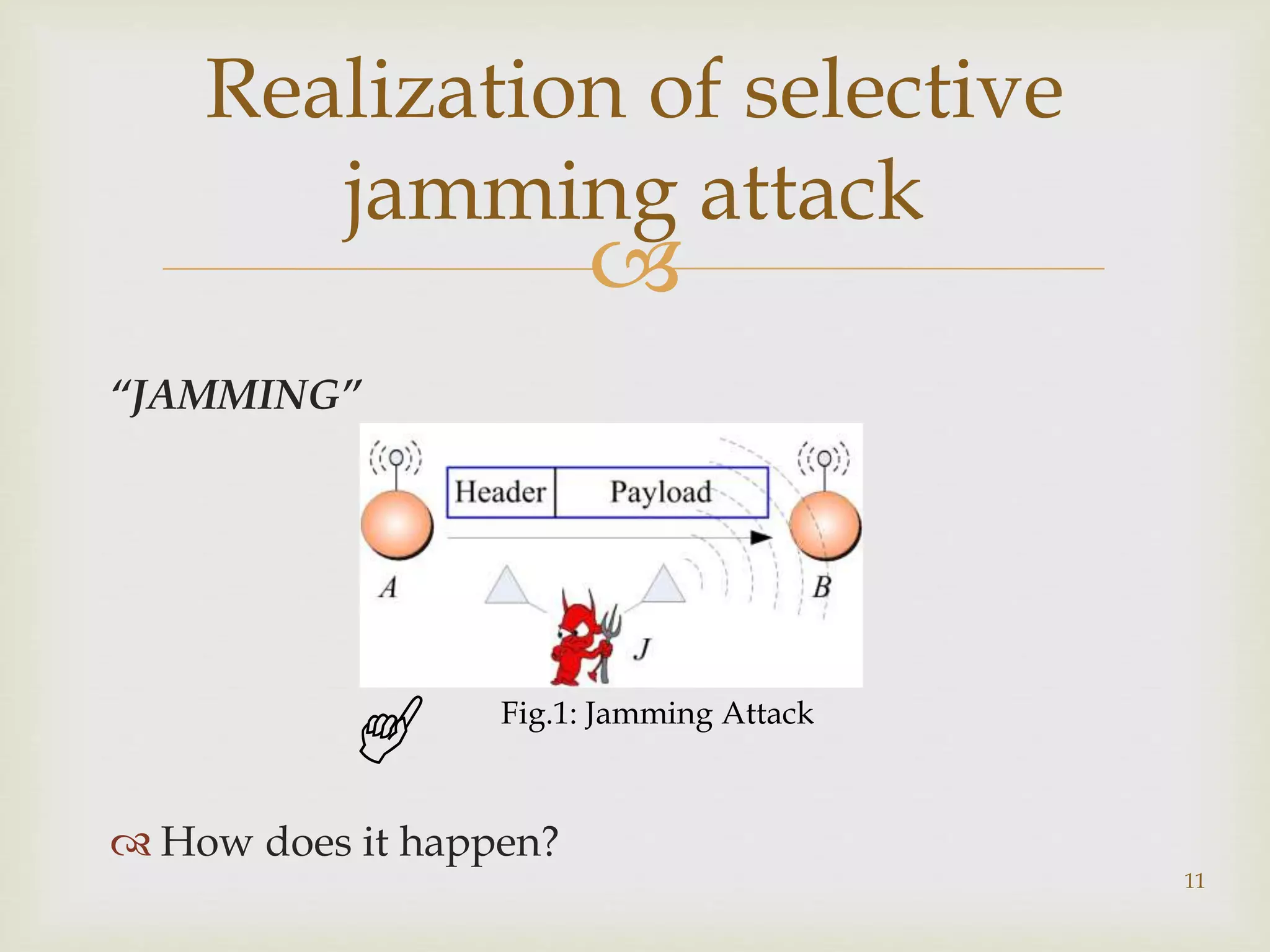
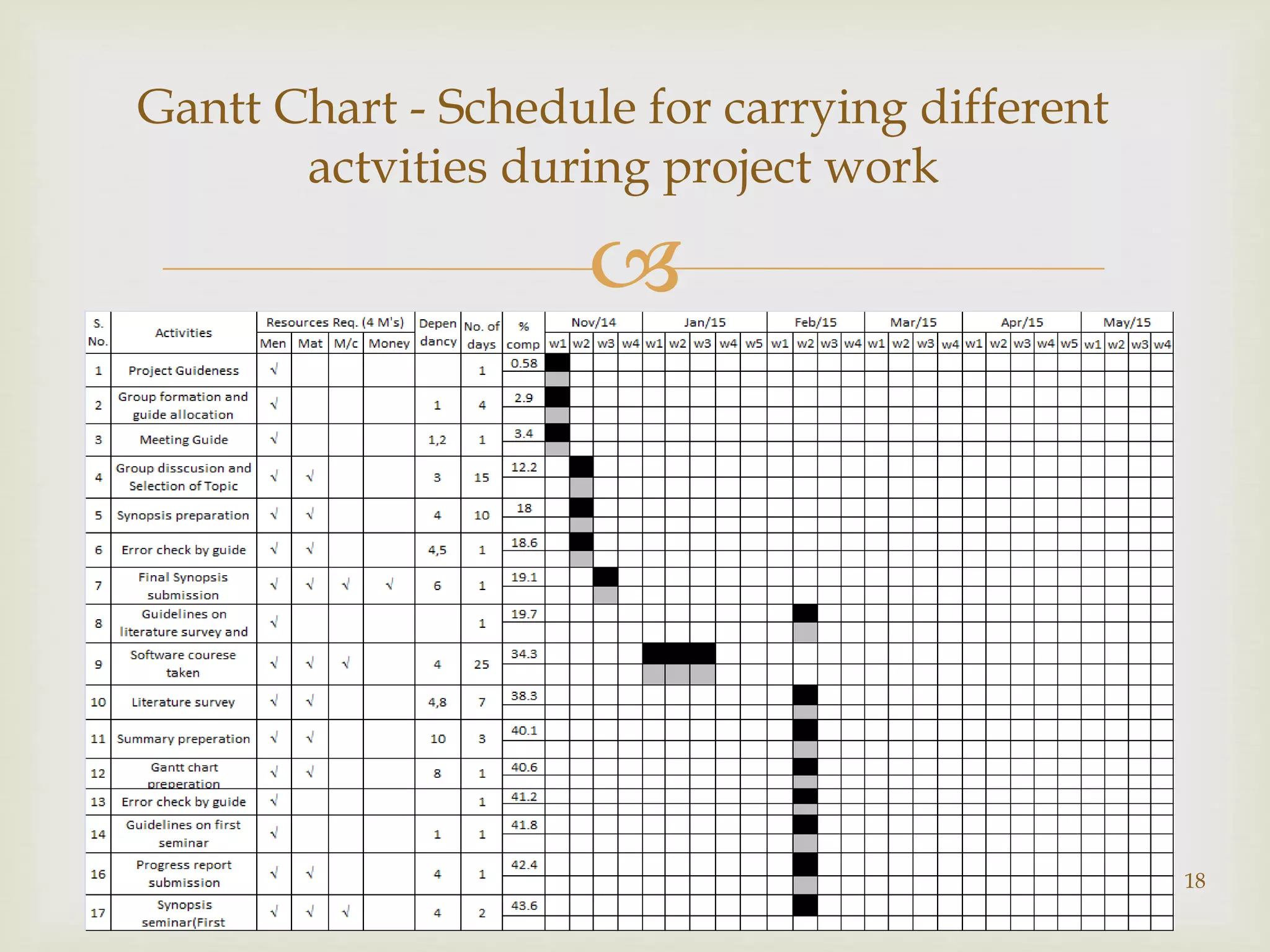
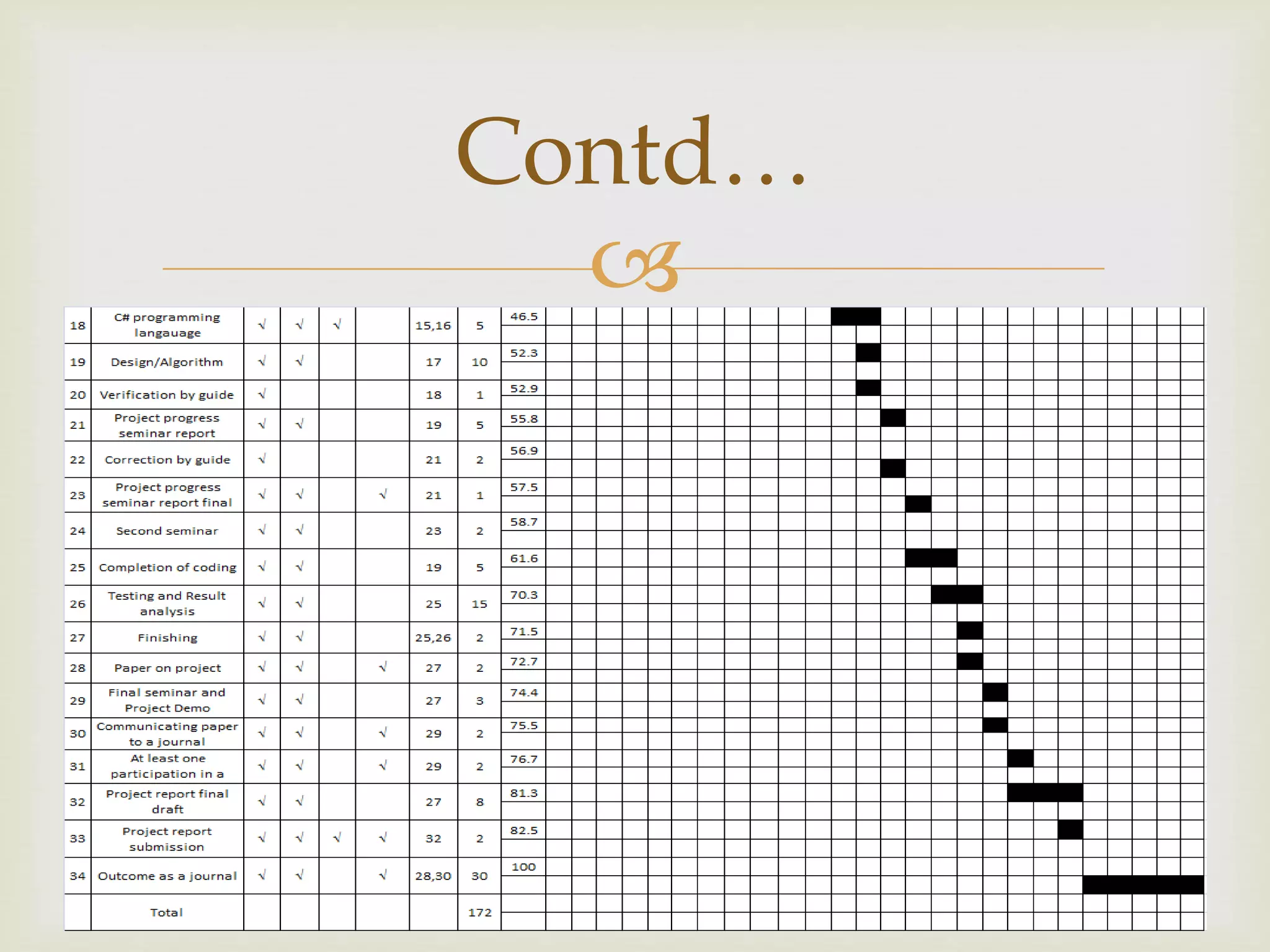
This document outlines a project to prevent selective jamming attacks in wireless networks. The project aims to combine three cryptographic schemes: 1) a strong hiding commitment scheme (SHCS) based on symmetric cryptography, 2) a cryptographic puzzle hiding scheme (CPHS) that forces recipients to perform computations before extracting secrets, and 3) an all-or-nothing transformation (AONT) scheme that sends pseudo-messages corresponding to original packets so the jammer cannot classify packets until all are received. The objectives are to prevent selective jamming, avoid packet dropouts, show a jammer's impact, and secure transmissions. A literature review analyzes previous work on jamming detection and prevention. The methodology describes each scheme and an






![
“Coping with a Smart Jammer in Wireless
Networks: A Stackelberg Game Approach”[2013]
-Dejun Yang
Technique used: Power Control Smart Jammer game.
Drawback: Jammer improves its utility in
UNAWARE condition.
7
Literature Survey](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slides-150322010544-conversion-gate01/75/Preventing-jamming-attack-by-combining-cryptography-7-2048.jpg)
![
“Denial of Service Attacks in Wireless Network: The
Case of Jammer”.[2011]
-Konstantinos Pelechrinis
Technique used: Intrusion Detection Scheme(IDS)
used to detect the attack.
Intrusion Prevention System(IPS) used to prevent
the attack.
8
Contd…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slides-150322010544-conversion-gate01/75/Preventing-jamming-attack-by-combining-cryptography-8-2048.jpg)
![
“Detection of Jamming Attacks in Wireless Ad Hoc
Networks using Error Distribution”.[2009]
-Ali Hamieh
Technique used: detection by correlation to detect
the jammer.
Drawback: to detect the jamming attack dependency
measure is needed from all nodes.
There is no technique to prevent selective jamming
attack
9
Contd…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slides-150322010544-conversion-gate01/75/Preventing-jamming-attack-by-combining-cryptography-9-2048.jpg)
![
“Effects of Denial-of-Sleep attacks on Wireless Sensor
Network mac protocols”.[2009]
-David R. Raymond
Technique used: jamming identification & mitigation,
anti-reply protection
Drawback: Transmitted message from a node can easily
read by attacker because message is not encrypted.
Attacker can access any node using received message as a
authorized and make busy state such attacks are selective
jamming attack.
10
Contd…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slides-150322010544-conversion-gate01/75/Preventing-jamming-attack-by-combining-cryptography-10-2048.jpg)