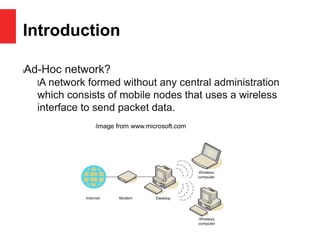
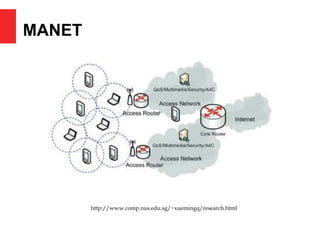
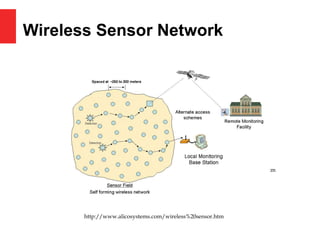
This document provides an overview of security issues in wireless ad-hoc networks. It discusses the properties and functions of mobile ad-hoc networks (MANETs) including availability, authentication, confidentiality, and data integrity. It classifies attacks as internal/external and active/passive. Specific attacks like wormhole and black hole are described. Solutions to these attacks include packet leashes to restrict travel distance and binding user identity to trust levels. Key management is important, using group, symmetric, and shared keys. In conclusion, more research is needed to fully address security challenges in unpredictable wireless networks.