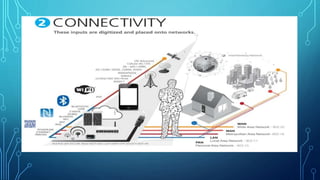
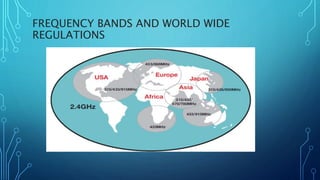
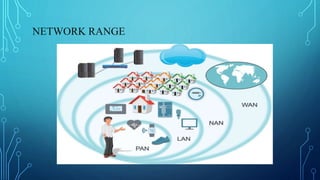
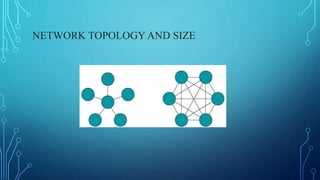
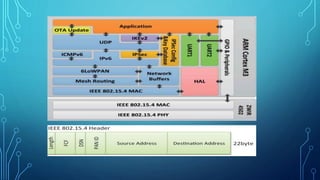
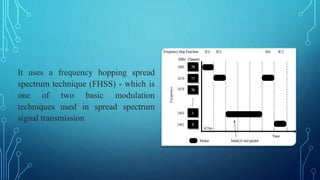
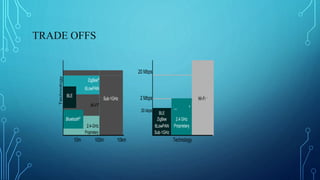
The document discusses various wireless connectivity technologies for internet of things applications. It introduces concepts like frequency bands, communication protocols, network topologies, and specific technologies including 6LoWPAN, Bluetooth, WiFi, and ZigBee. Each technology is described in terms of its data rates, range, advantages, and disadvantages. The conclusion states that the key challenge is selecting the appropriate connectivity technology for effective implementation of internet of things applications.