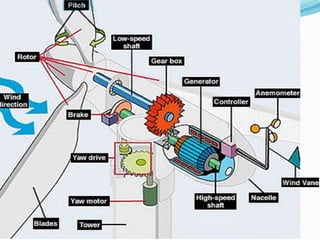
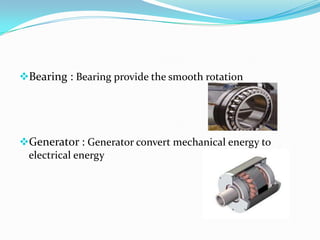
A wind power station uses multiple wind turbines located together to produce electricity. It works by using blades to capture kinetic energy from wind and convert it to mechanical energy through a gearbox and generator, producing electrical energy. Modern turbines can generate between 0.5-2.5 megawatts of power annually, though their efficiency is typically around 30% of maximum theoretical capacity due to variable wind speeds. Wind power provides environmental and economic benefits but also has disadvantages like unreliable output, noise pollution, and impacts on wildlife. Future developments may improve flow modeling, remote sensing, and understanding of efficiency losses.