Embed presentation
Download to read offline








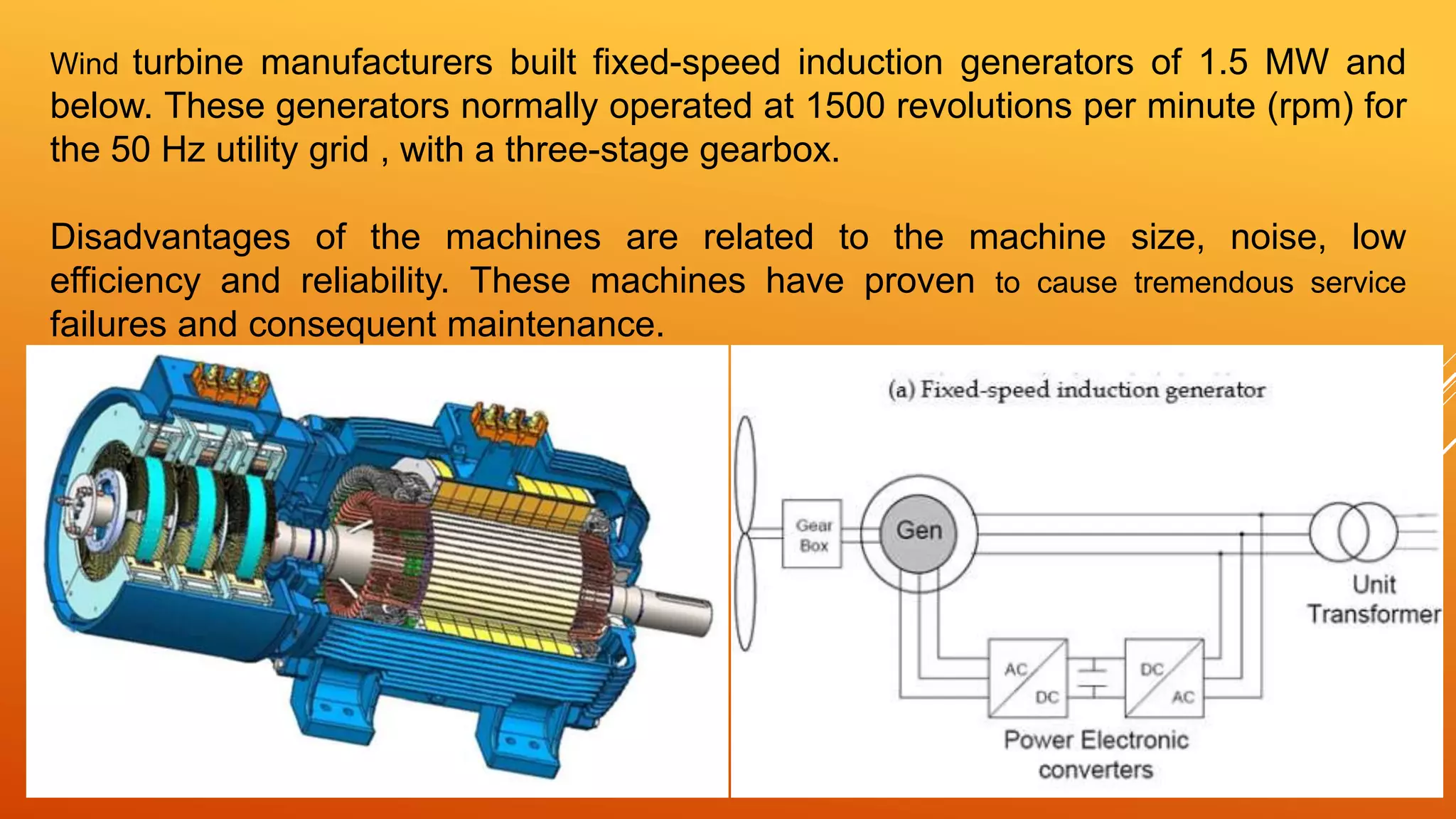



This document discusses different types of wind turbine generators (WTGs) including direct current (DC), alternating current (AC) synchronous and asynchronous generators, and switched reluctance generators. It provides details on the principles and technologies of each type, including their advantages and disadvantages. Some key considerations for WTG design are also outlined such as choice of machine, drive train type, rated speeds and torques, cooling arrangement, and cost.












