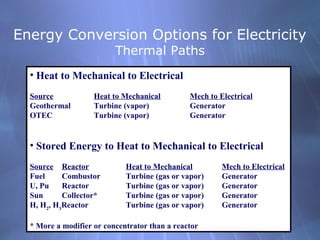
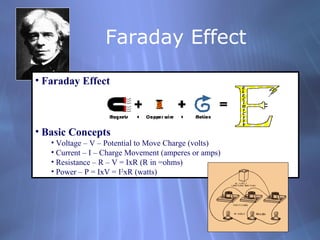
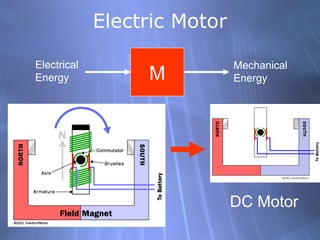
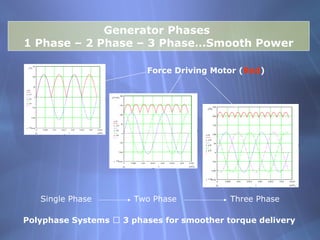
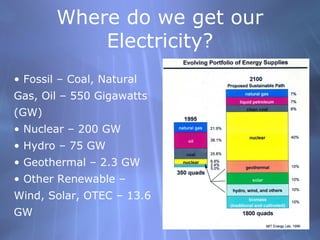
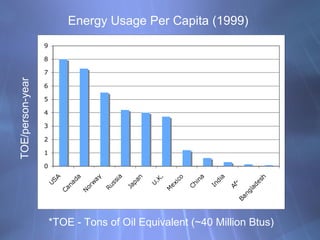
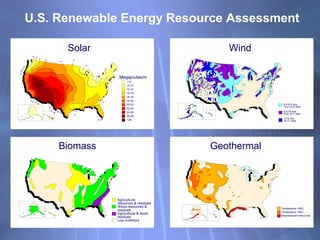
This document discusses electricity generation and energy conversion. It explains that electricity is generated by converting other energy sources, like heat, wind, or sunlight into electrical energy using devices like generators. Generators convert mechanical energy, like from moving water or wind, into electrical energy using the Faraday effect. Motors operate on the same principles but convert electrical energy back into mechanical motion. Most large-scale electricity generation uses alternating current due to its advantages over direct current for transmission. Fossil fuels currently provide the majority of electricity but renewable sources are growing.