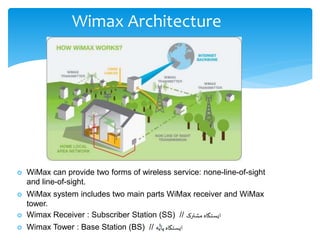
This document discusses Wimax security. It begins by providing background on Wimax and describing its architecture, which includes the physical layer, MAC layer with its convergence, common part, and security sublayers, and the security steps of authentication and authorization, key exchange, and traffic encryption. It then outlines some security issues in Wimax, including physical layer attacks like jamming, man-in-the-middle attacks during authentication and key exchange, and replay and denial of service attacks against subscriber stations. It concludes by listing several references on Wimax security.