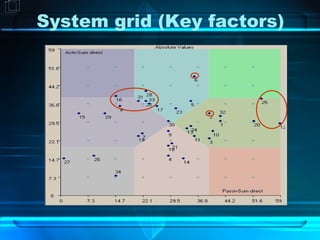
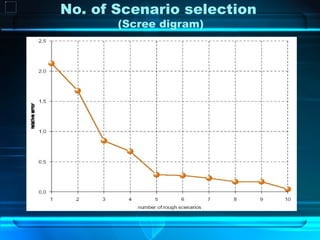
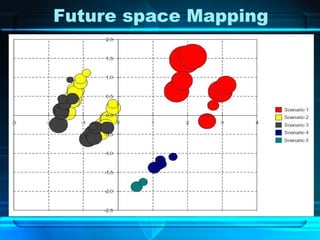
WiMAX is a wireless technology aimed at providing high-speed broadband access, especially in developing countries, with a focus on its standards and capabilities. The document assesses its potential impact based on regulatory support, market dynamics, social demographics, and economic factors while projecting various scenarios for its adoption and success. The conclusions emphasize the need for monitoring WiMAX's implementation and the importance of government incentives to enhance connectivity.