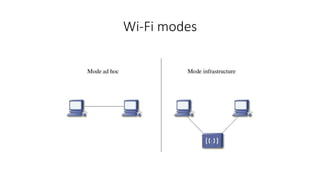
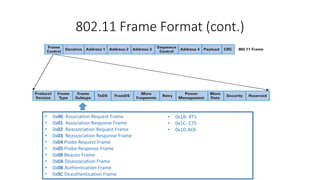
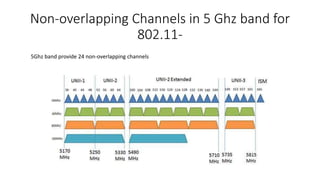
Wi-Fi is a wireless networking technology that uses radio waves to enable wireless local area networking with devices. It uses the IEEE 802.11 standards and was introduced in 1998. The document discusses the evolution of Wi-Fi standards from 802.11 to 802.11ac, explaining key features such as OFDM, MIMO, and MU-MIMO that have increased data rates and throughput over time. The latest standards discussed are 802.11ac, which supports speeds up to 3.5Gbps using 256-QAM and 802.11ad which operates at 60GHz and supports speeds up to 7.2Gbps.