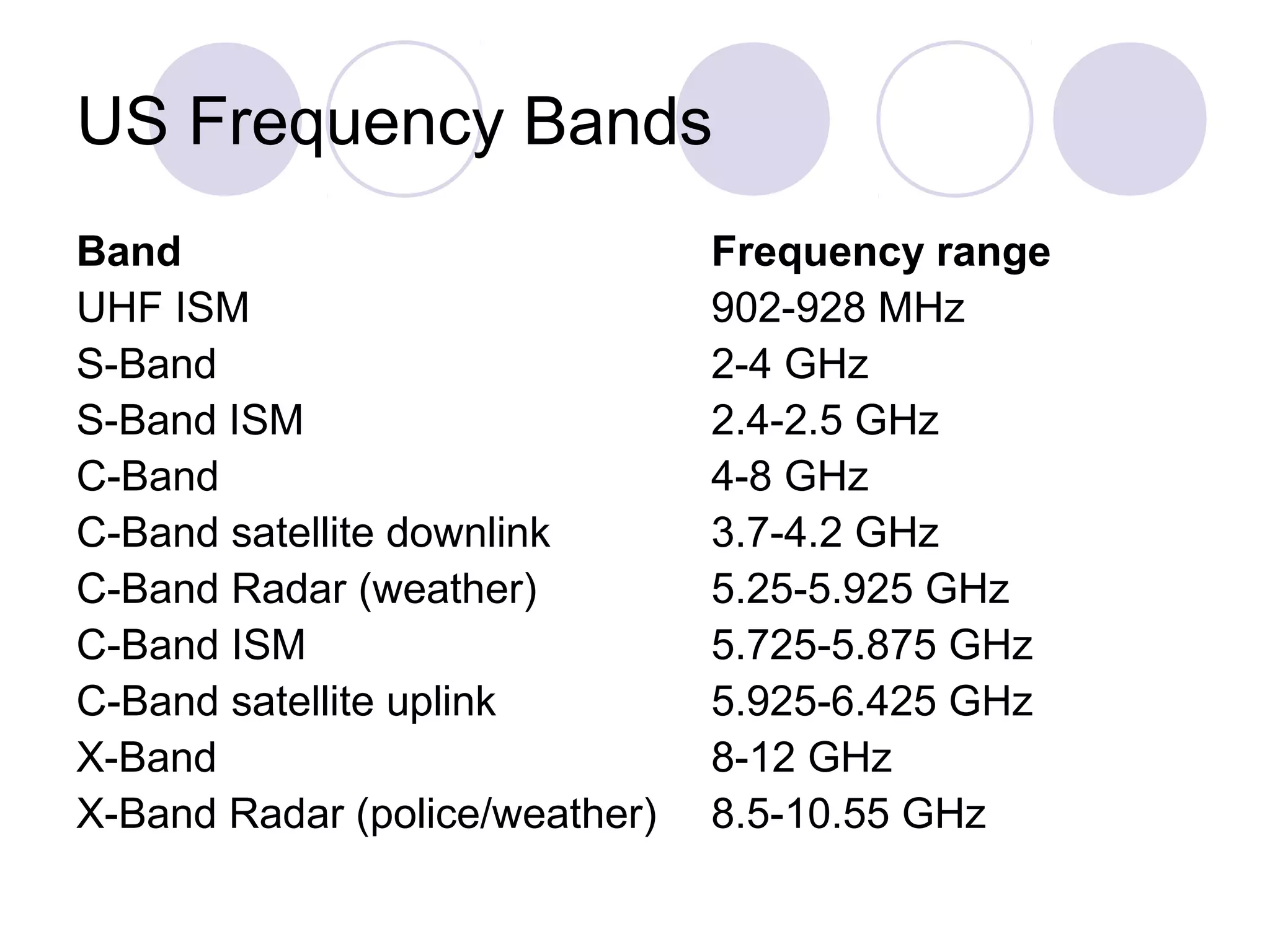
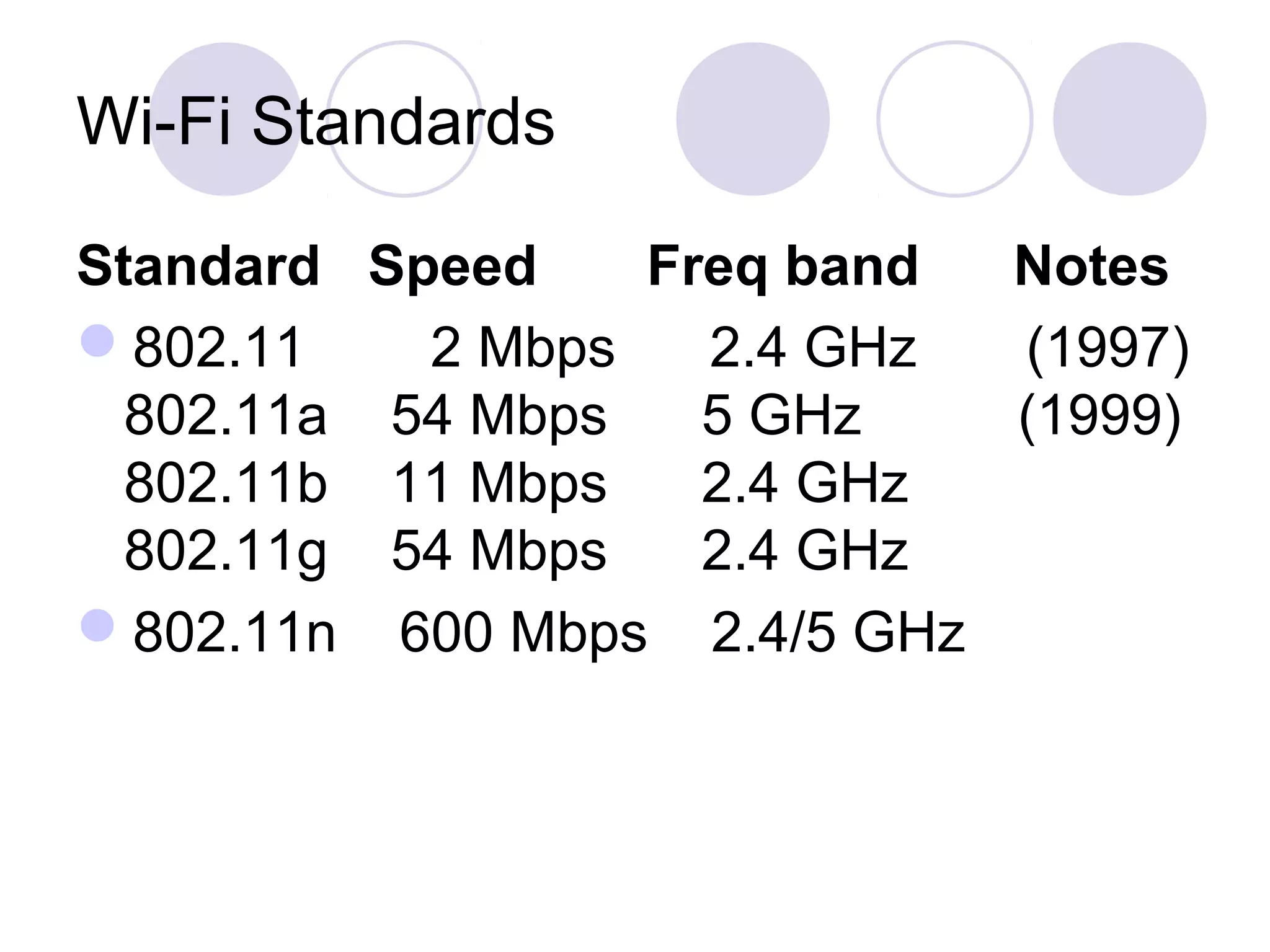
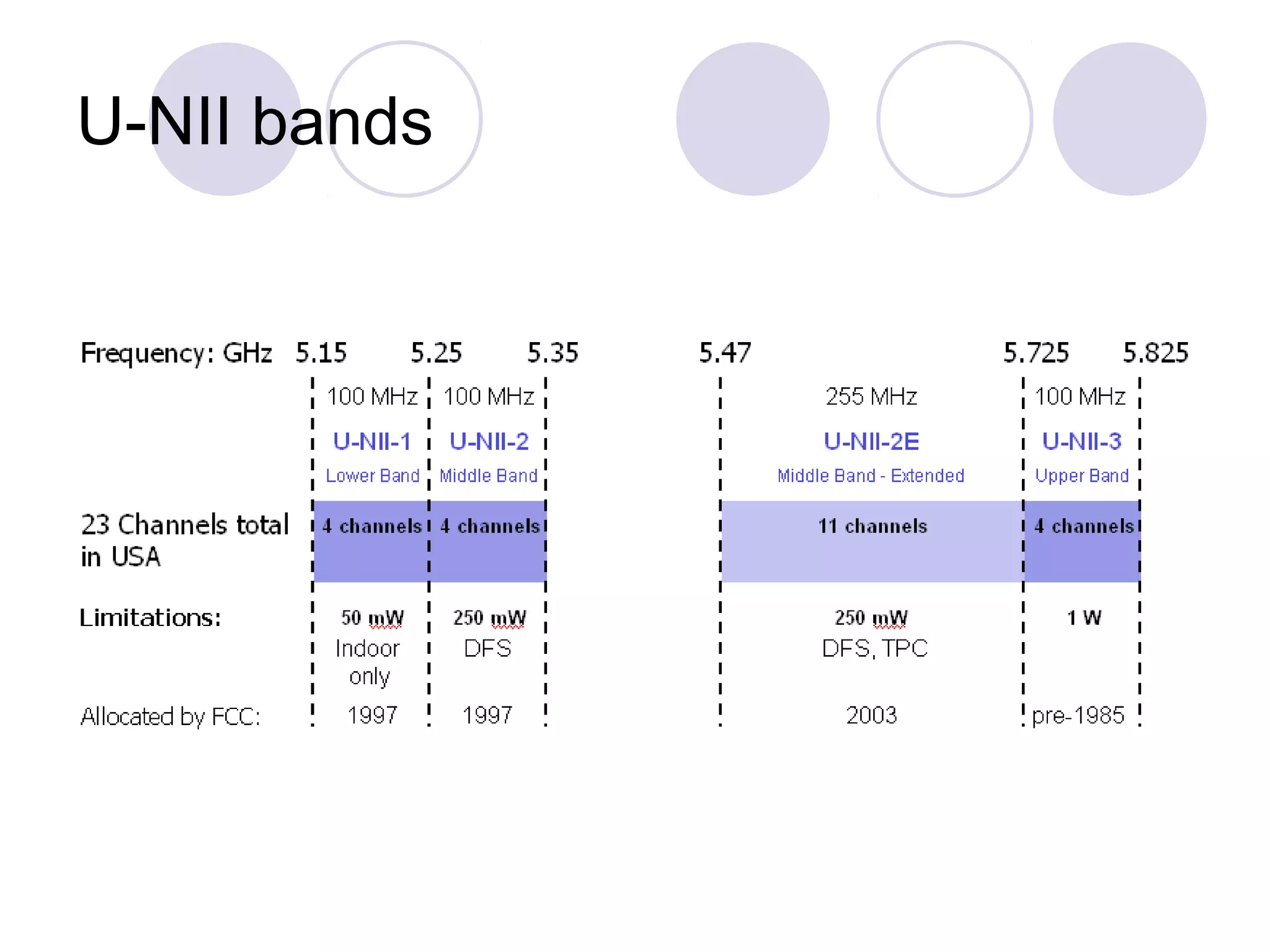
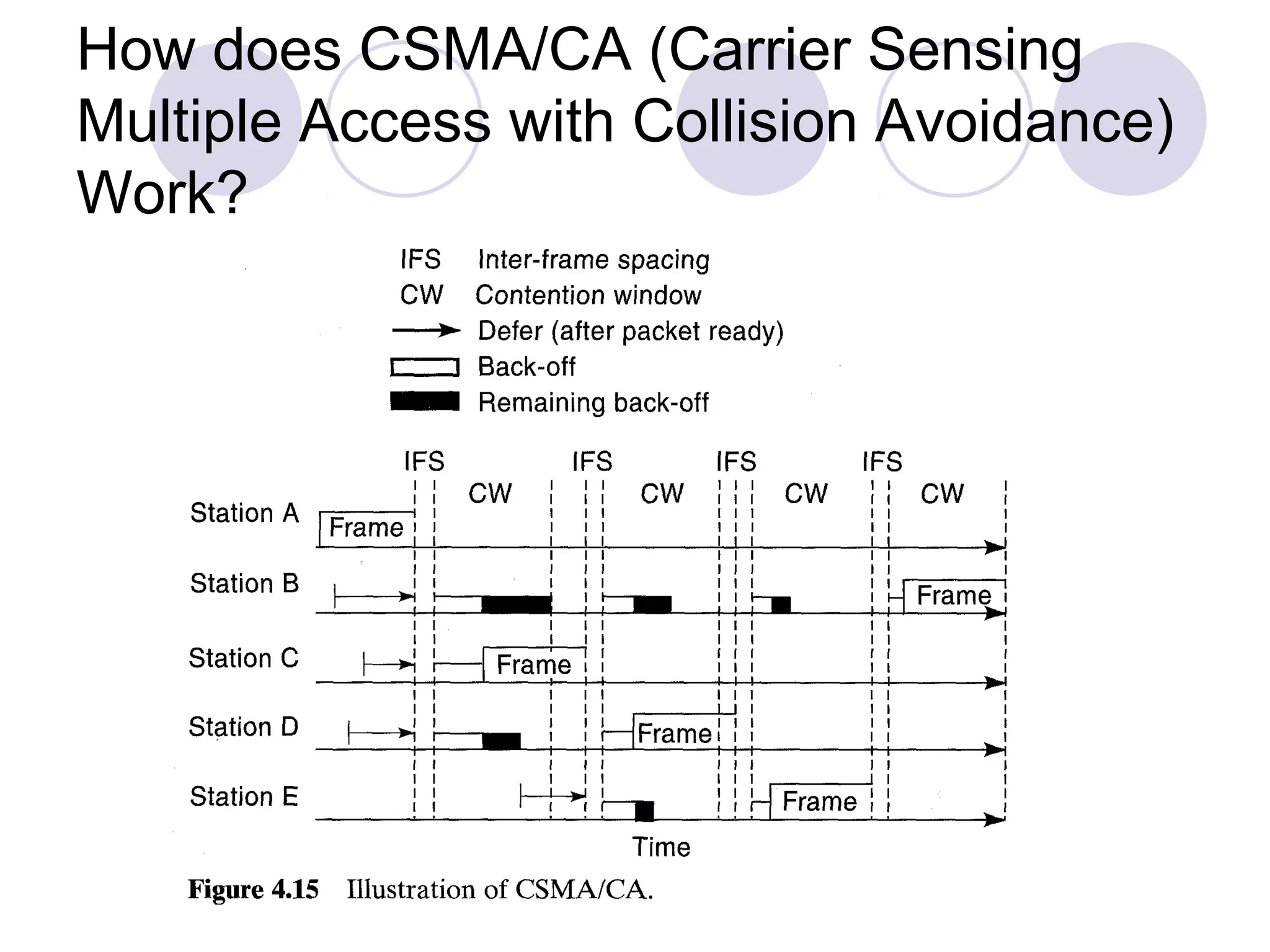
Wi-Fi, also known as IEEE 802.11, allows wireless devices to communicate using radio signals in the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands. It uses CSMA/CA to allow multiple devices to share bandwidth and avoid collisions. Devices can connect to each other directly in ad hoc mode or through an access point in infrastructure mode. Access points allow devices to roam between different coverage areas. Security features include authentication to verify devices and encryption to protect data transmissions.