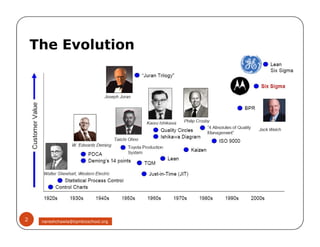
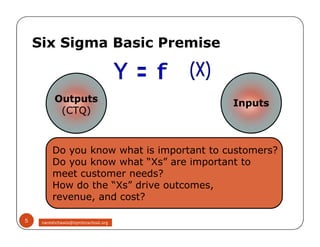
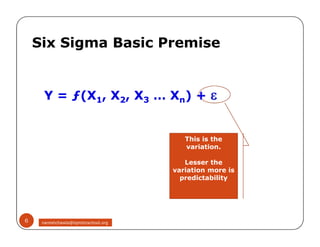
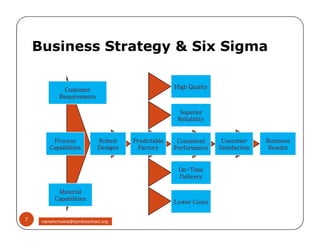
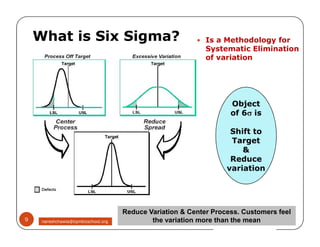
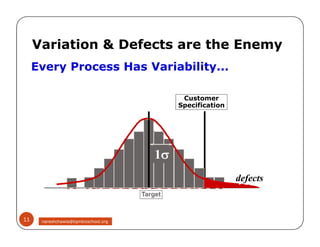
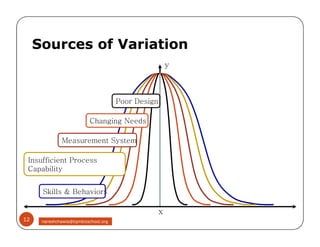
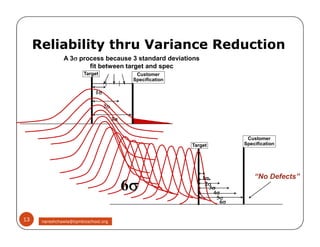
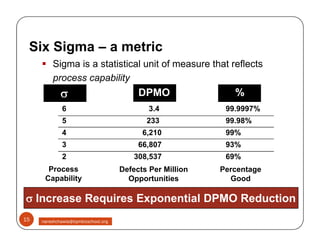
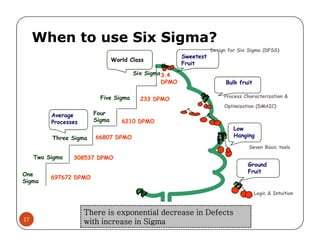
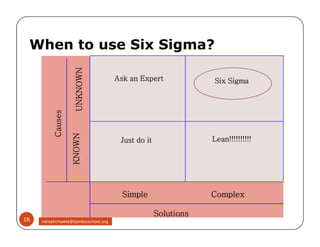
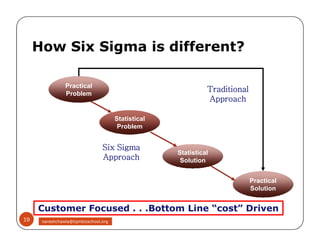
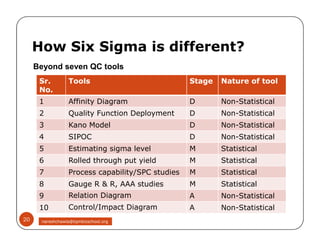
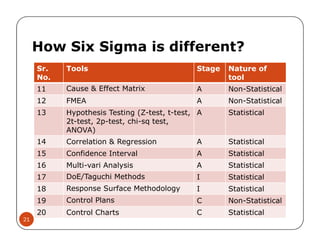
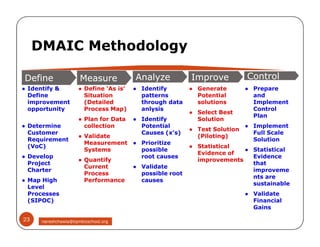
The document discusses Six Sigma, which is a business strategy and methodology for improving quality, reliability, and responsiveness. It aims to make products and services faster, better, and cheaper. Six Sigma seeks to systematically eliminate defects and variation from processes by lowering the defect rate to 3.4 defects per million opportunities. It uses a set of tools and problem-solving techniques like DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) to statistically analyze processes and identify and address root causes of defects. Six Sigma has been successfully applied across various industries to drive process improvement and customer satisfaction.