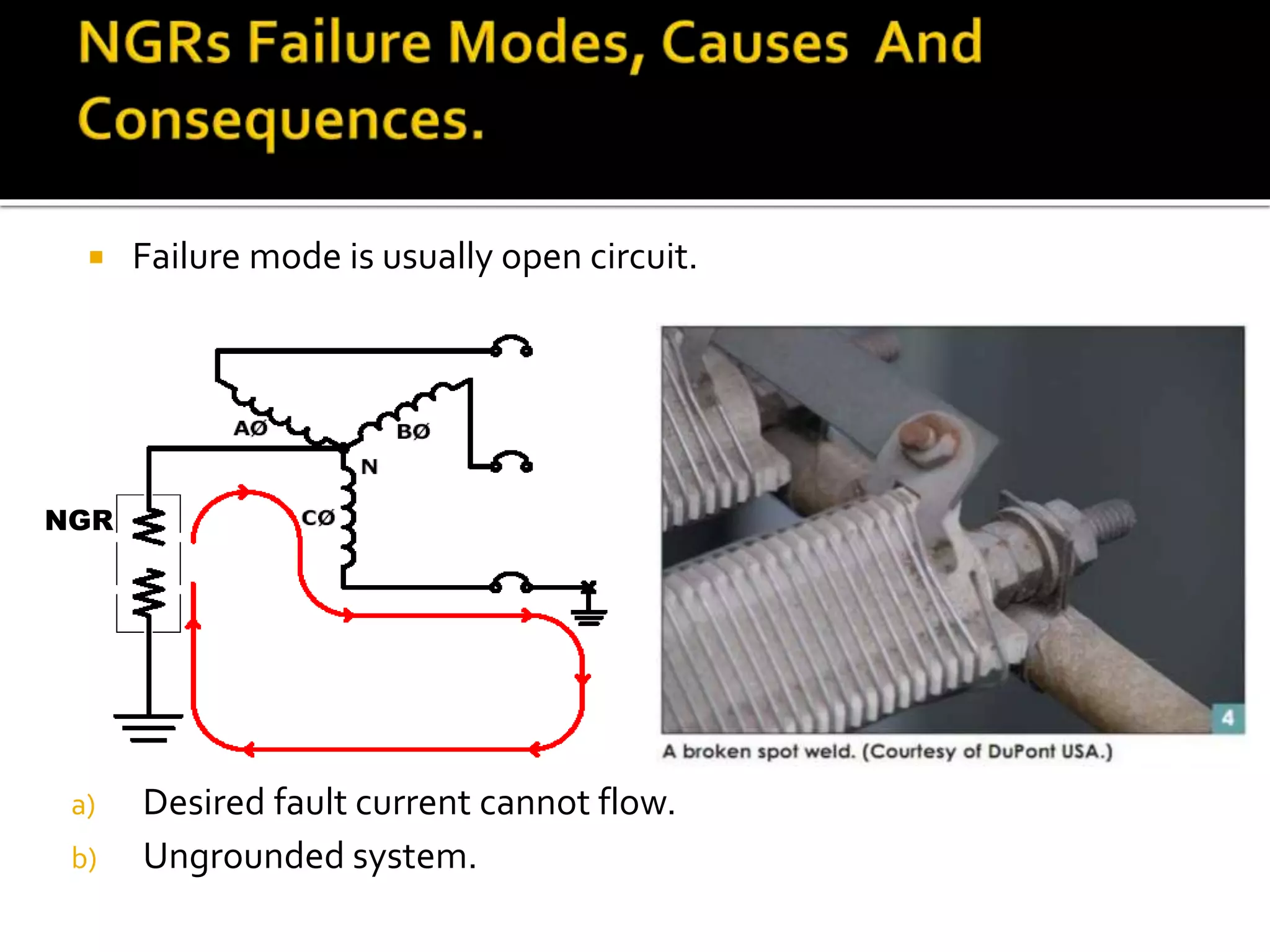
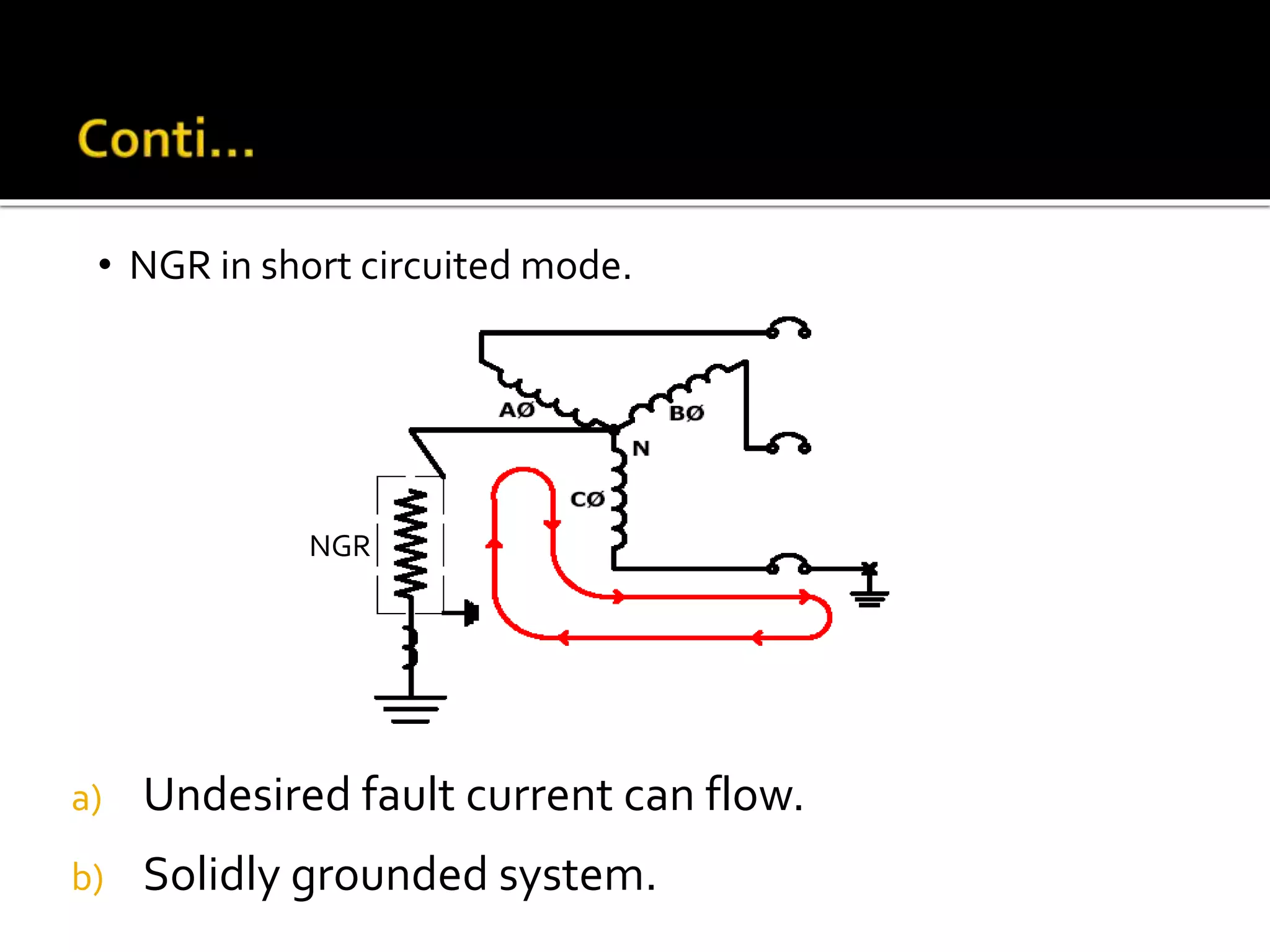
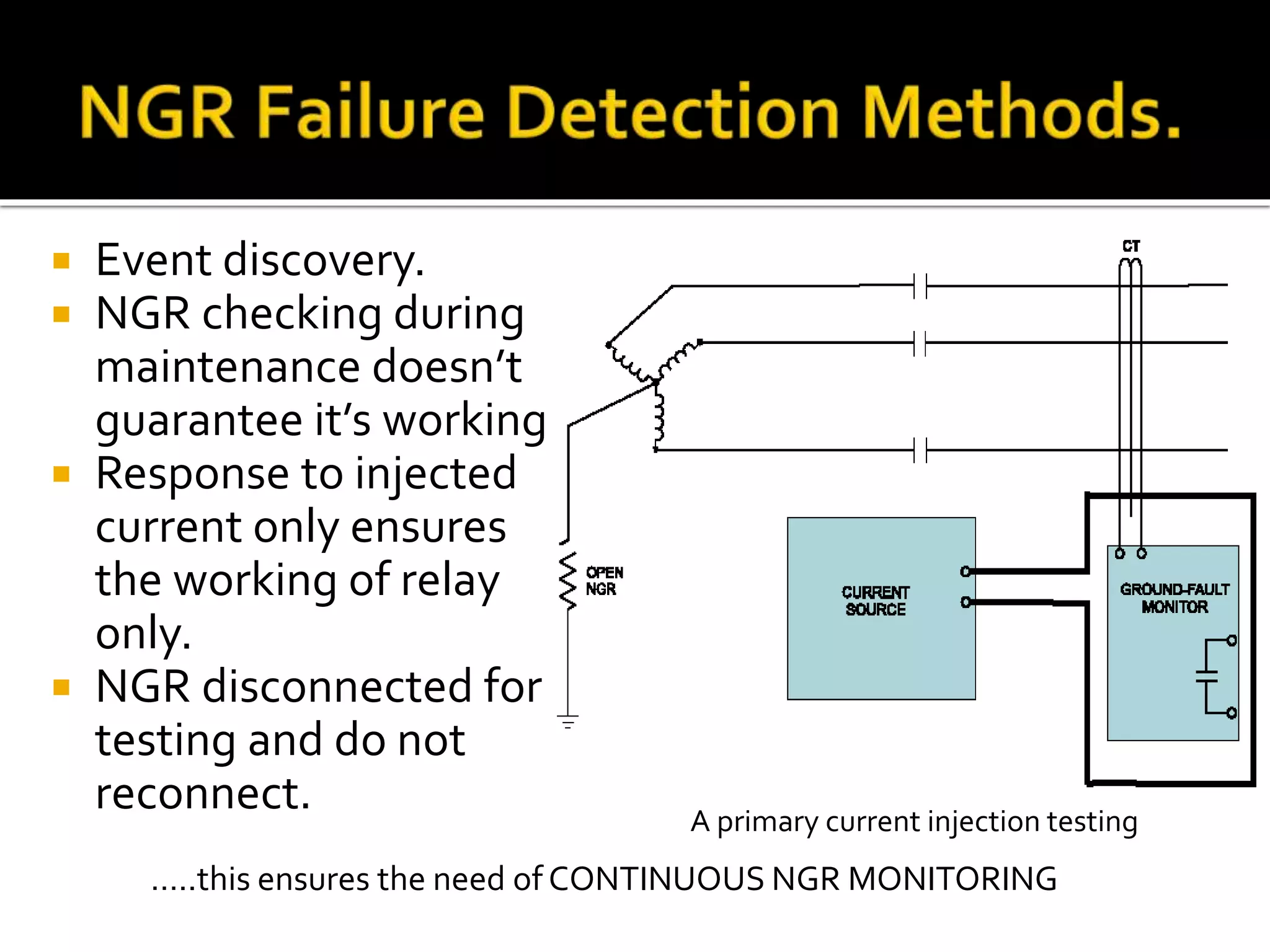
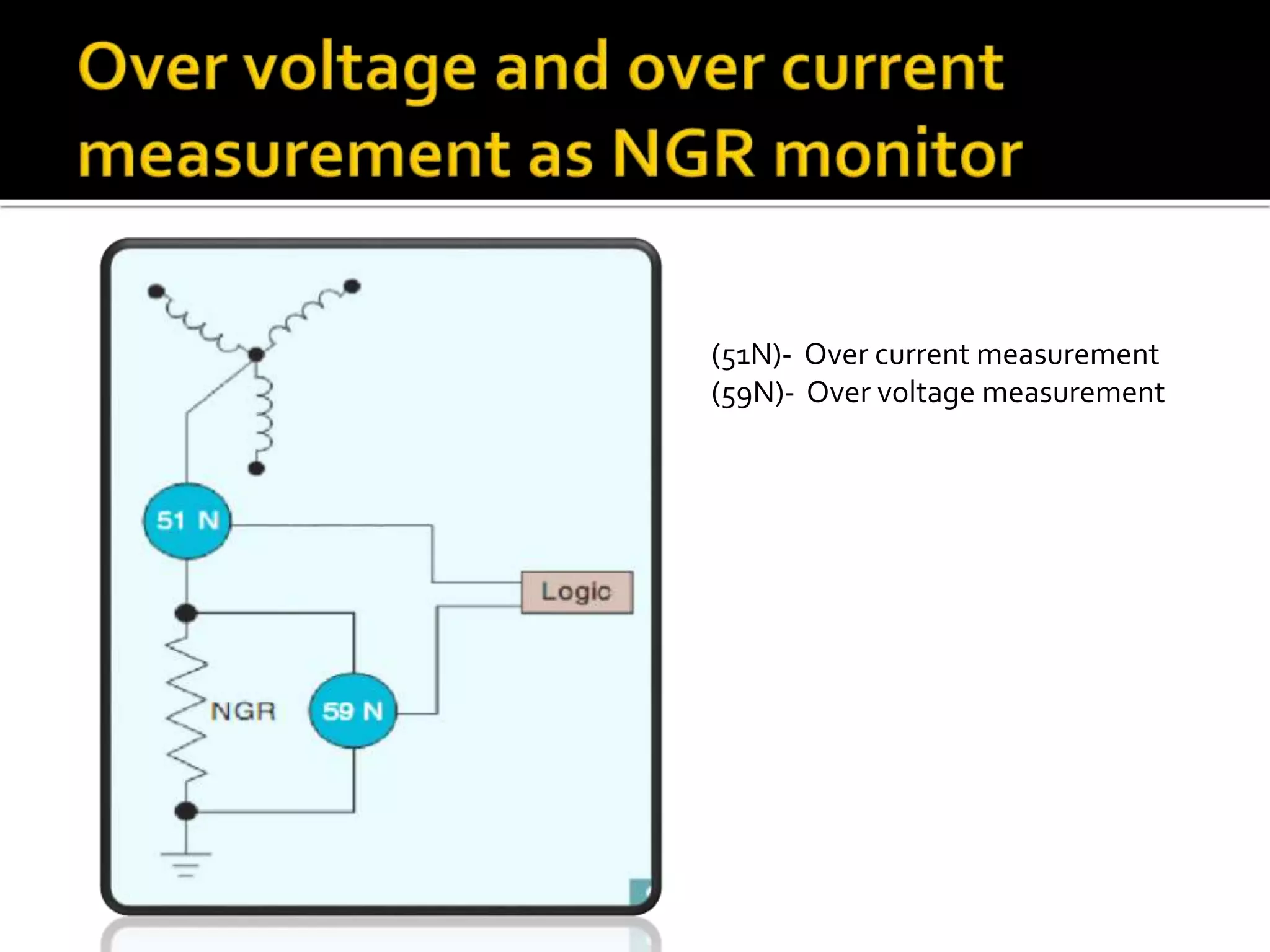
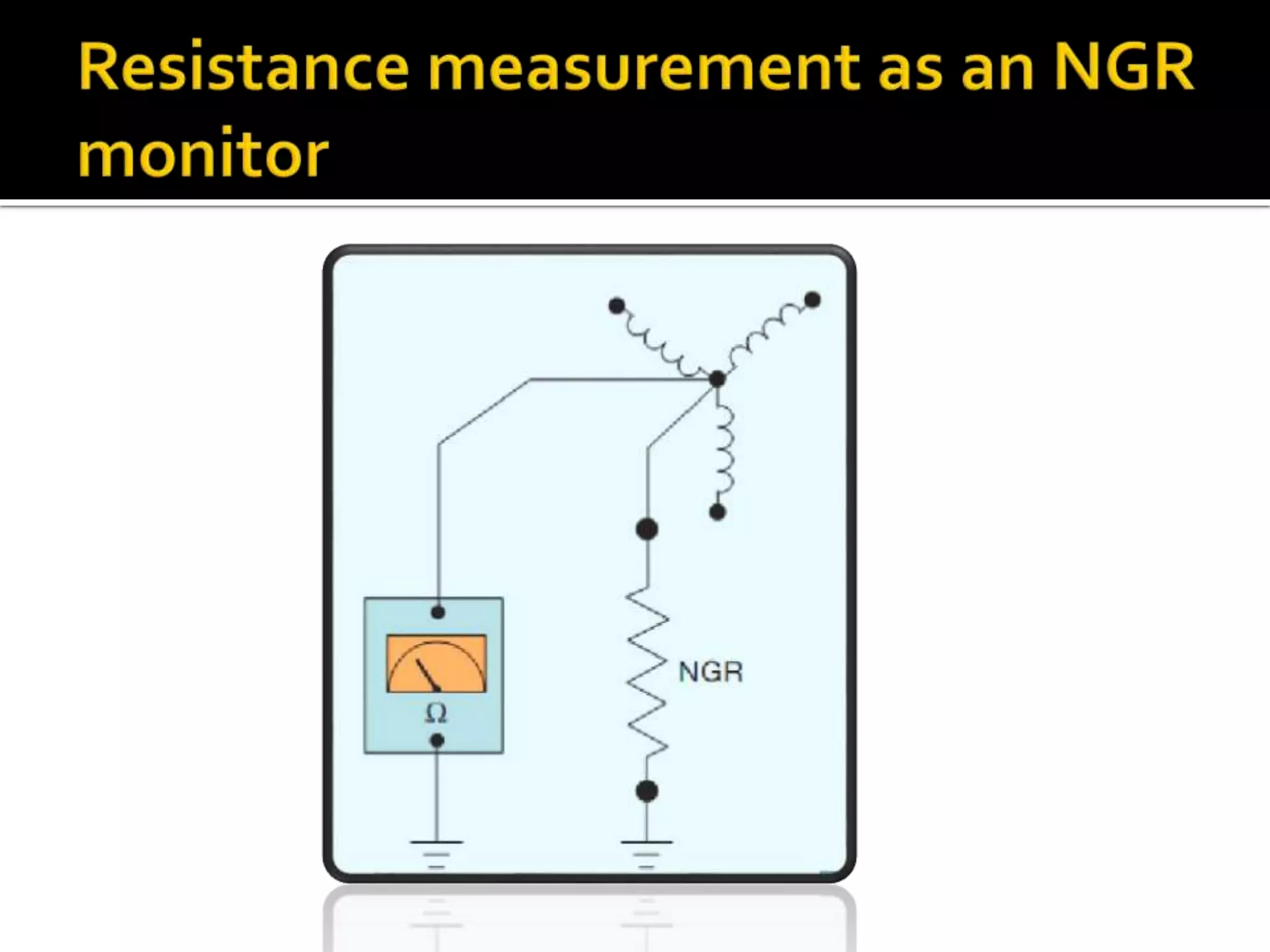
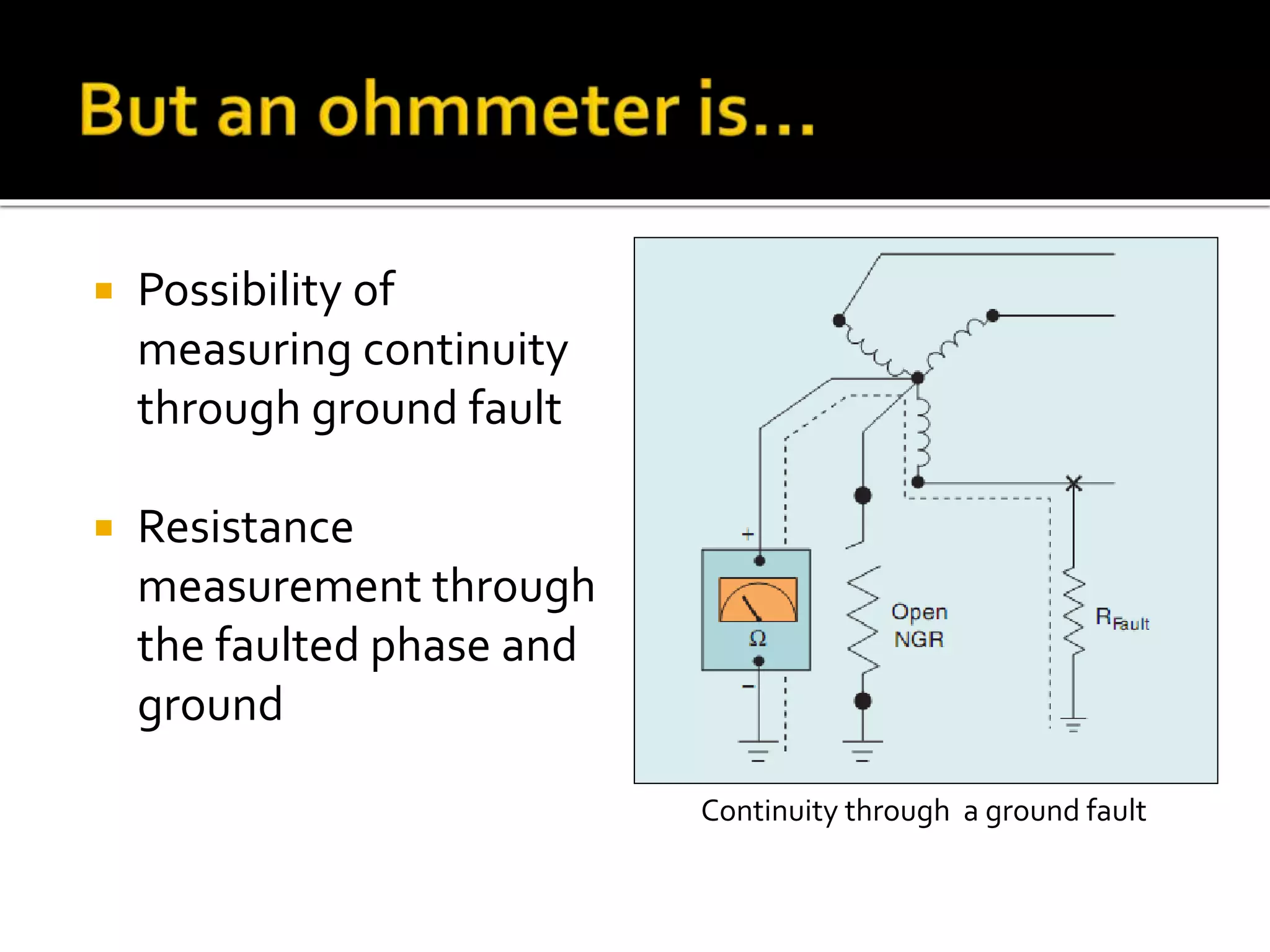
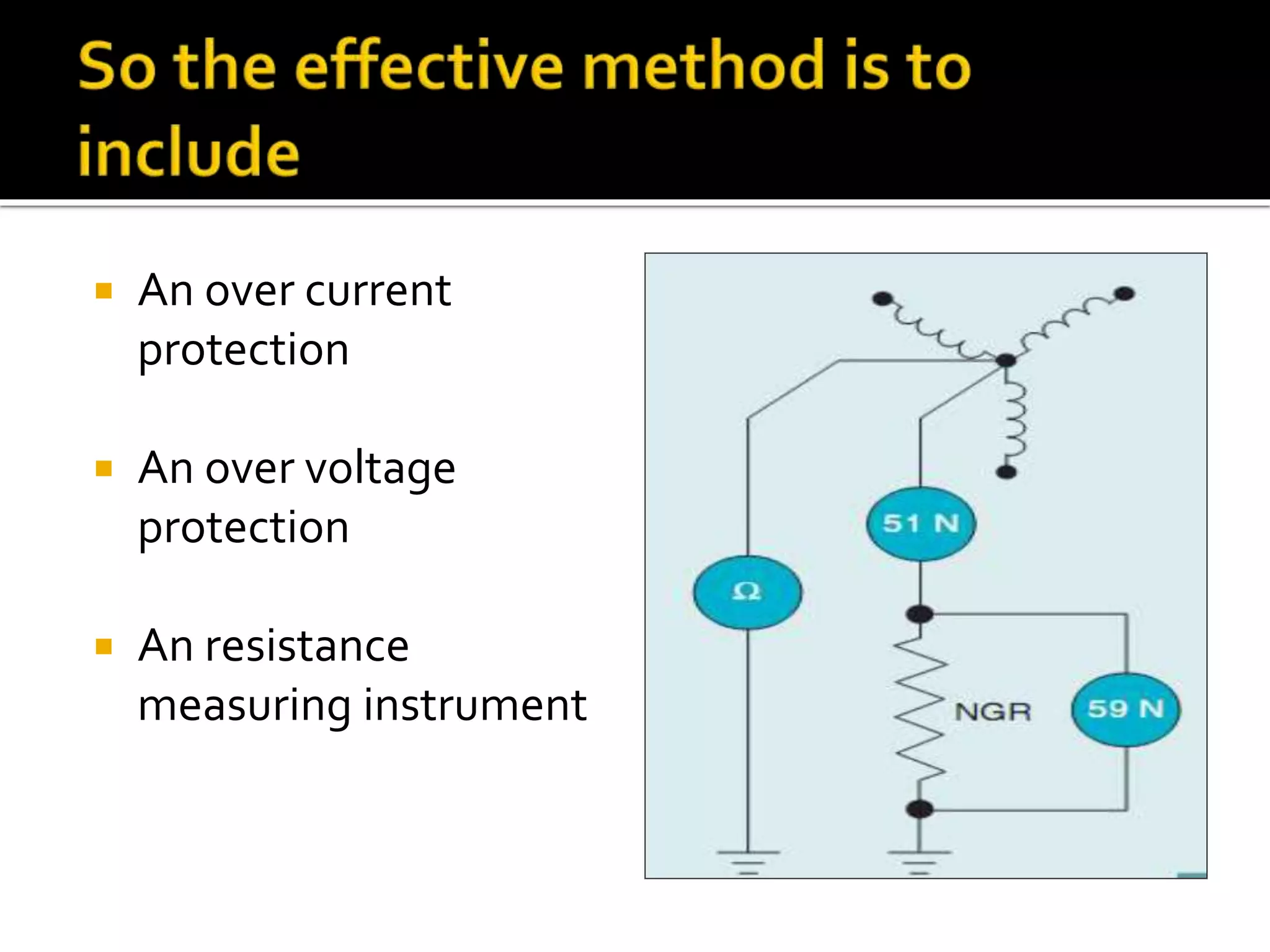
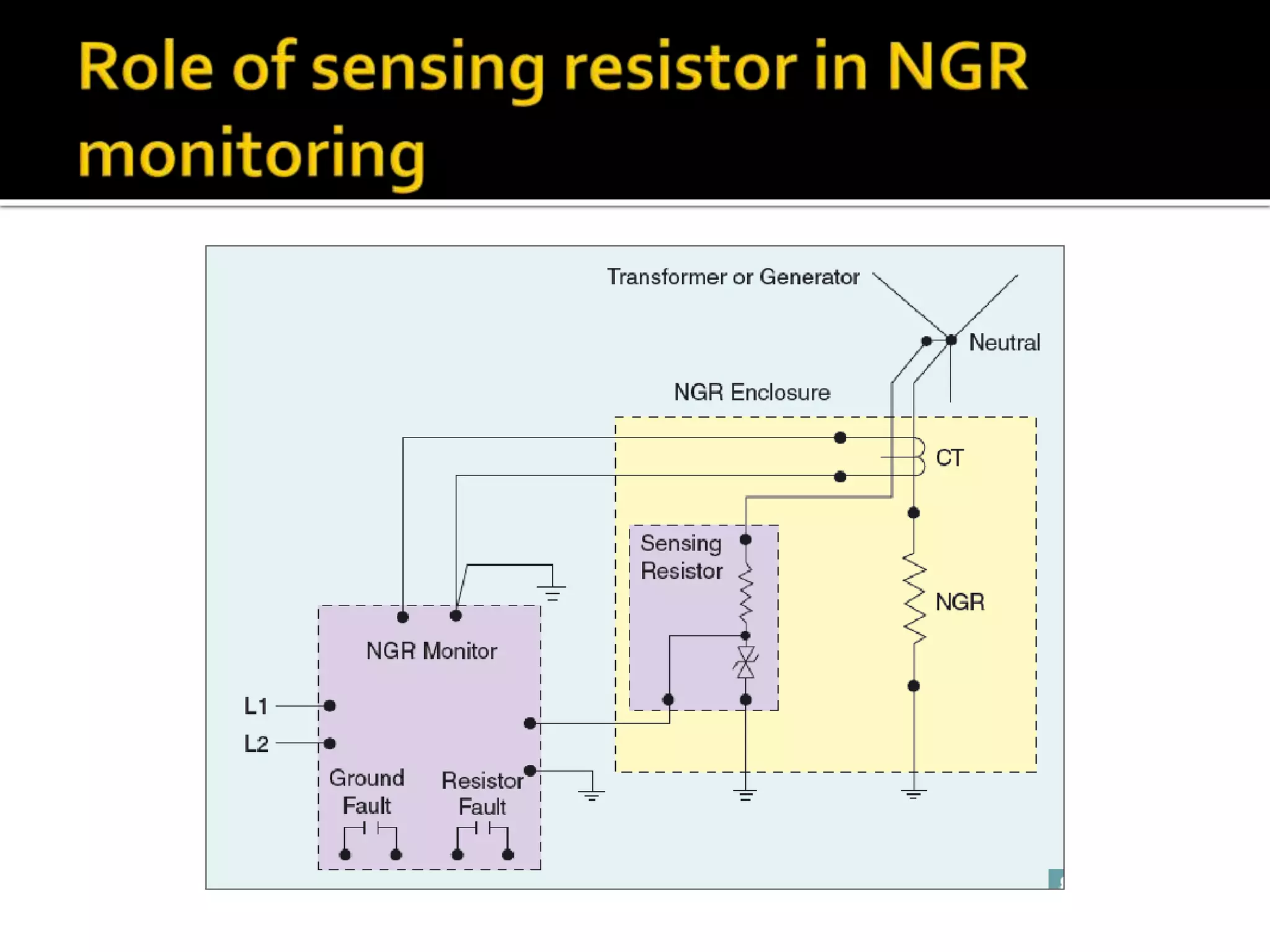
This document discusses neutral grounding resistors (NGRs) and the importance of continuously monitoring them. It provides examples of problems that can occur if an NGR fails or loses connection, such as soft starter failures or transient overvoltages. Continuous monitoring can detect NGR issues and ensure ground fault protection still functions properly. An effective monitor measures resistance through the NGR to identify connectivity issues, and protects against failures that could leave systems unprotected from ground faults.