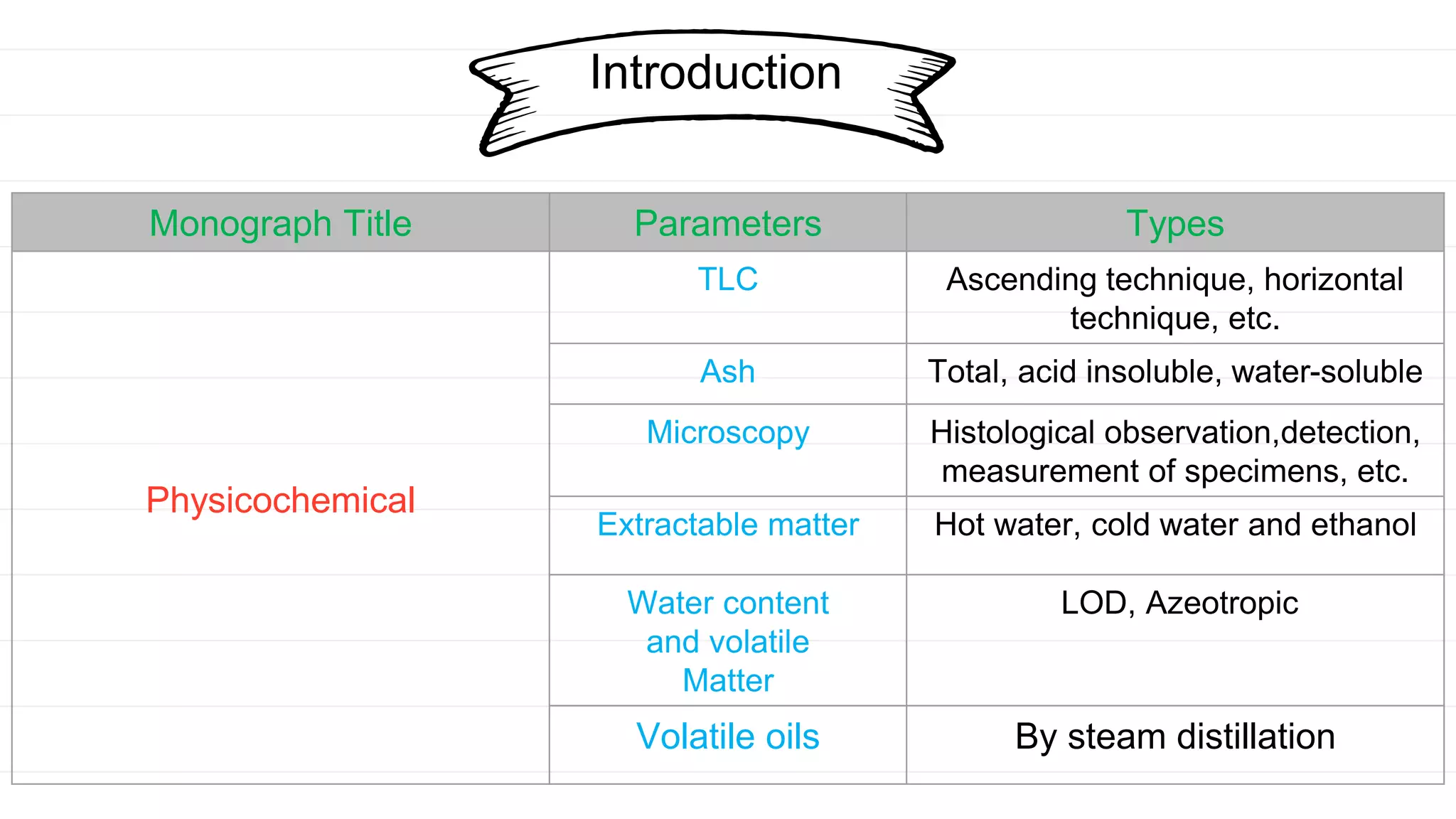
The document outlines the WHO guidelines for the quality control and standardization of herbal drugs, emphasizing the importance of consistency, safety, and efficacy. It details various parameters for testing herbal medicine quality, including chemical fingerprinting, physicochemical analysis, and toxicological assessments. Additionally, it mentions methods for monitoring microbial contamination and the use of irradiation to ensure safety.