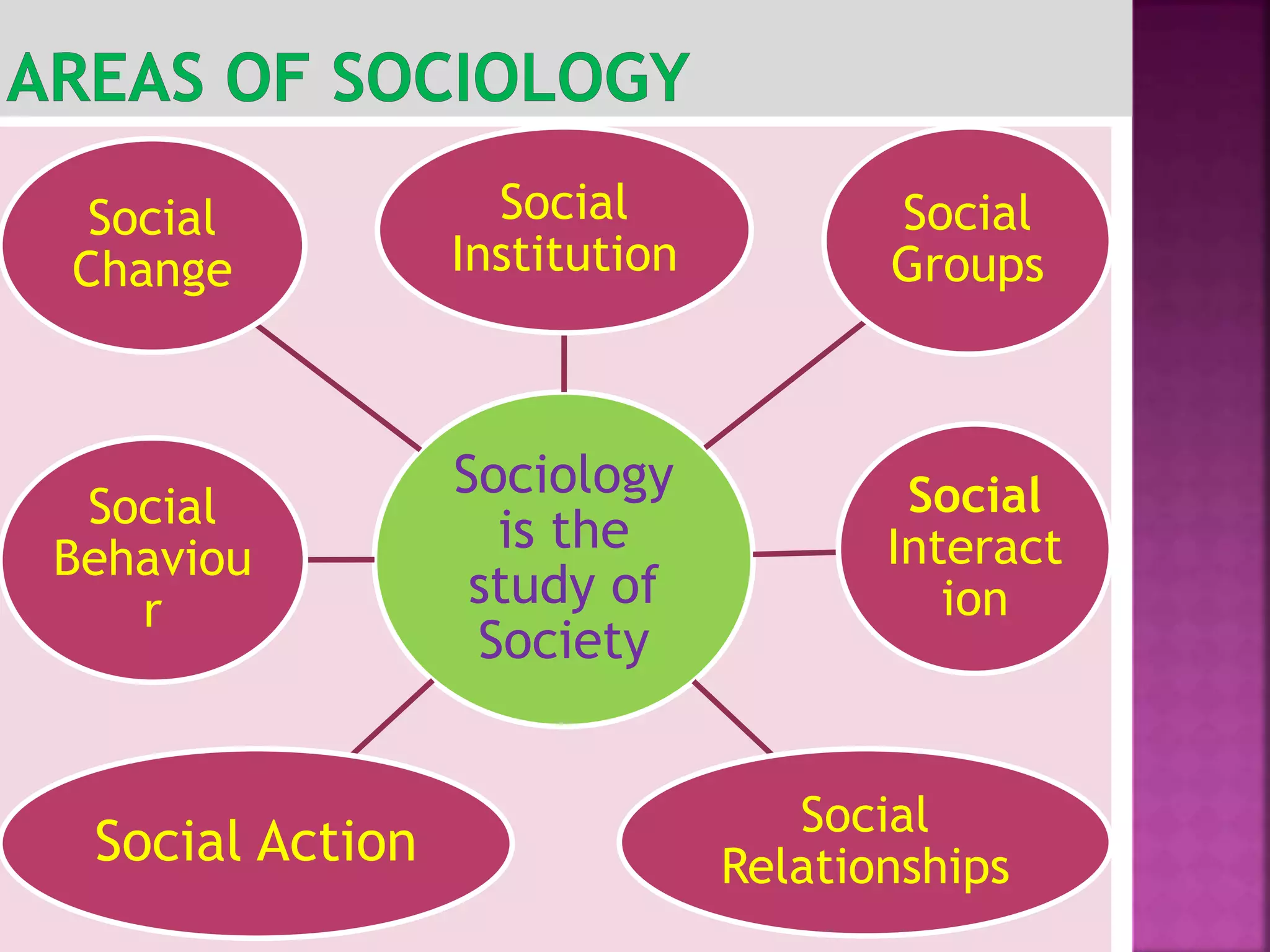
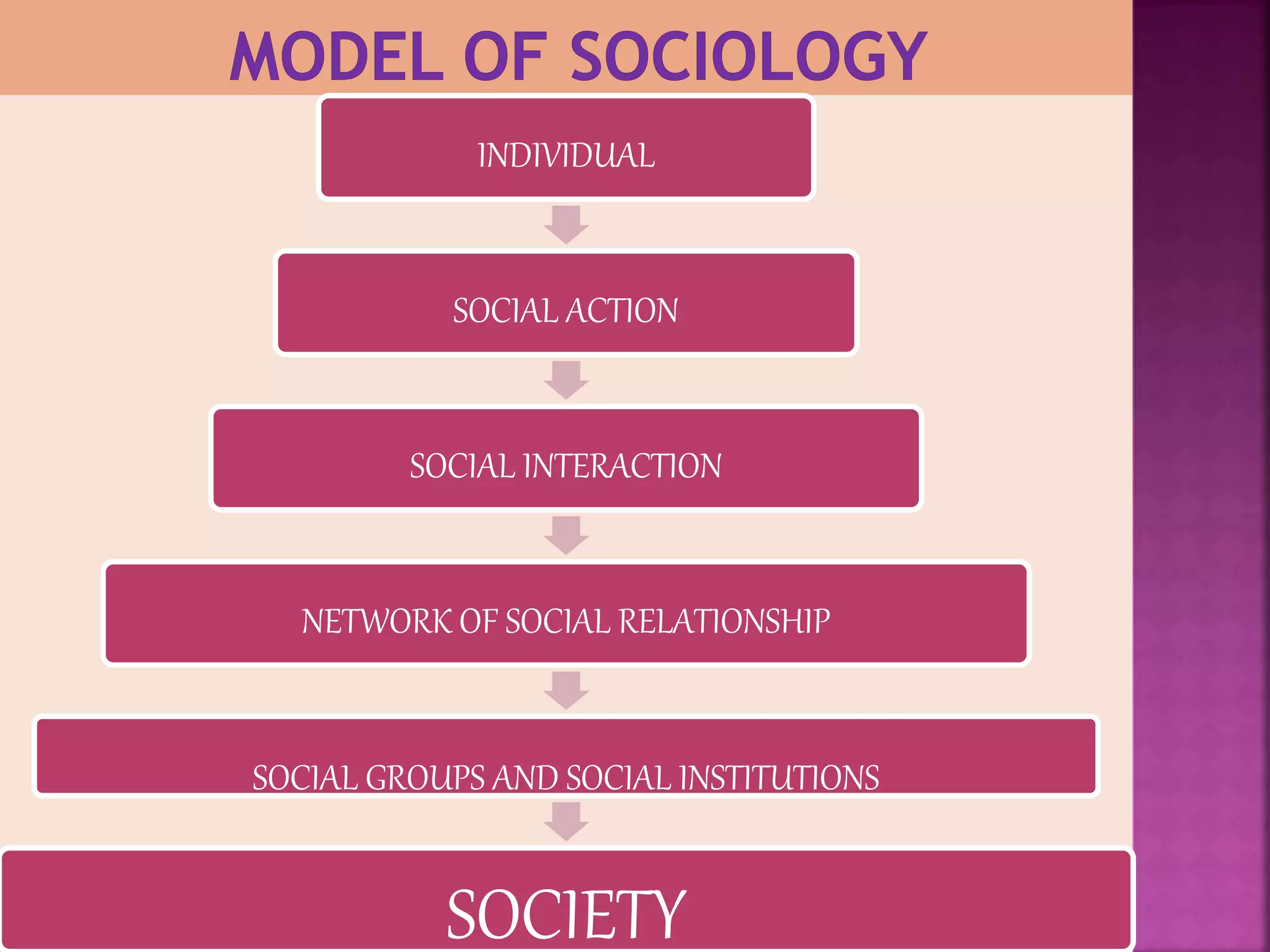
Sociology, coined by August Comte in 1838, is the study of society encompassing social life, change, and human behavior. It investigates structures and interactions within groups and institutions, making it a diverse social science. Key contributors like Comte, Durkheim, and others have shaped its scope, which includes topics ranging from crime and religion to social institutions and relationships.