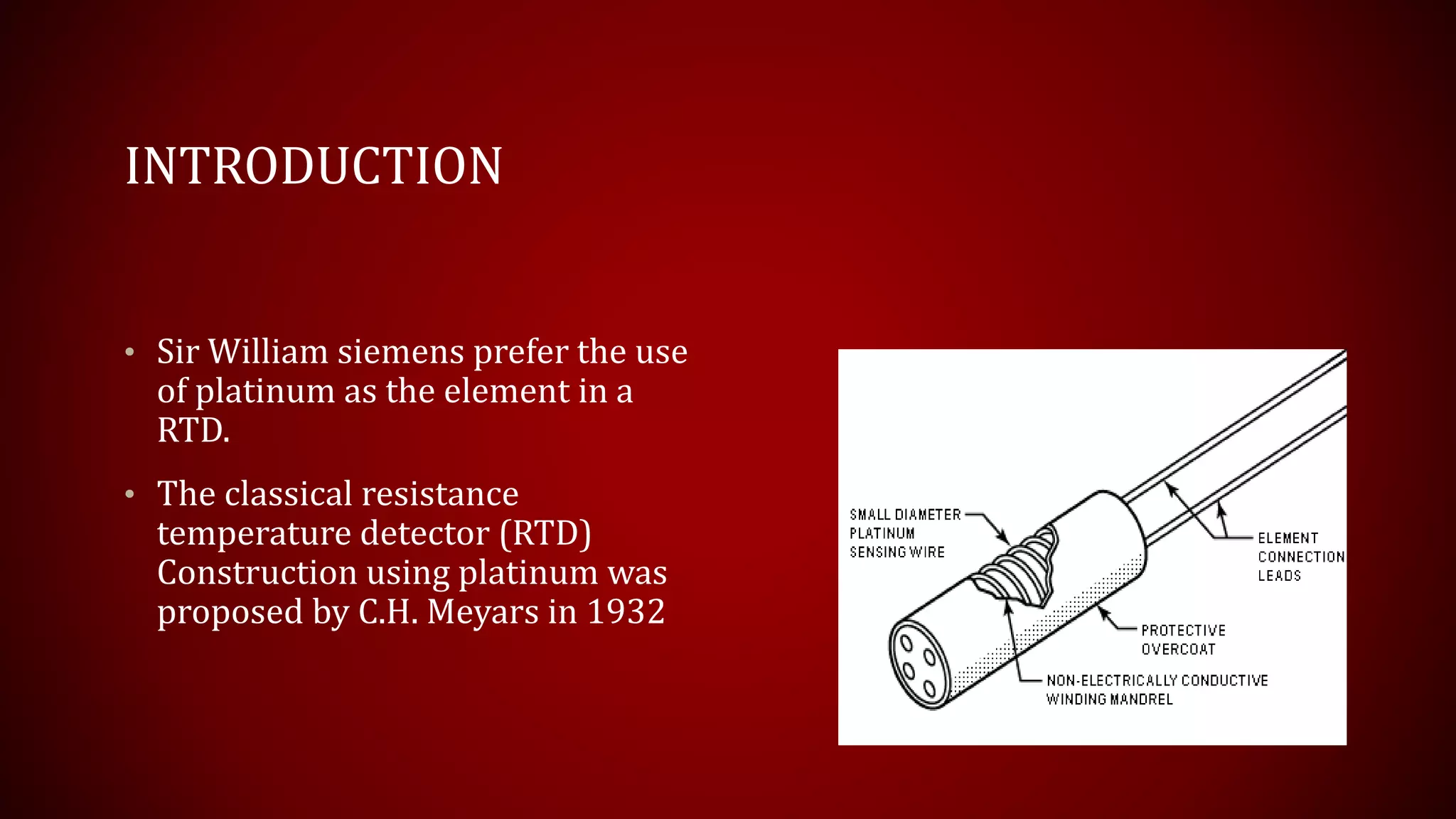
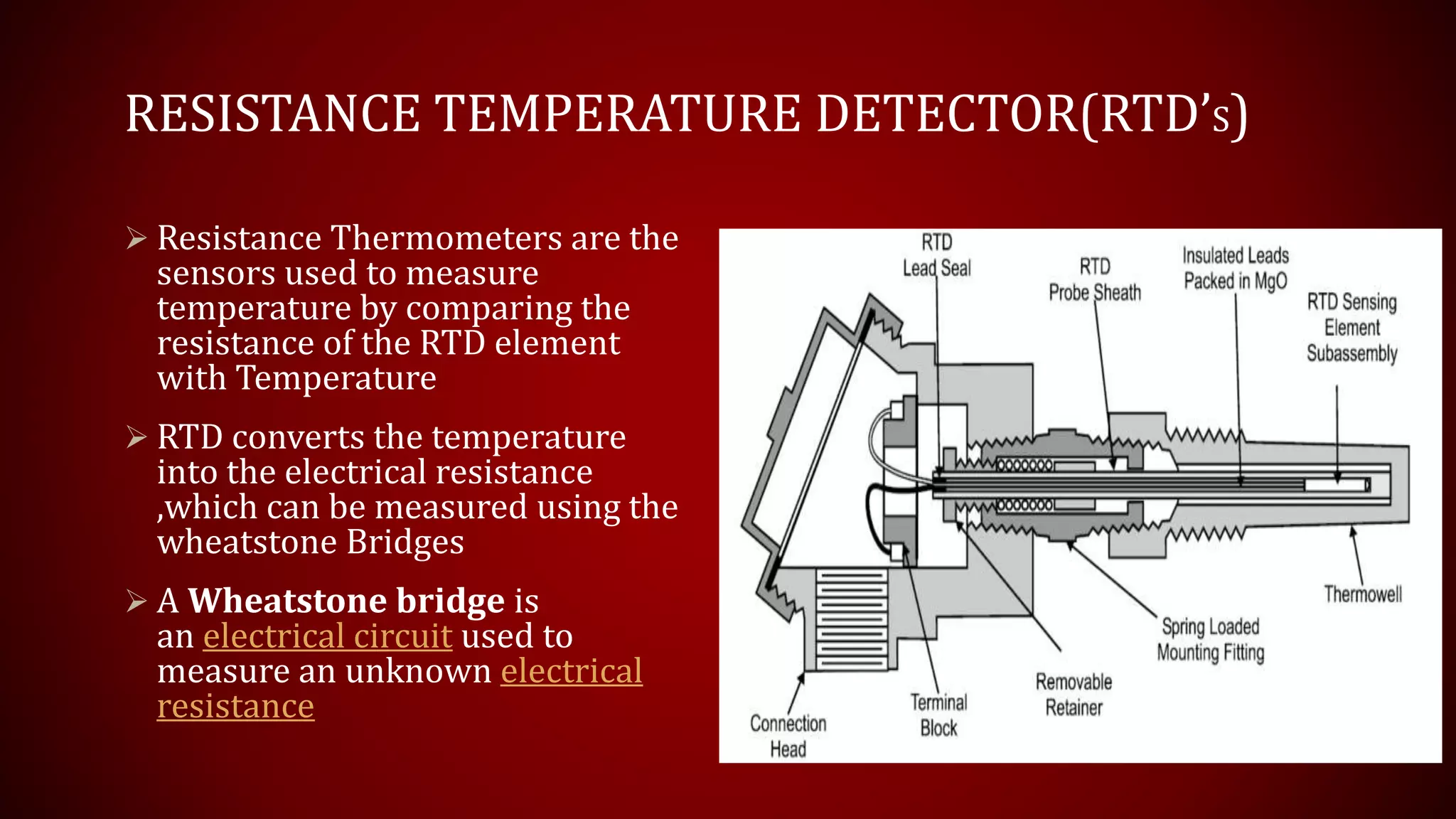
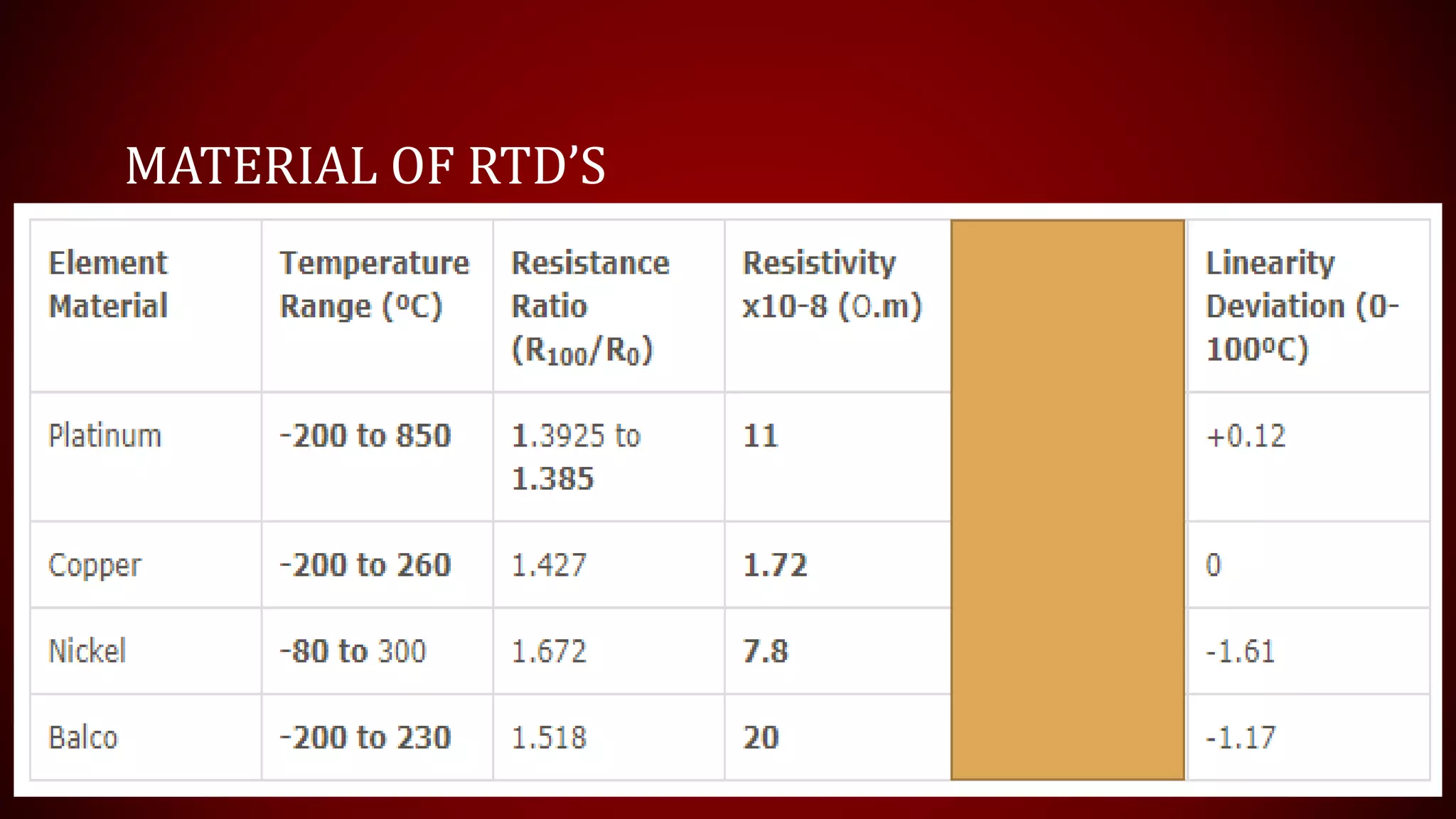
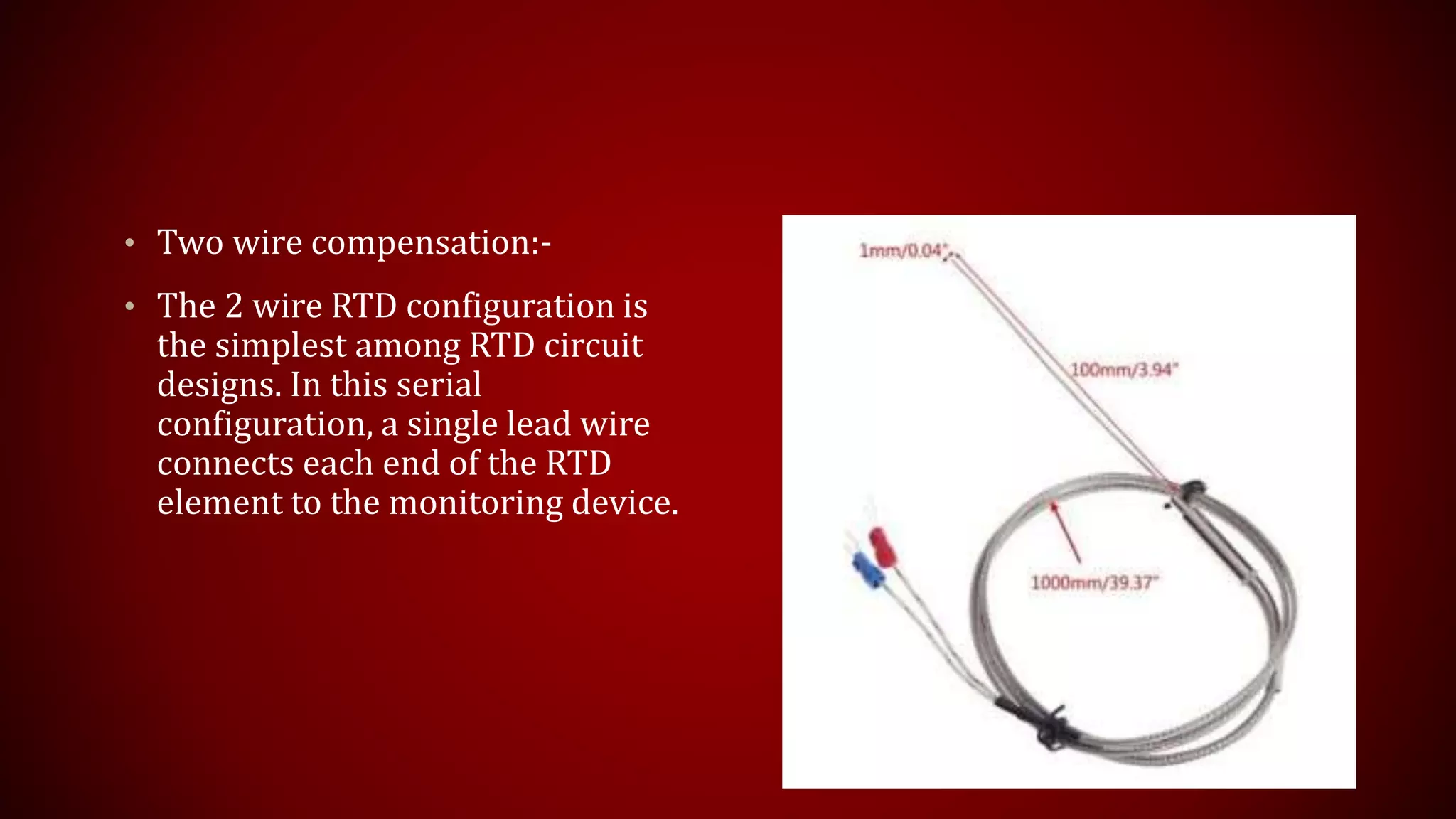
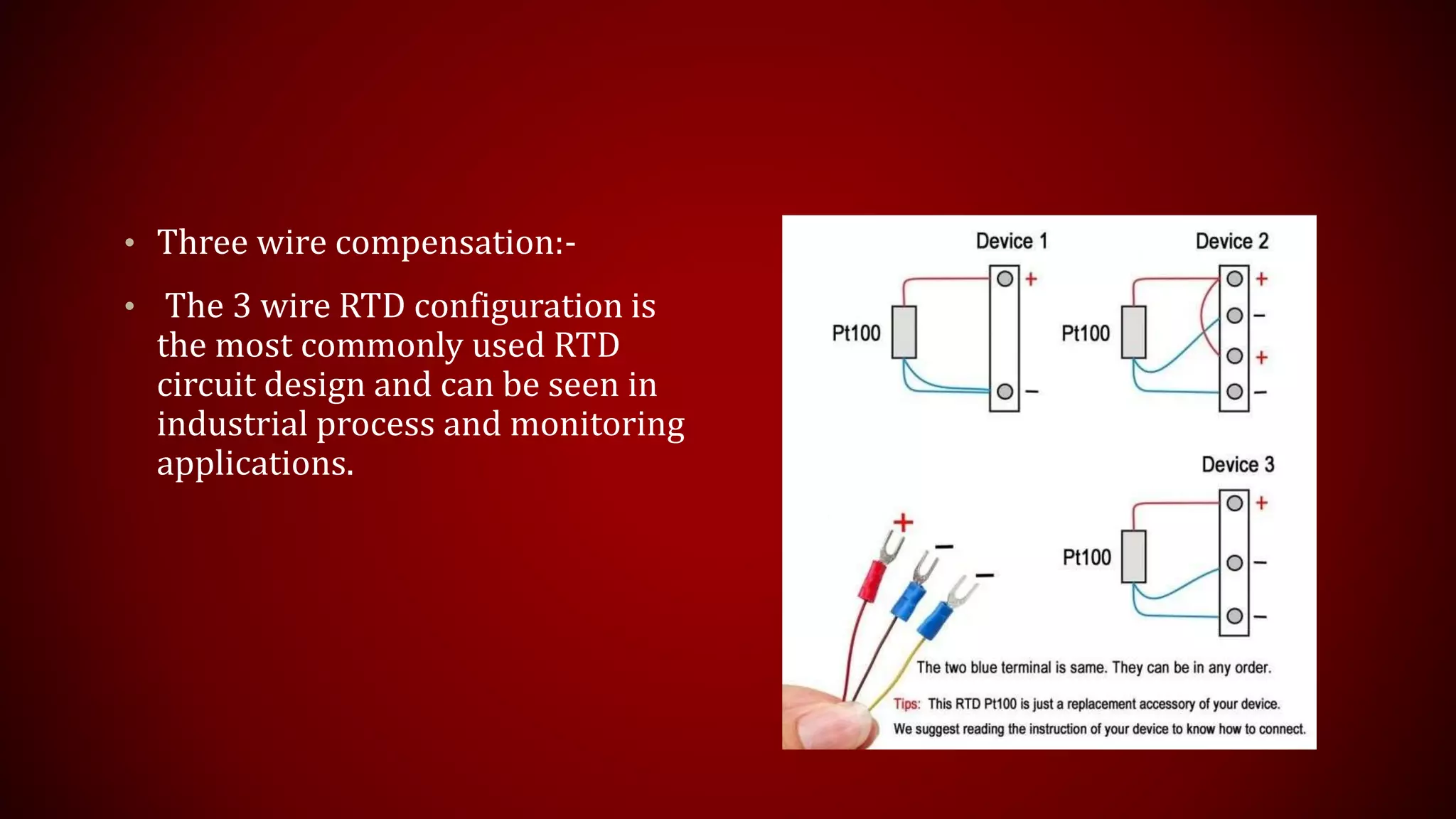
This document provides an overview of Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDs), highlighting their configurations, working principles, applications, advantages, and disadvantages. RTDs, particularly the widely used PT-100, measure temperature through resistance changes and can be configured in two, three, or four wire systems. While they offer high accuracy and stability, they come with complexities and limitations such as a restricted temperature range and higher costs.