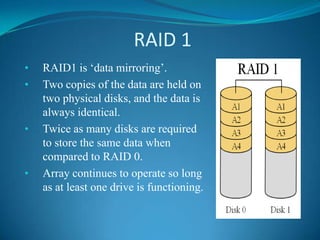
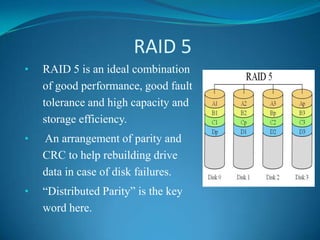
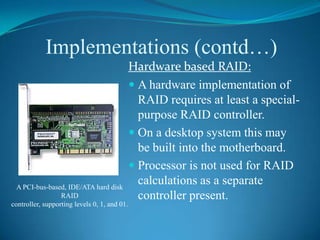
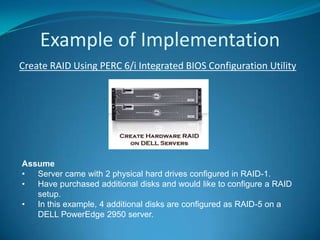
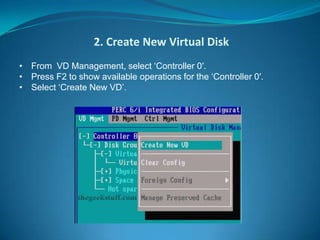
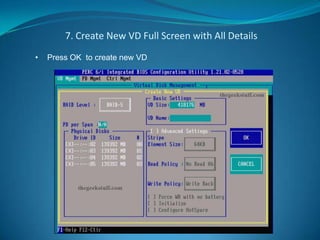
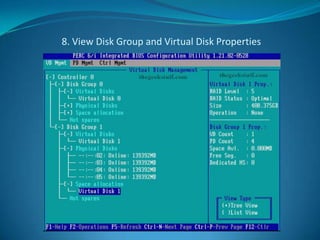
The document explains RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) technology, which enhances storage reliability and performance by using multiple disk drives for redundancy. It outlines various RAID configurations, such as RAID 0, 1, 5, and combinations like RAID 1+0, detailing their benefits and drawbacks. Additionally, the document describes both software and hardware implementations of RAID, including a practical example of configuring a RAID setup using a specific controller on a Dell PowerEdge server.


![What is RAID?RAID, an acronym first defined by David A. Patterson, Garth A. Gibson, and Randy Katz at the University of California, Berkeley in 1987 to describe a redundant array of inexpensive disks,[1] a technology that allowed computer users to achieve high levels of storage reliability from low-cost and less reliable PC-class disk-drive components, via the technique of arranging the devices into arrays for redundancy.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/raidpres-091030090131-phpapp01/85/What-is-R-A-I-D-3-320.jpg)