This document provides an overview of computer fundamentals including:
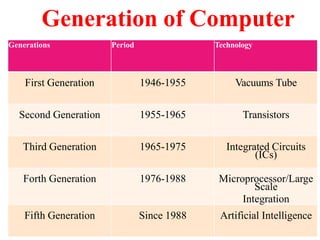
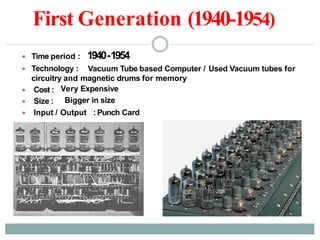
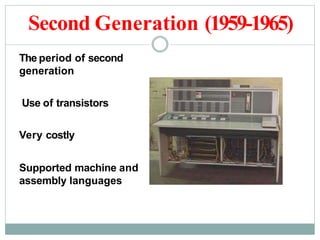
- The five generations of computers from the first generation using vacuum tubes to the current fifth generation using artificial intelligence.
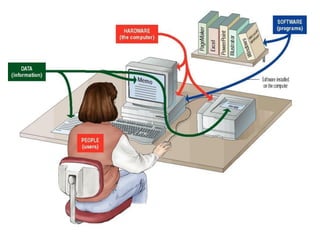
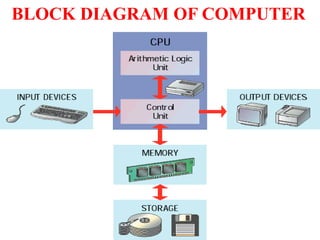
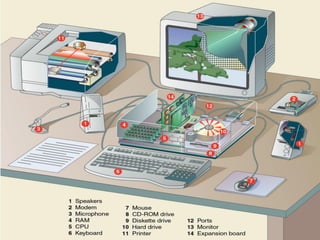
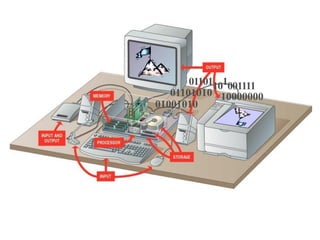
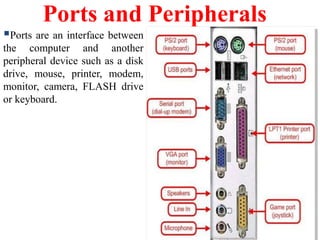
- Descriptions of the internal components of a computer including the central processing unit, memory, storage devices, input/output ports, and peripheral devices.
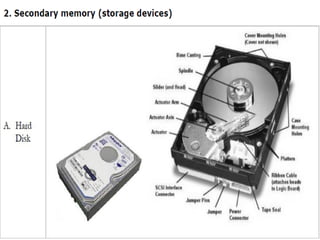
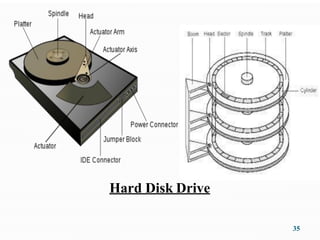
- Explanations of different types of input devices like keyboards and mice, output devices like monitors and printers, and storage devices like hard drives and optical drives.
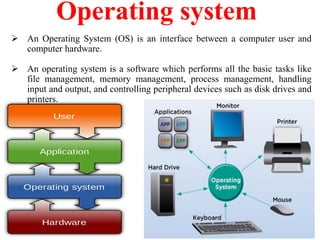
- An introduction to operating systems, networking components like modems, and examples of popular operating systems like Windows and Linux distributions.