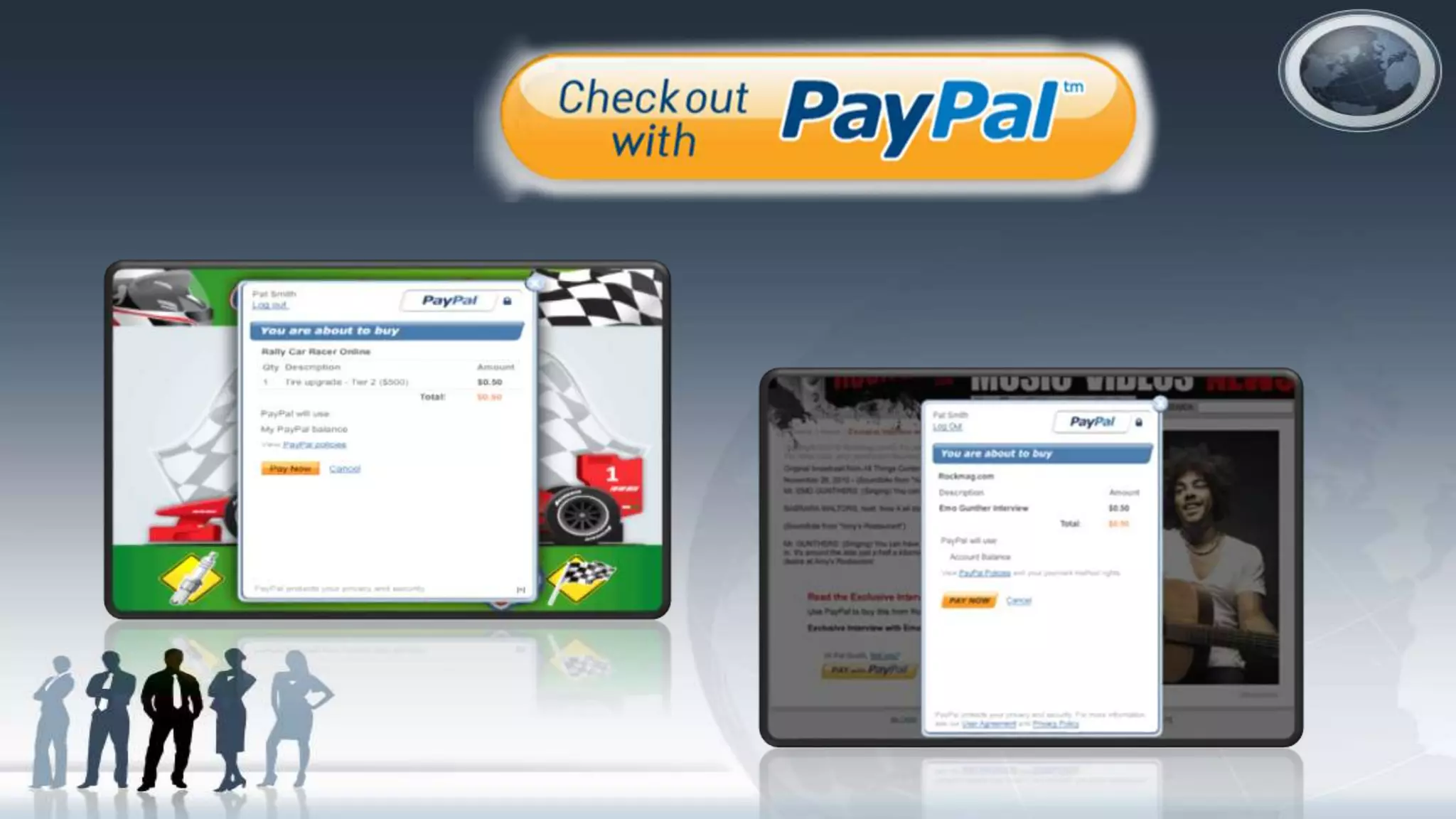
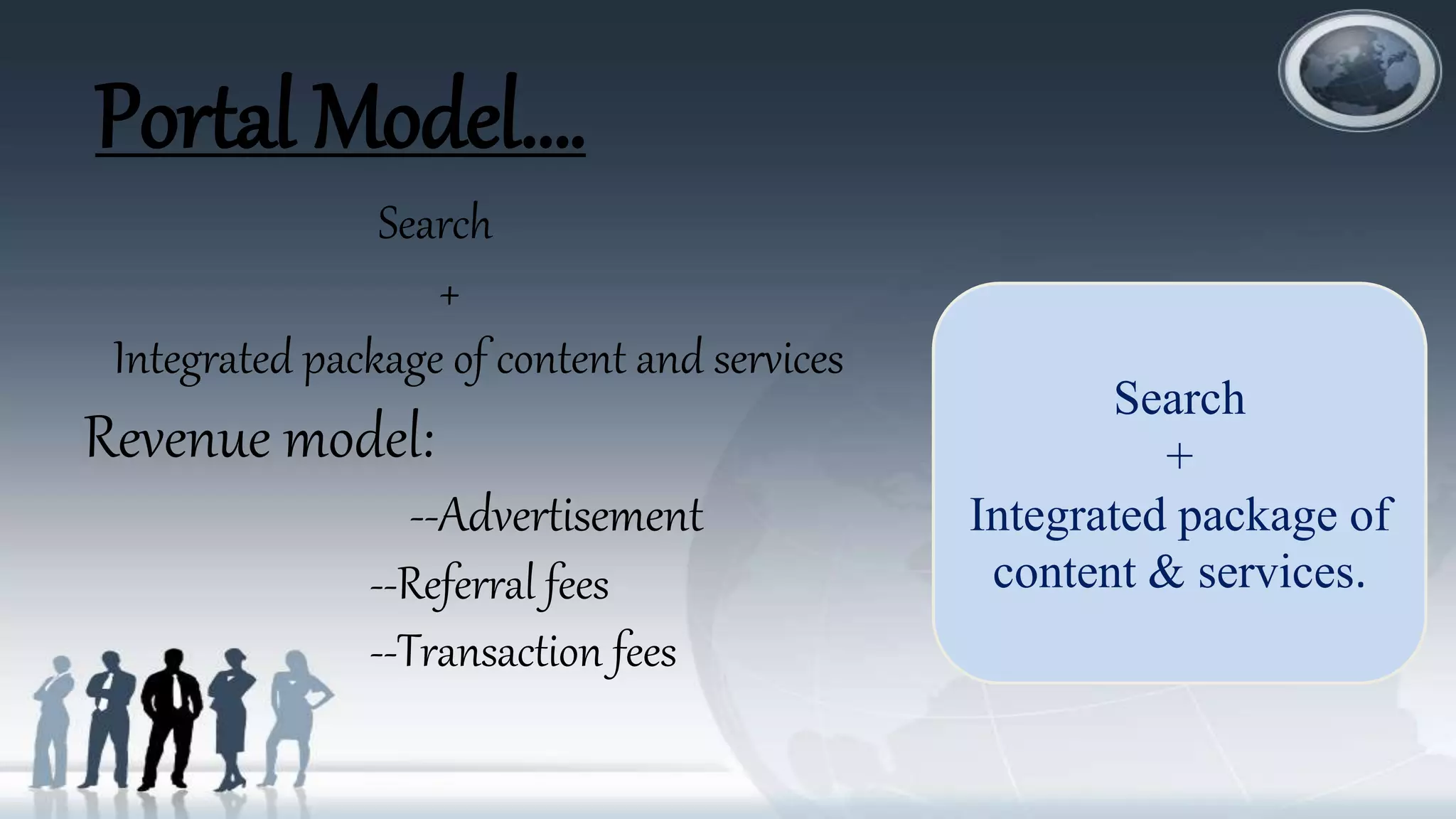
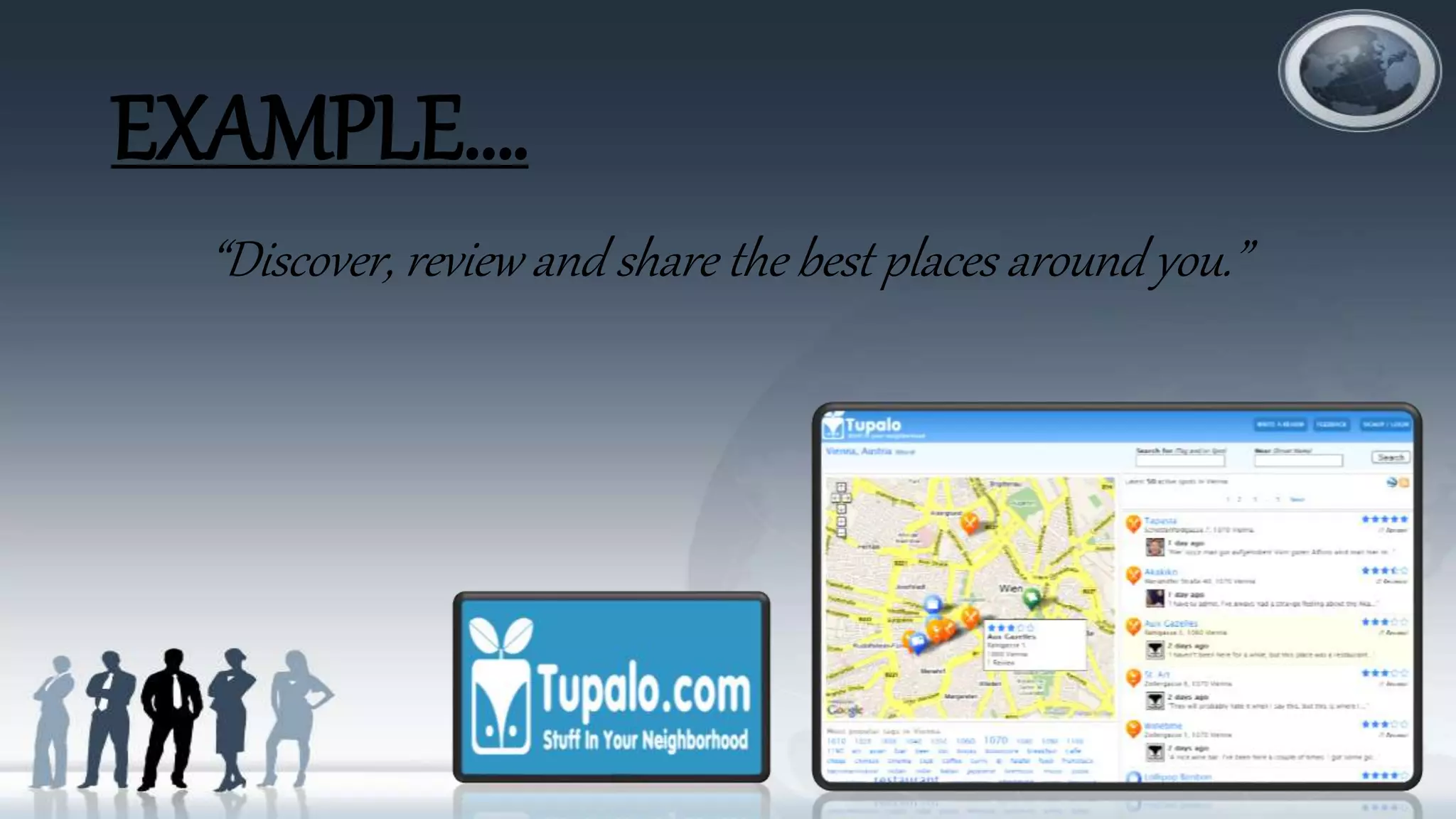
The document discusses various topics related to electronic commerce (e-commerce) and mobile commerce (m-commerce). It defines e-commerce as the process of buying and selling goods and services over computer networks, and defines m-commerce as buying and selling via wireless devices. The document then covers the history of e-commerce and m-commerce, examples of different e-commerce models and revenue models, types of e-commerce transactions, electronic payment systems, and m-commerce applications and services.