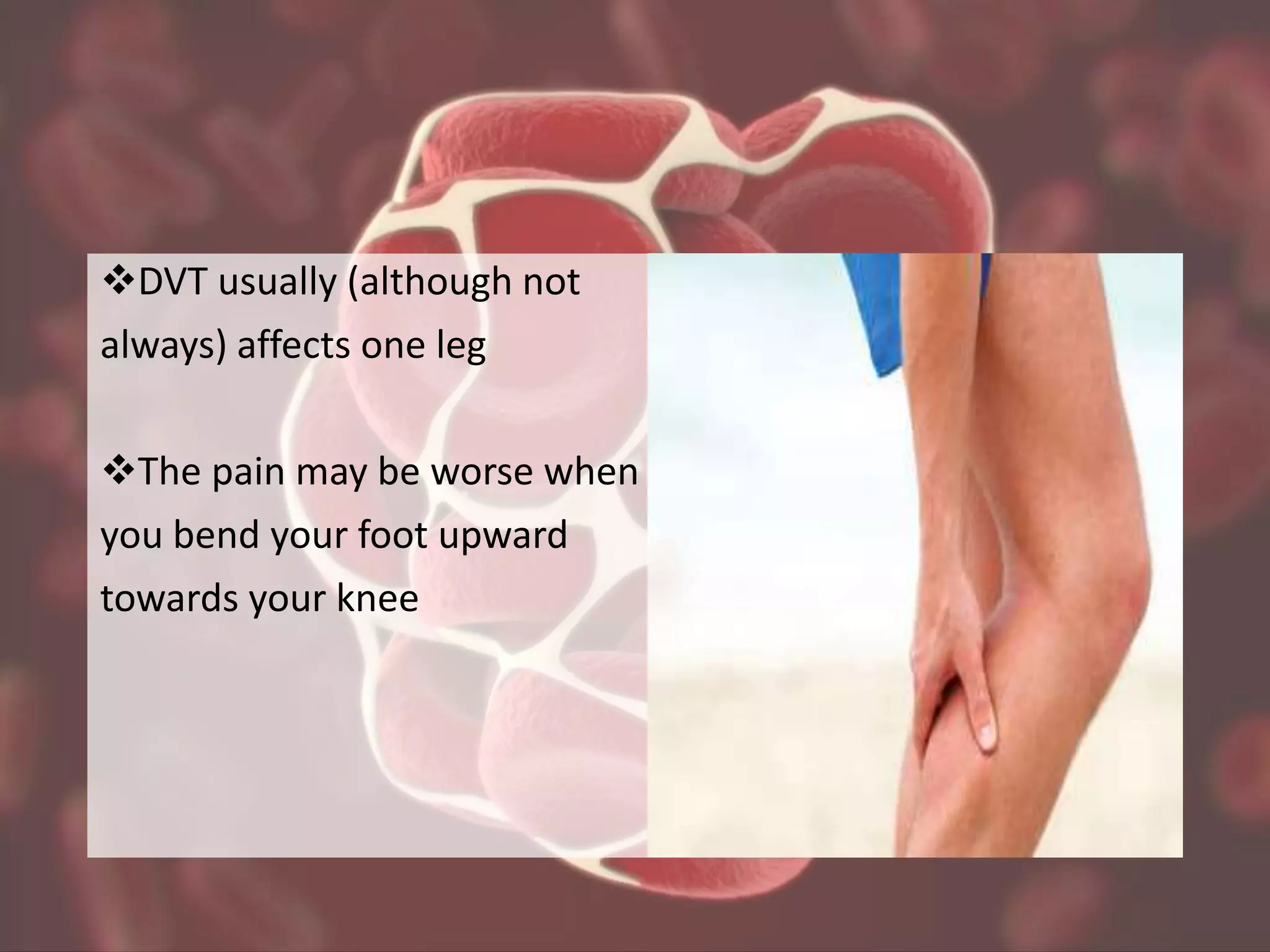
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot that develops in a deep vein, usually in the leg. It can cause pain, swelling and tenderness in the leg. DVT is diagnosed through tests like a D-dimer test, ultrasound scan or venogram. Treatment involves anticoagulant medicines to reduce clotting and prevent existing clots from growing. Preventing DVT involves not smoking, regular exercise and avoiding long periods of inactivity. Untreated DVT can potentially lead to a pulmonary embolism.