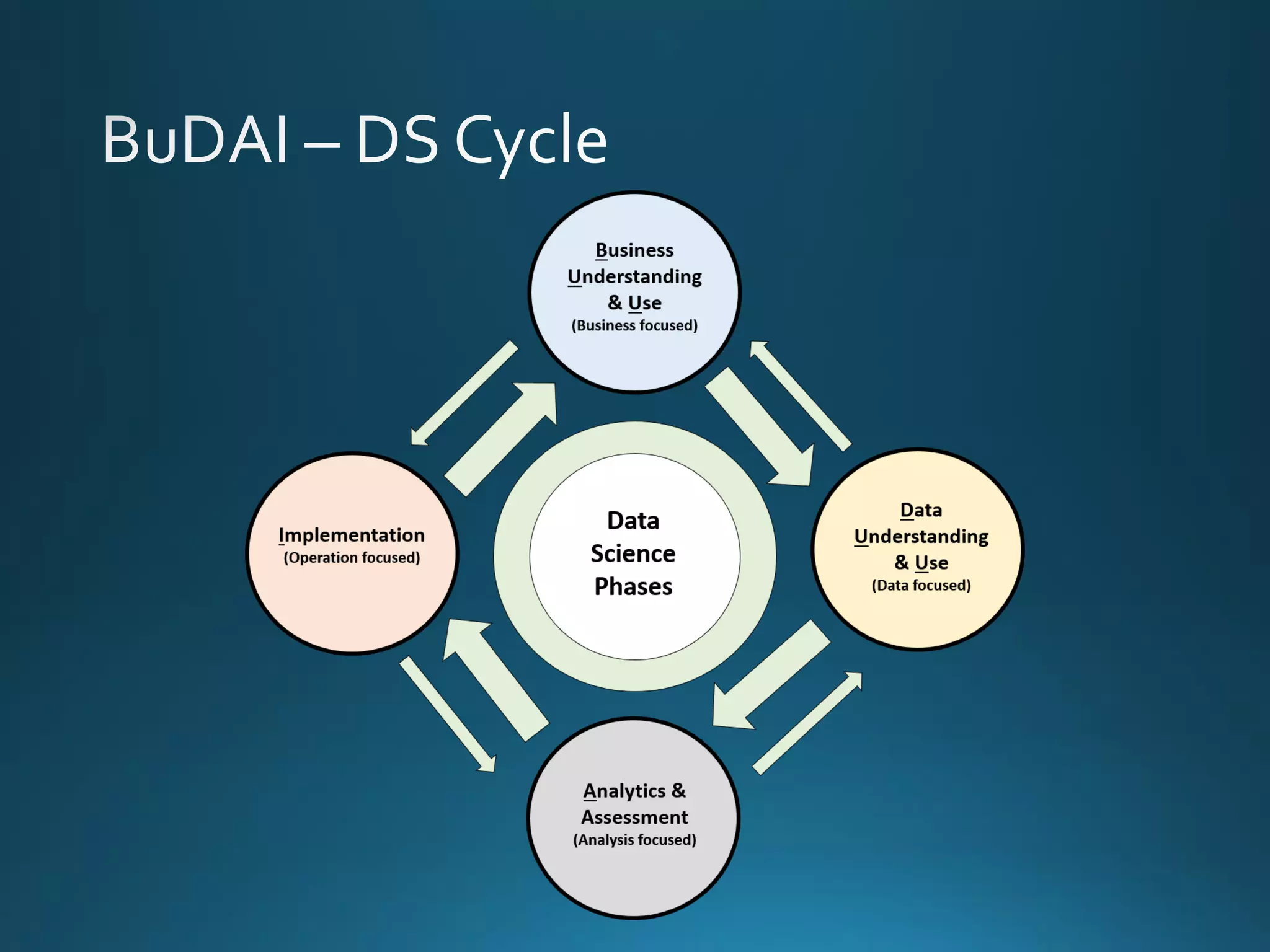
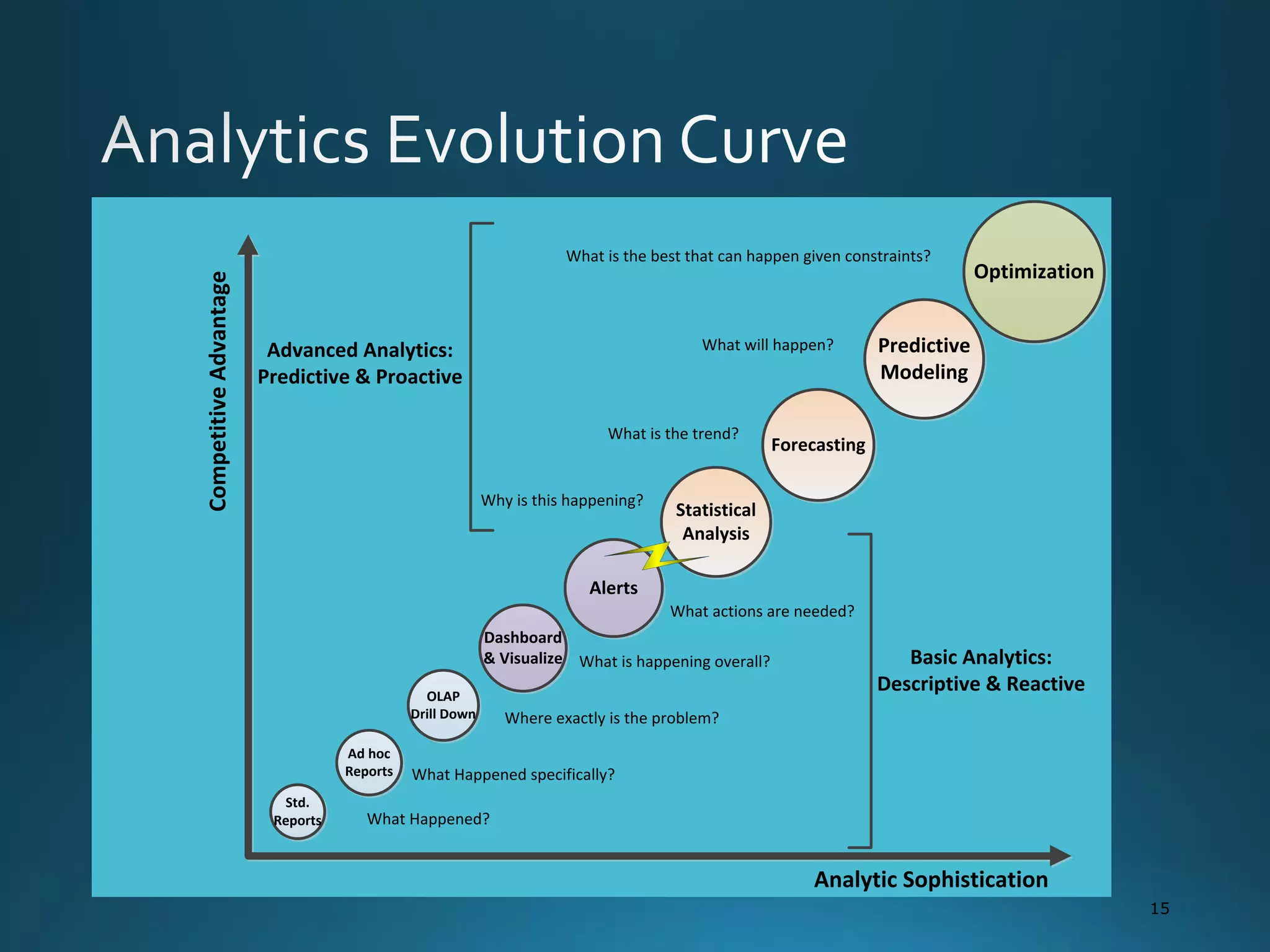
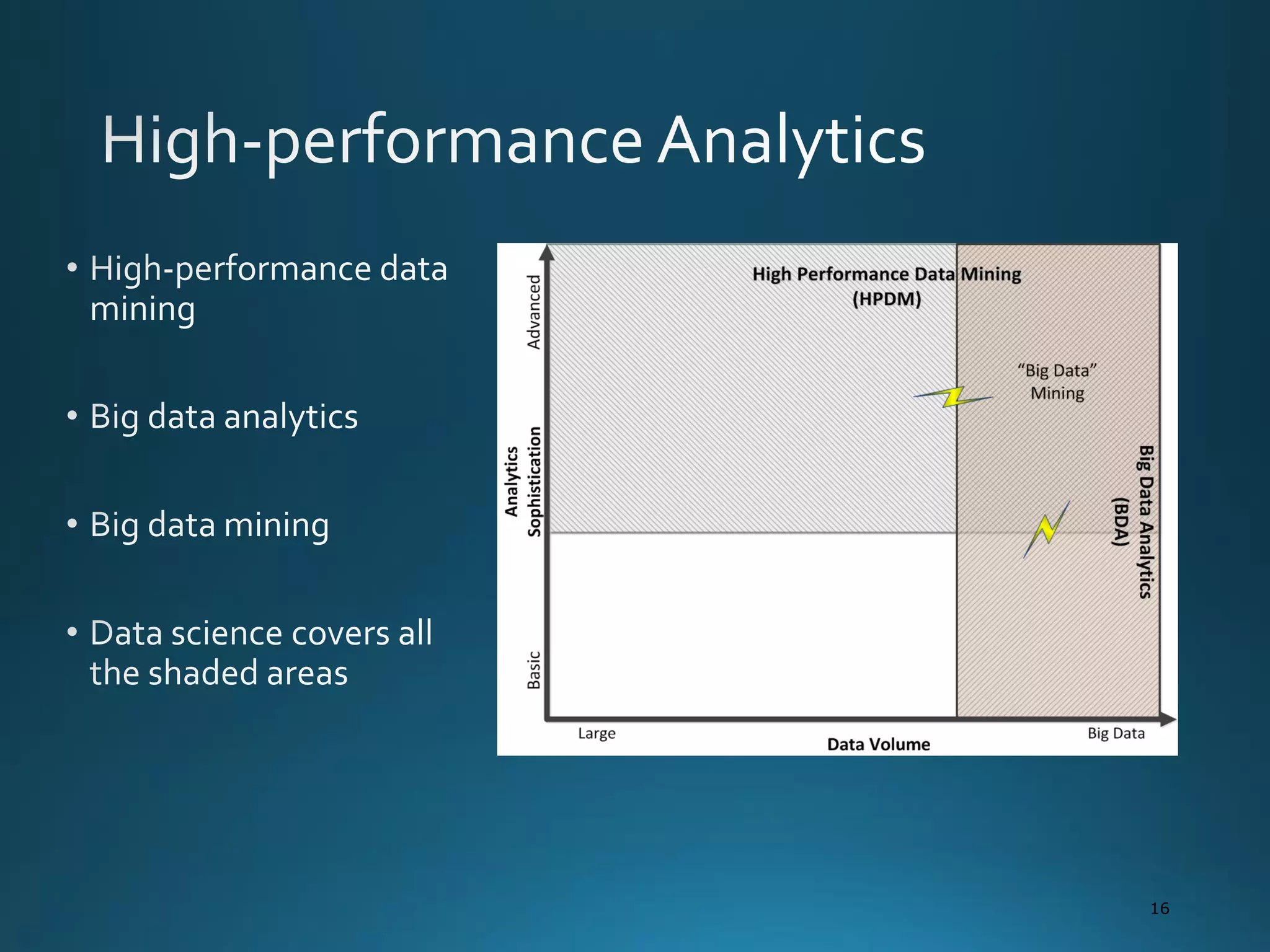
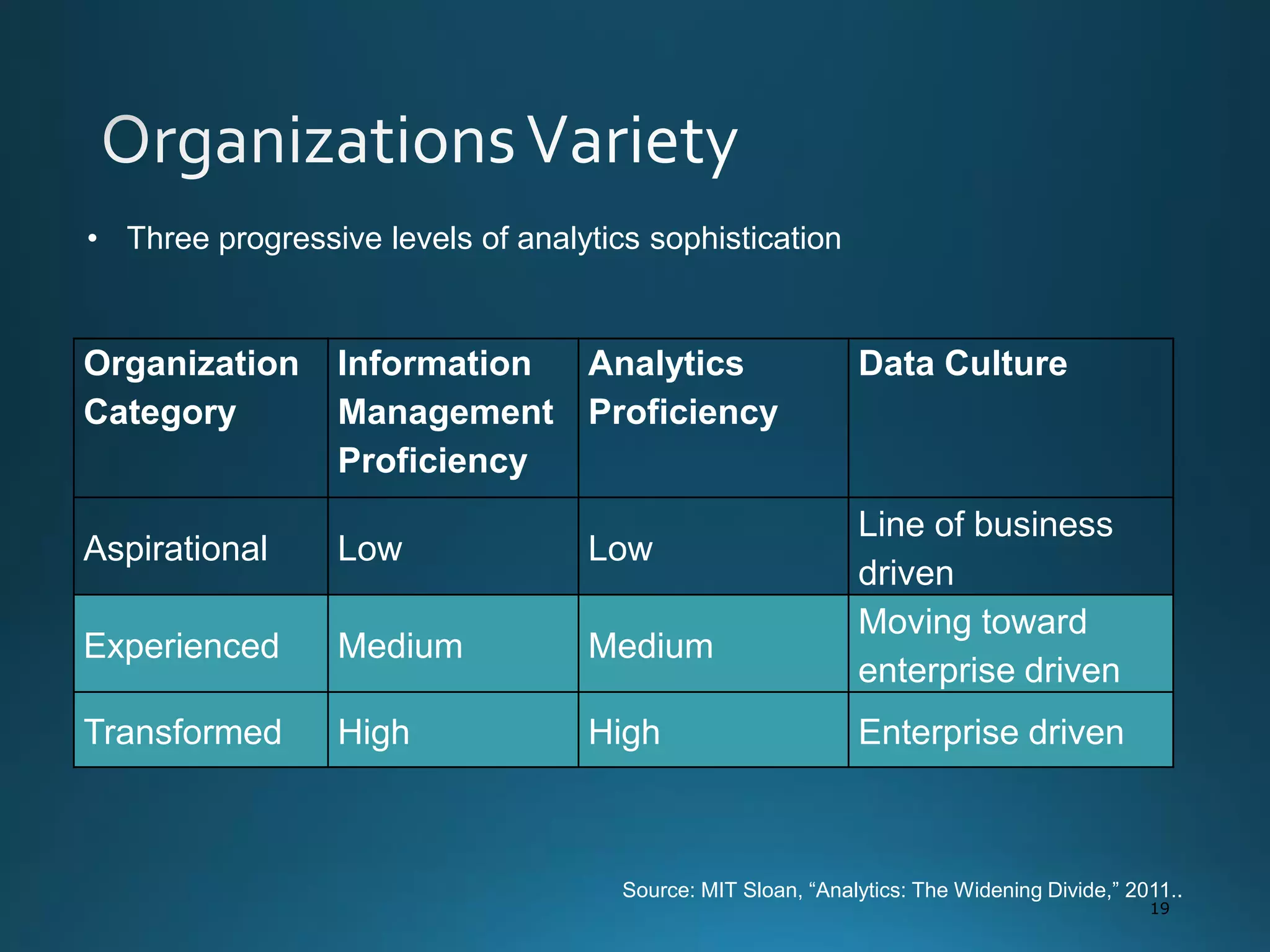
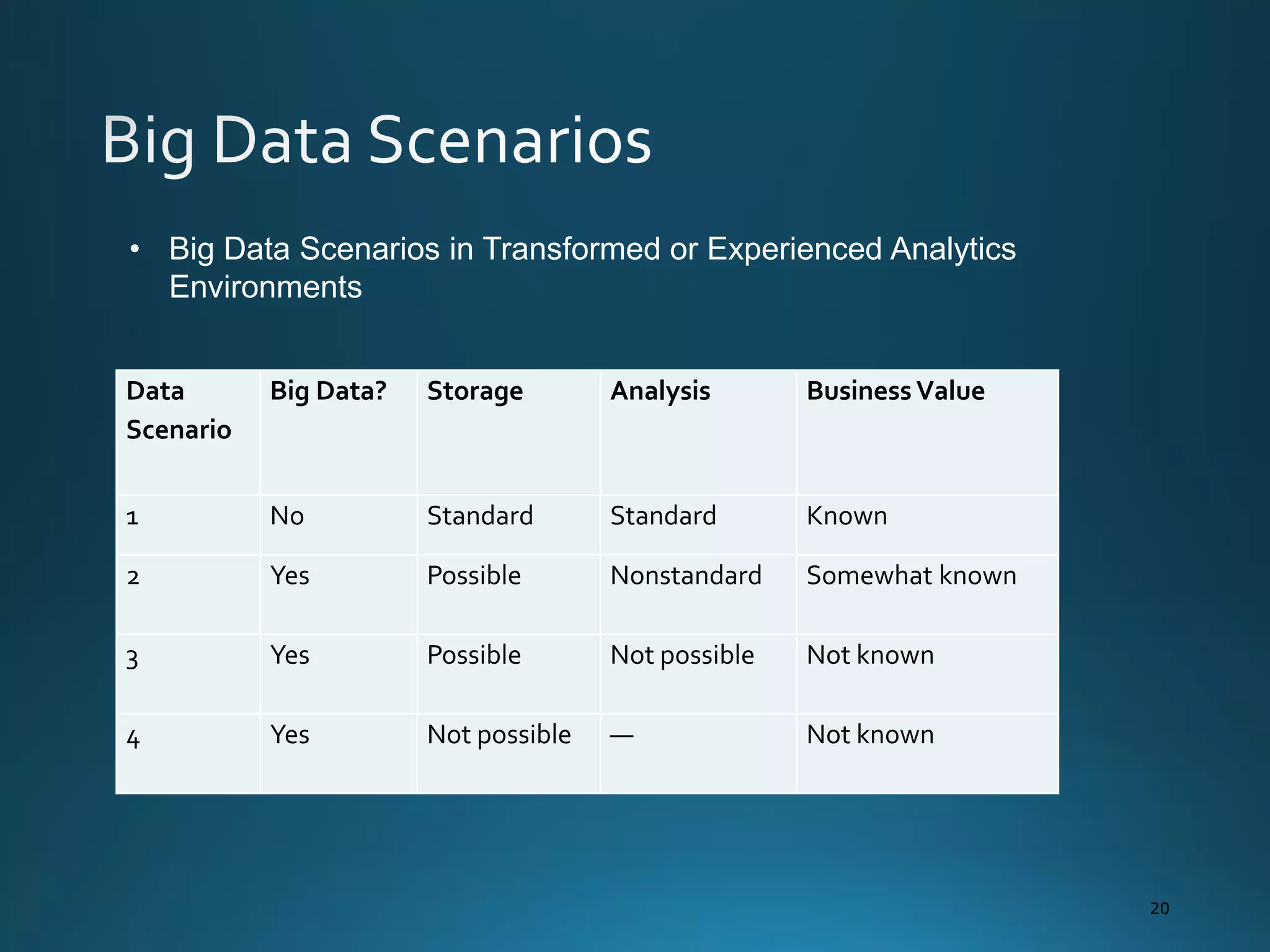
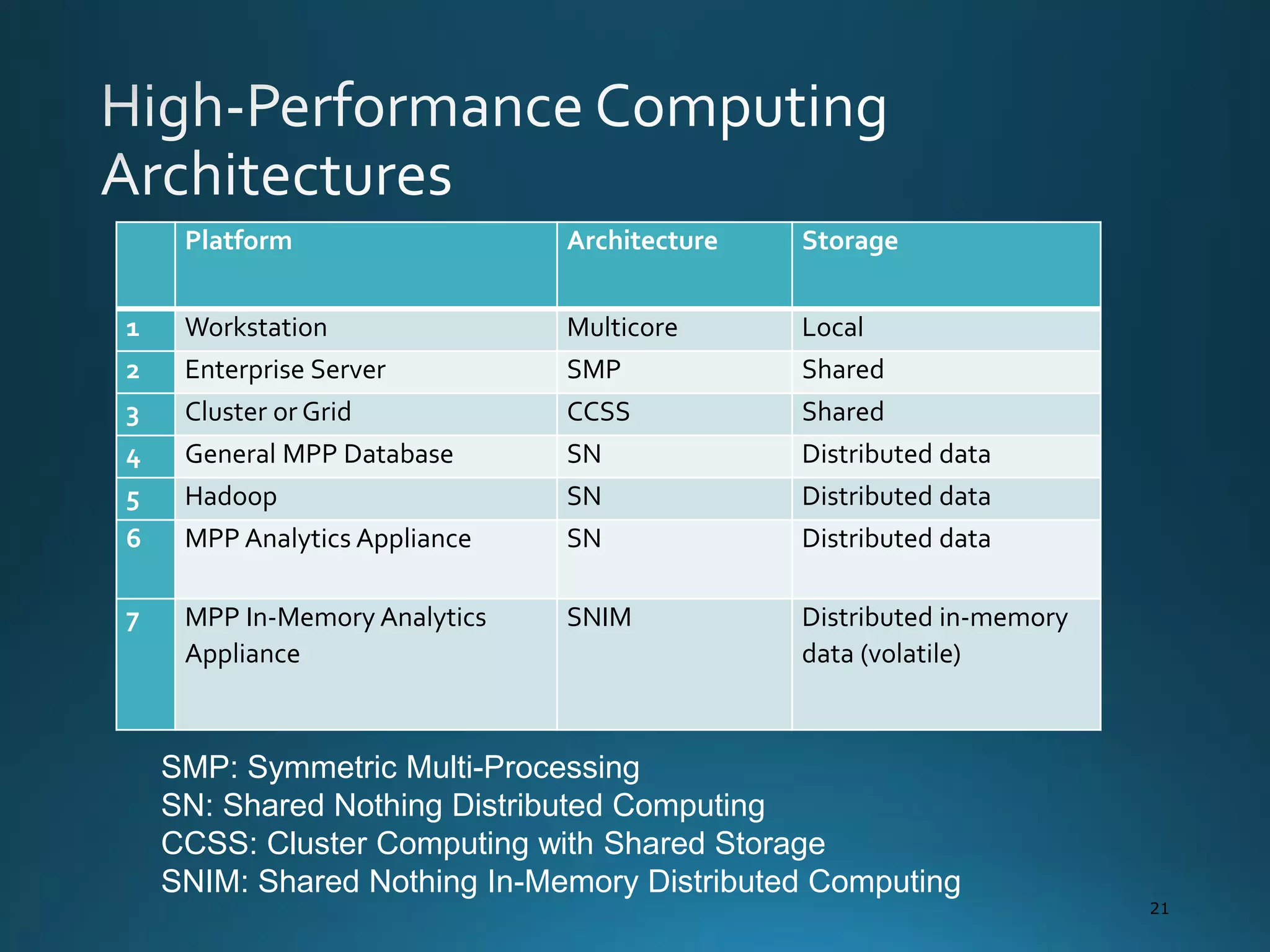
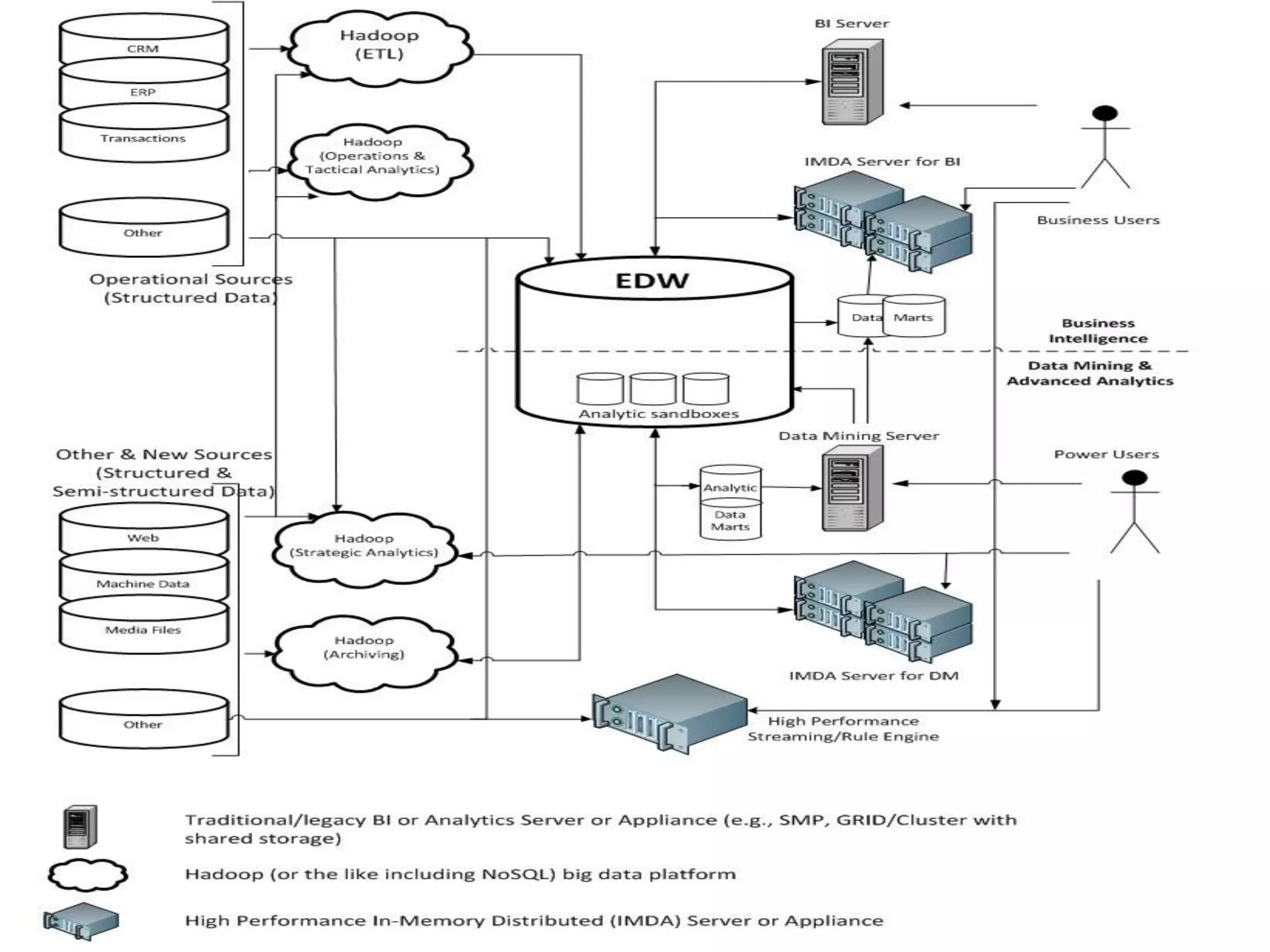
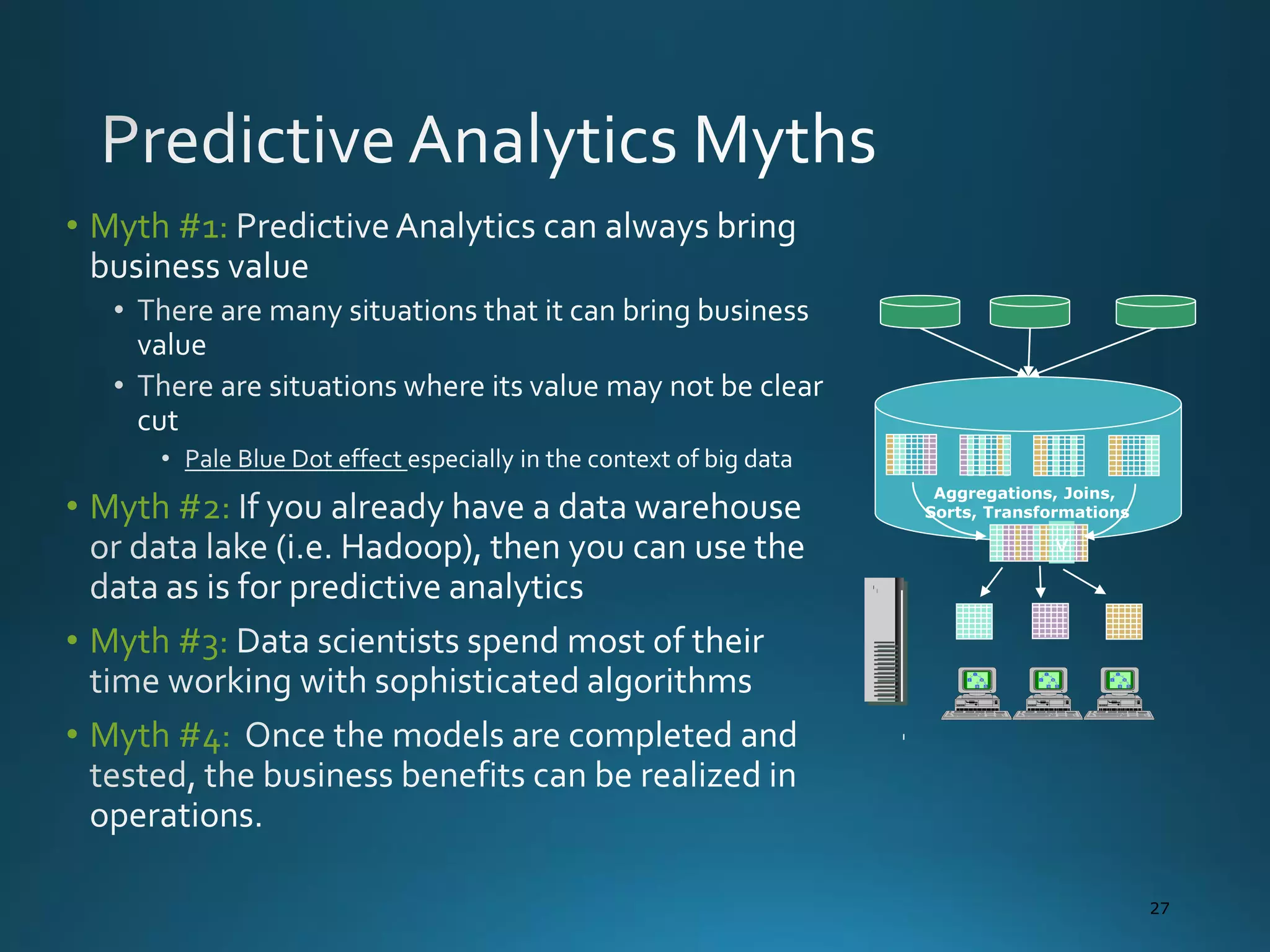
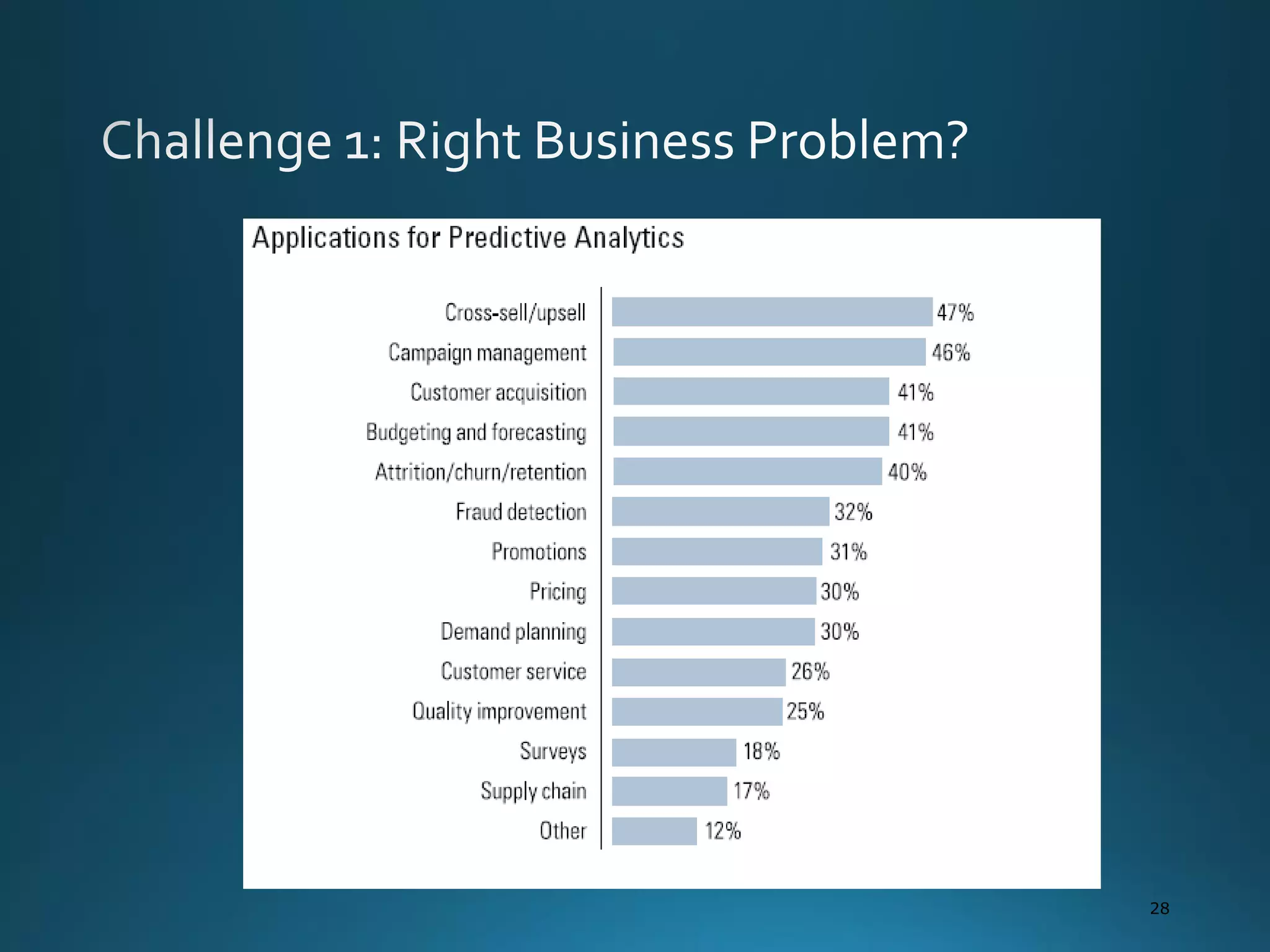
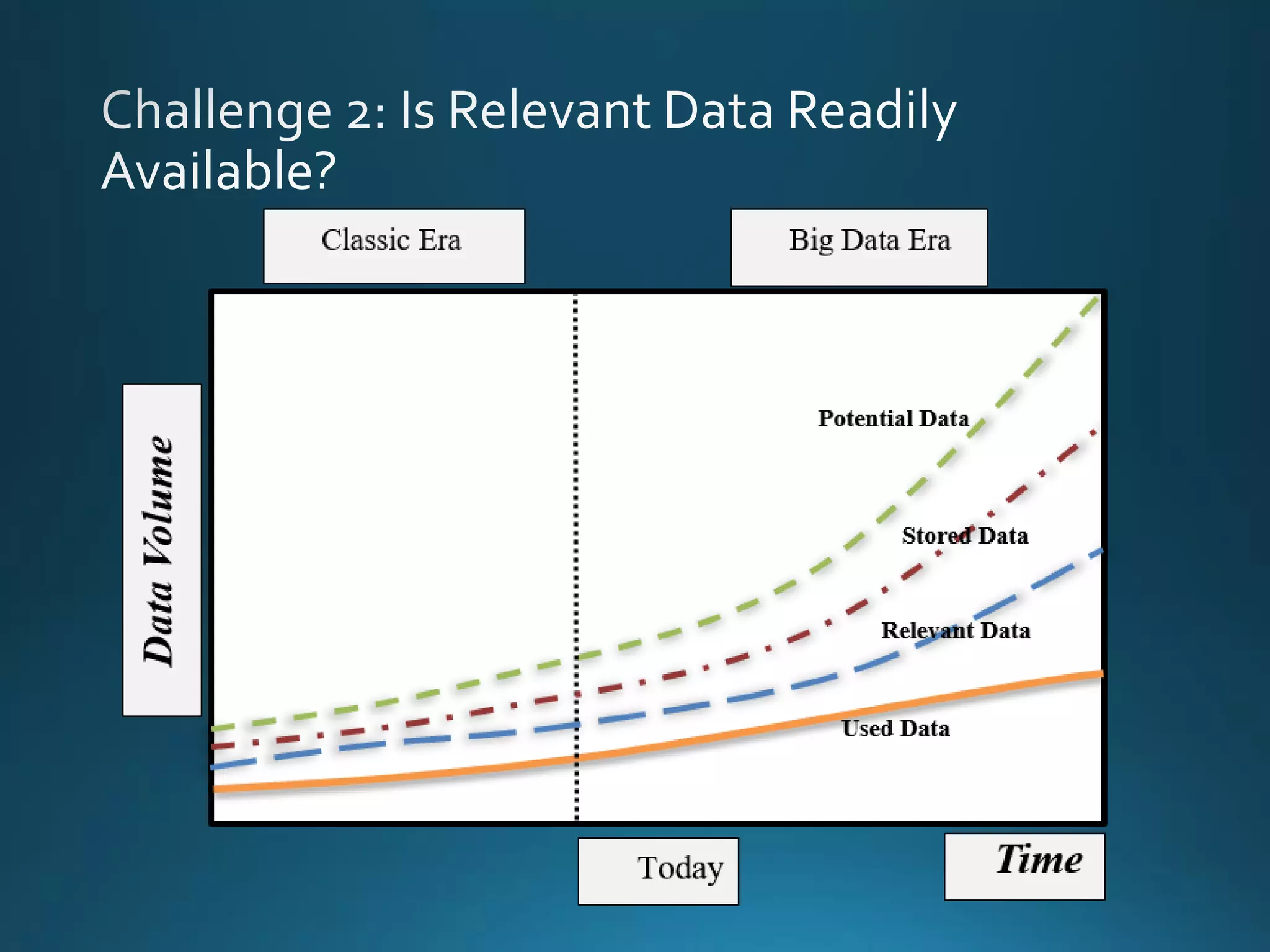
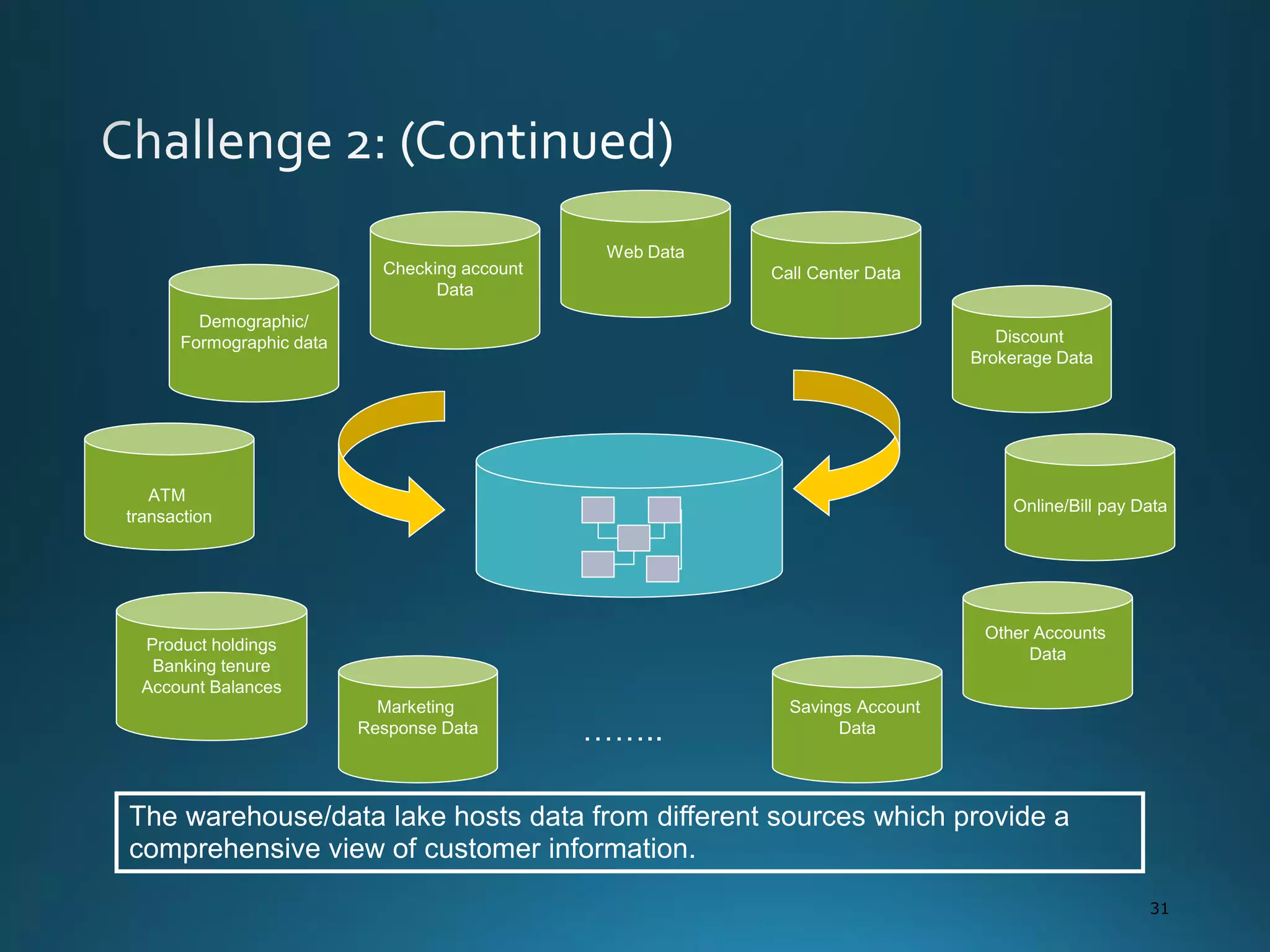
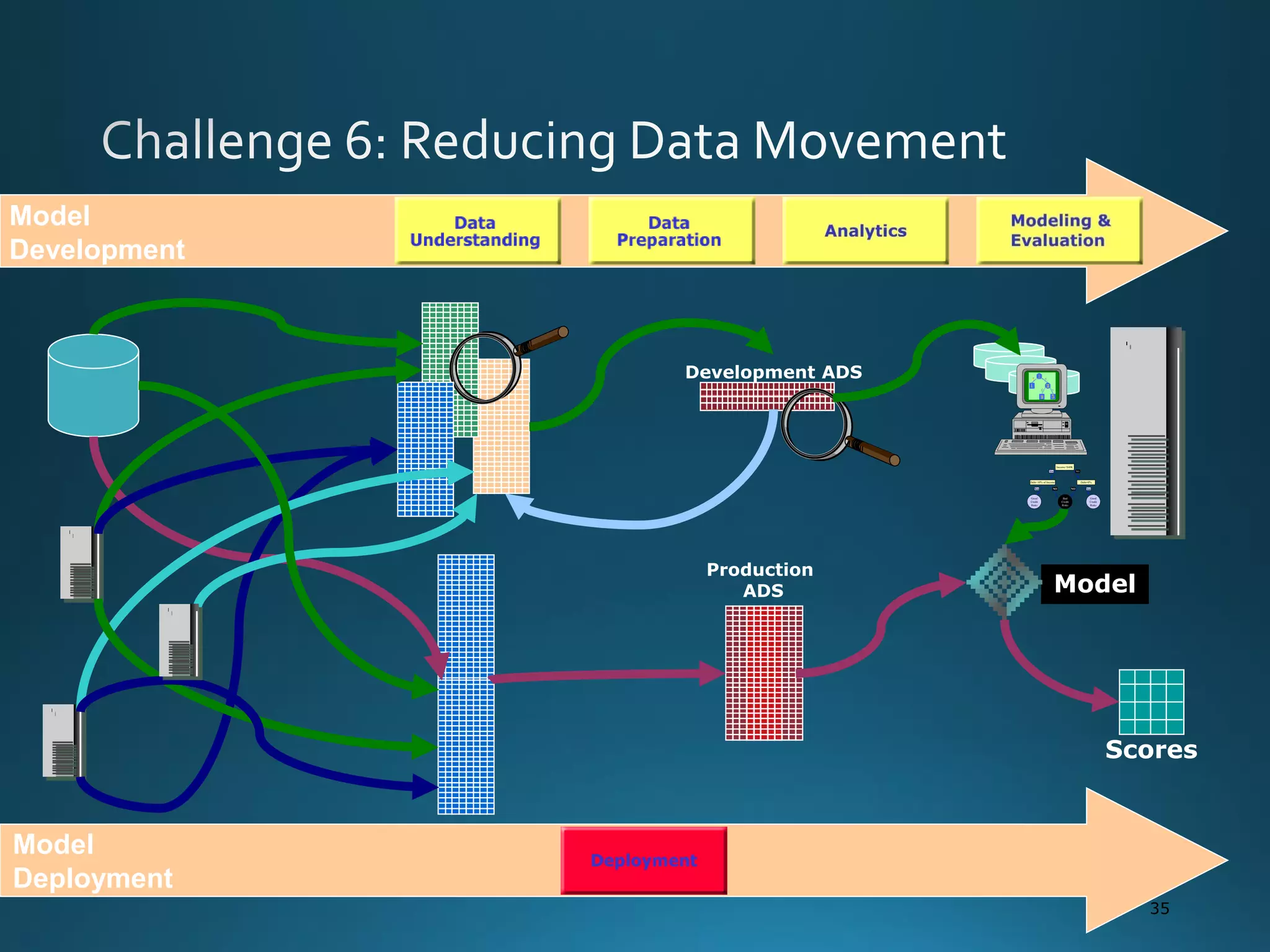
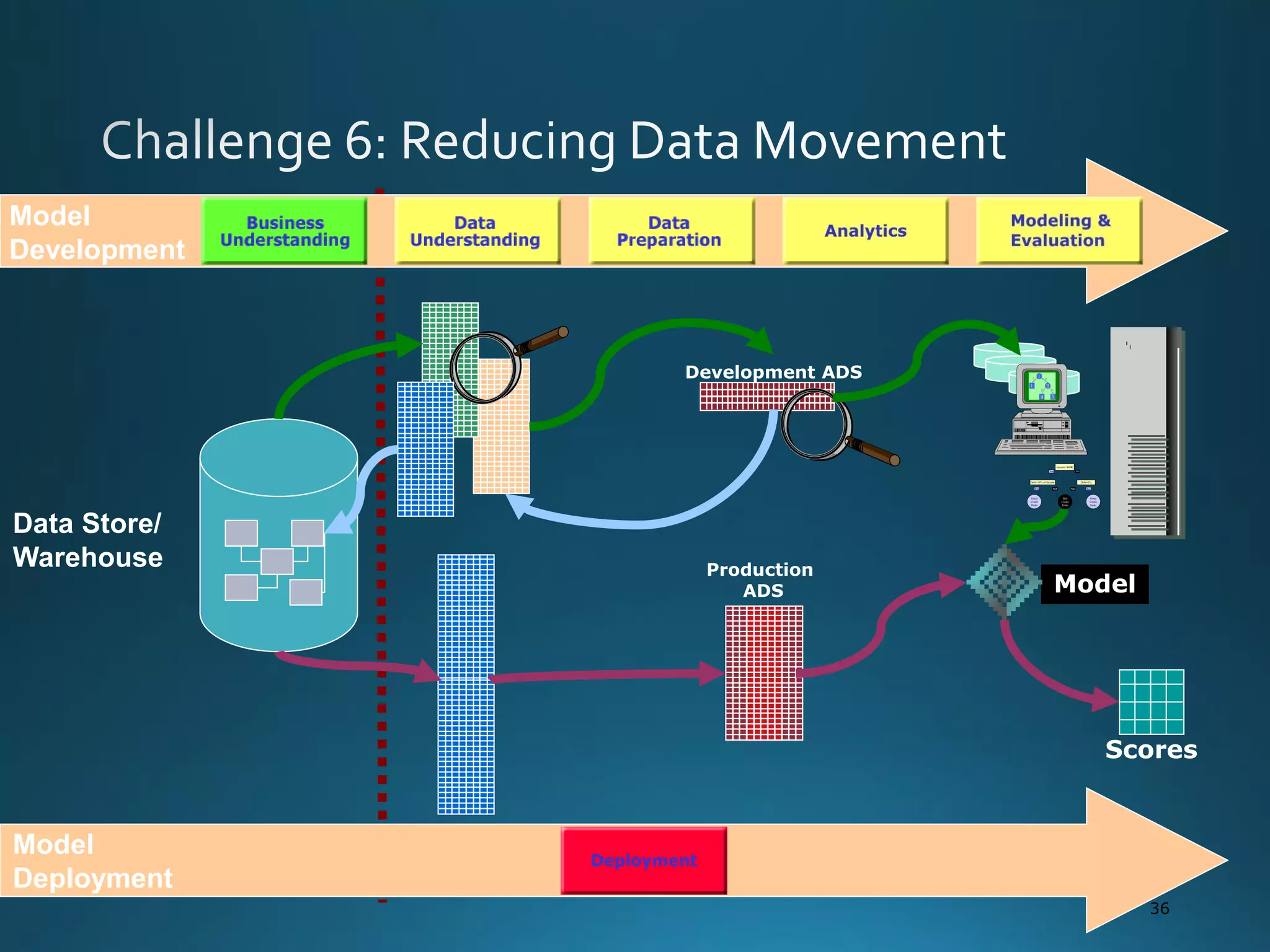
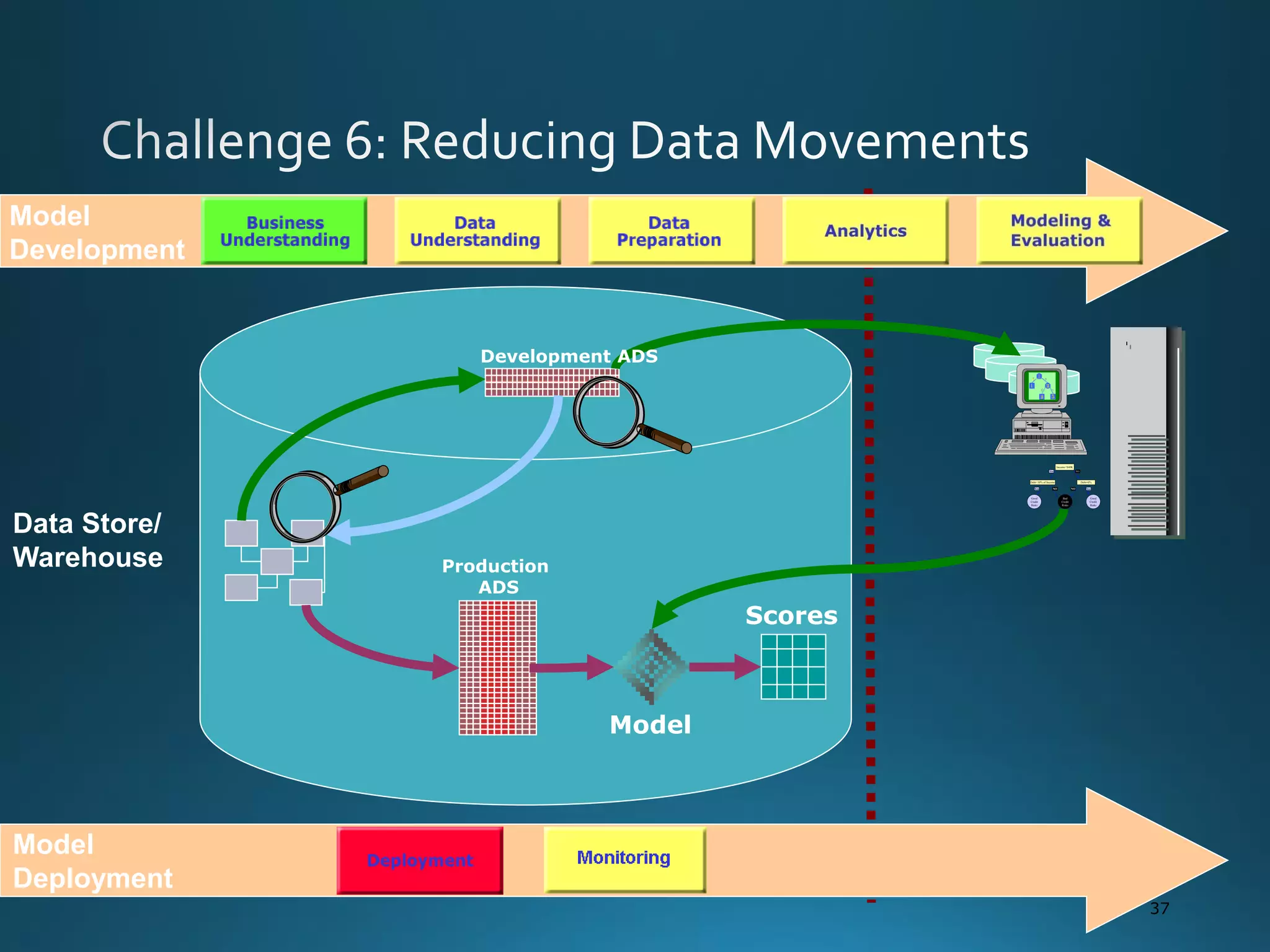
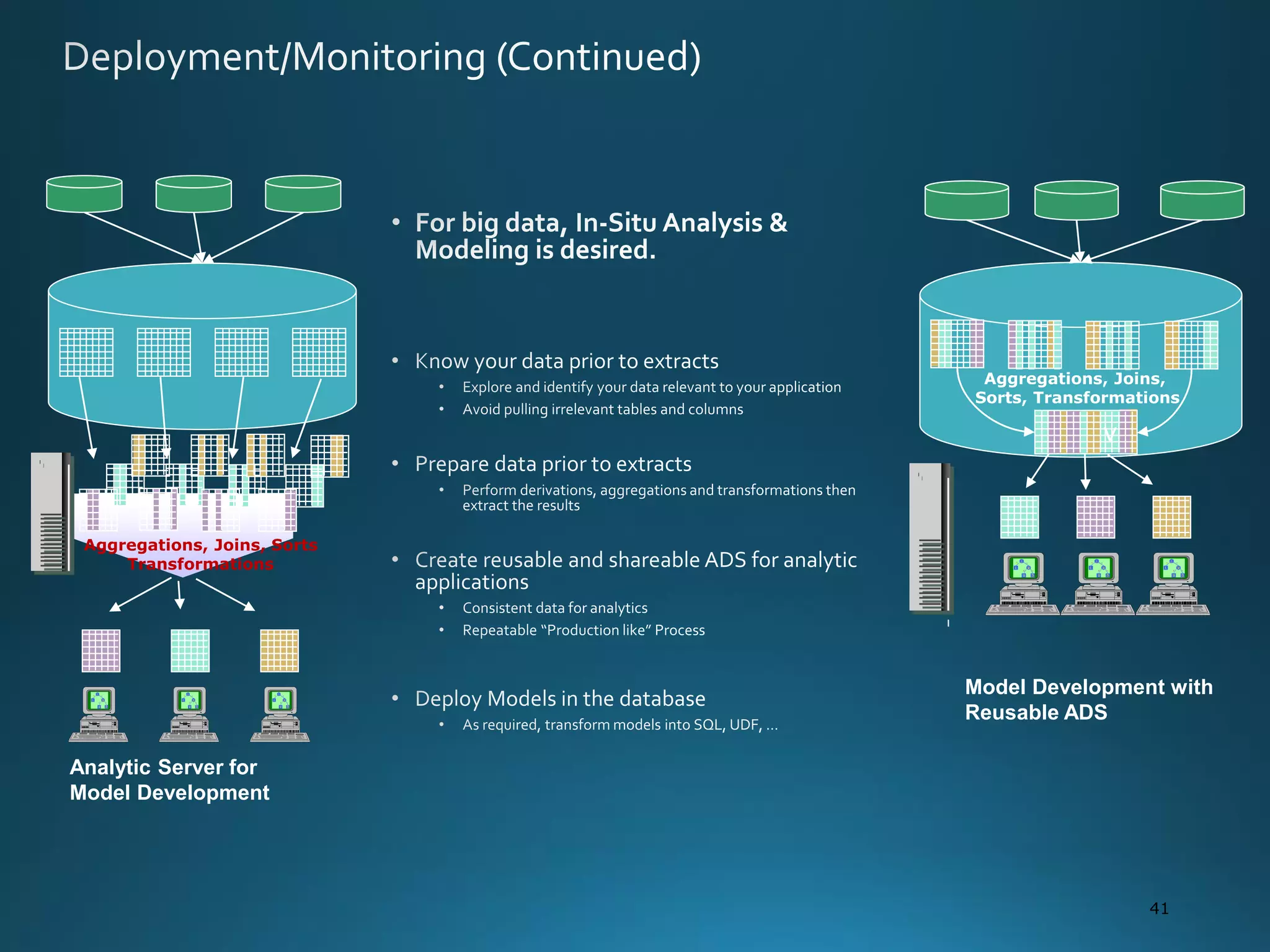
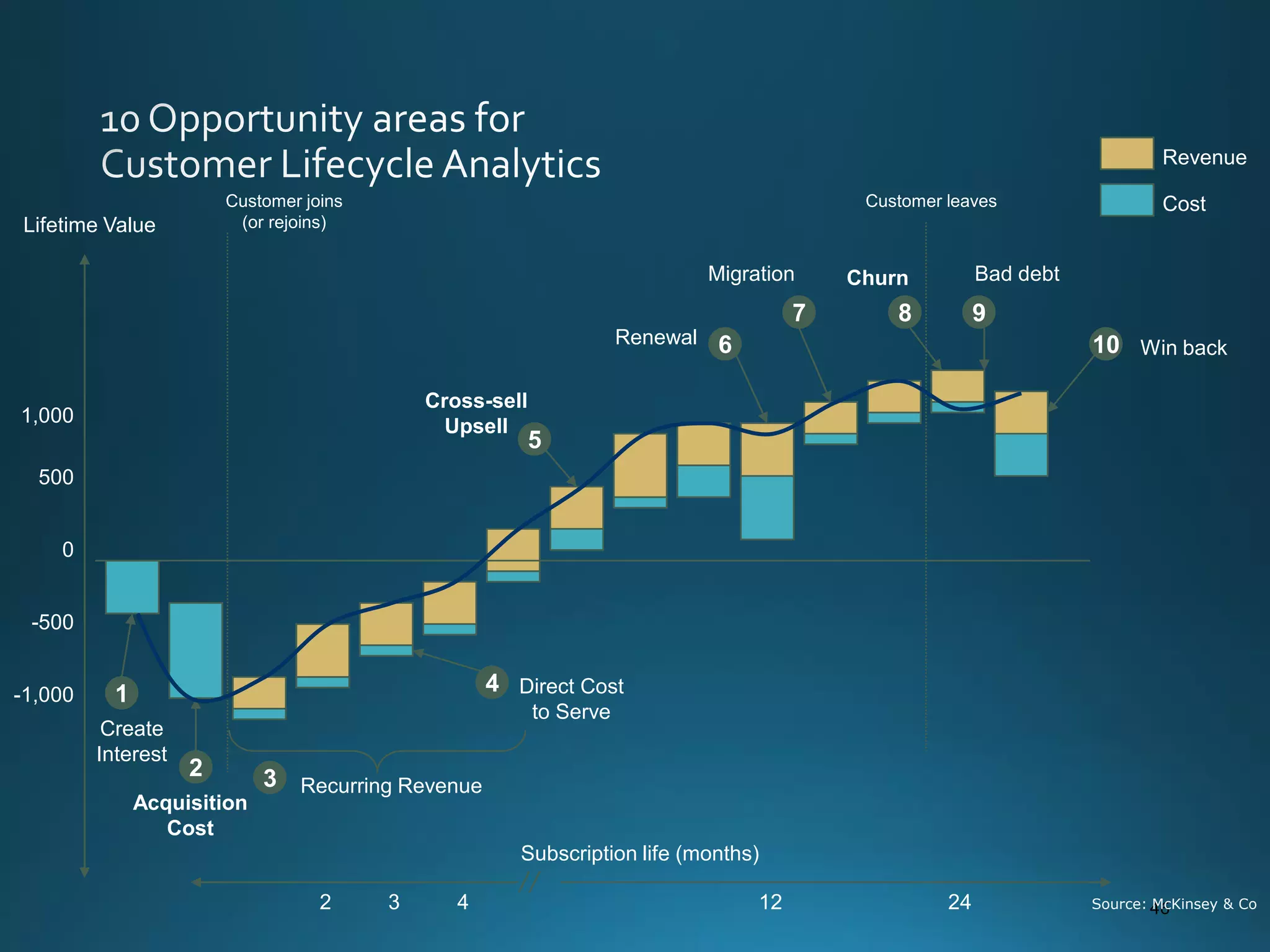
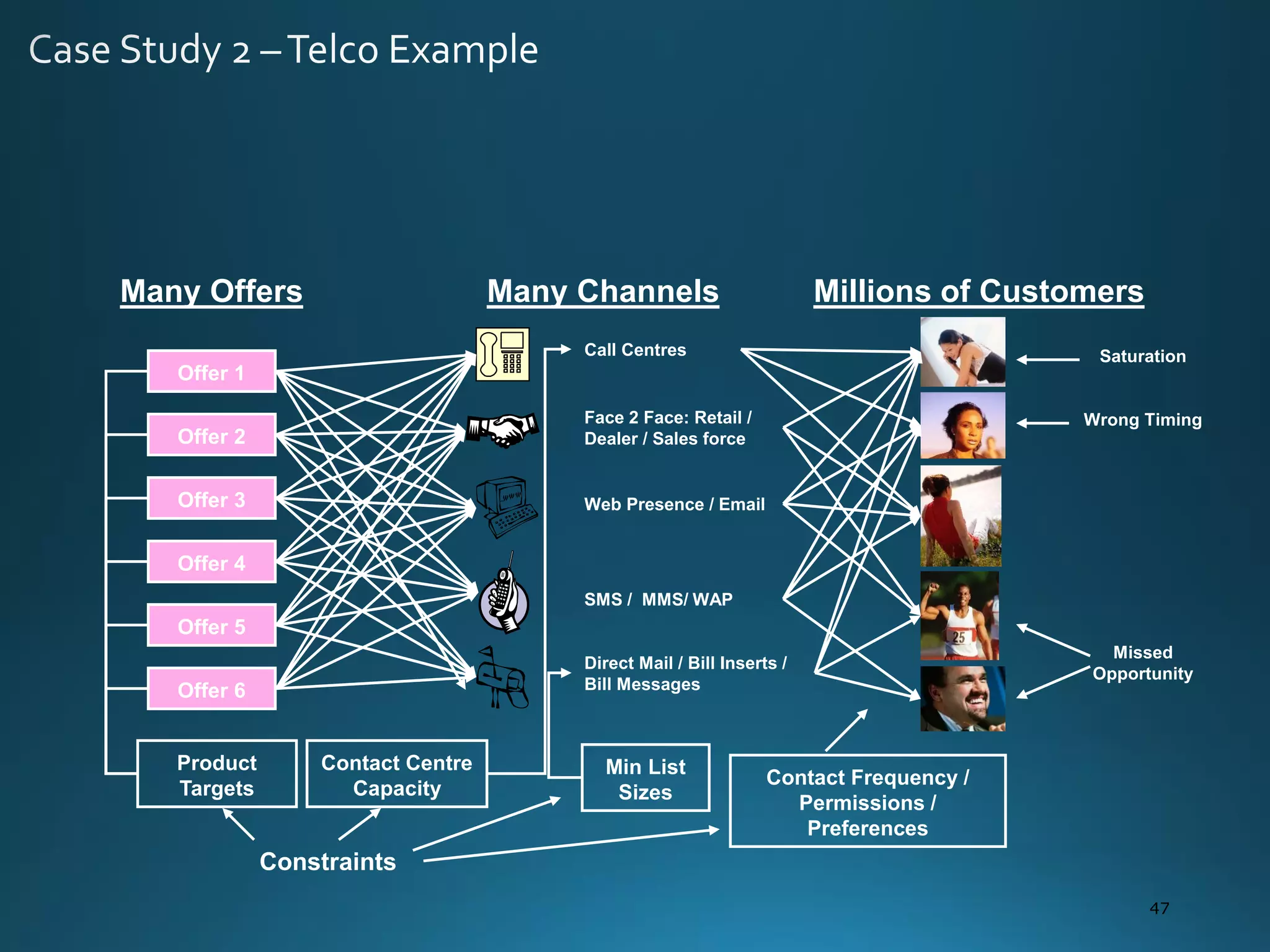
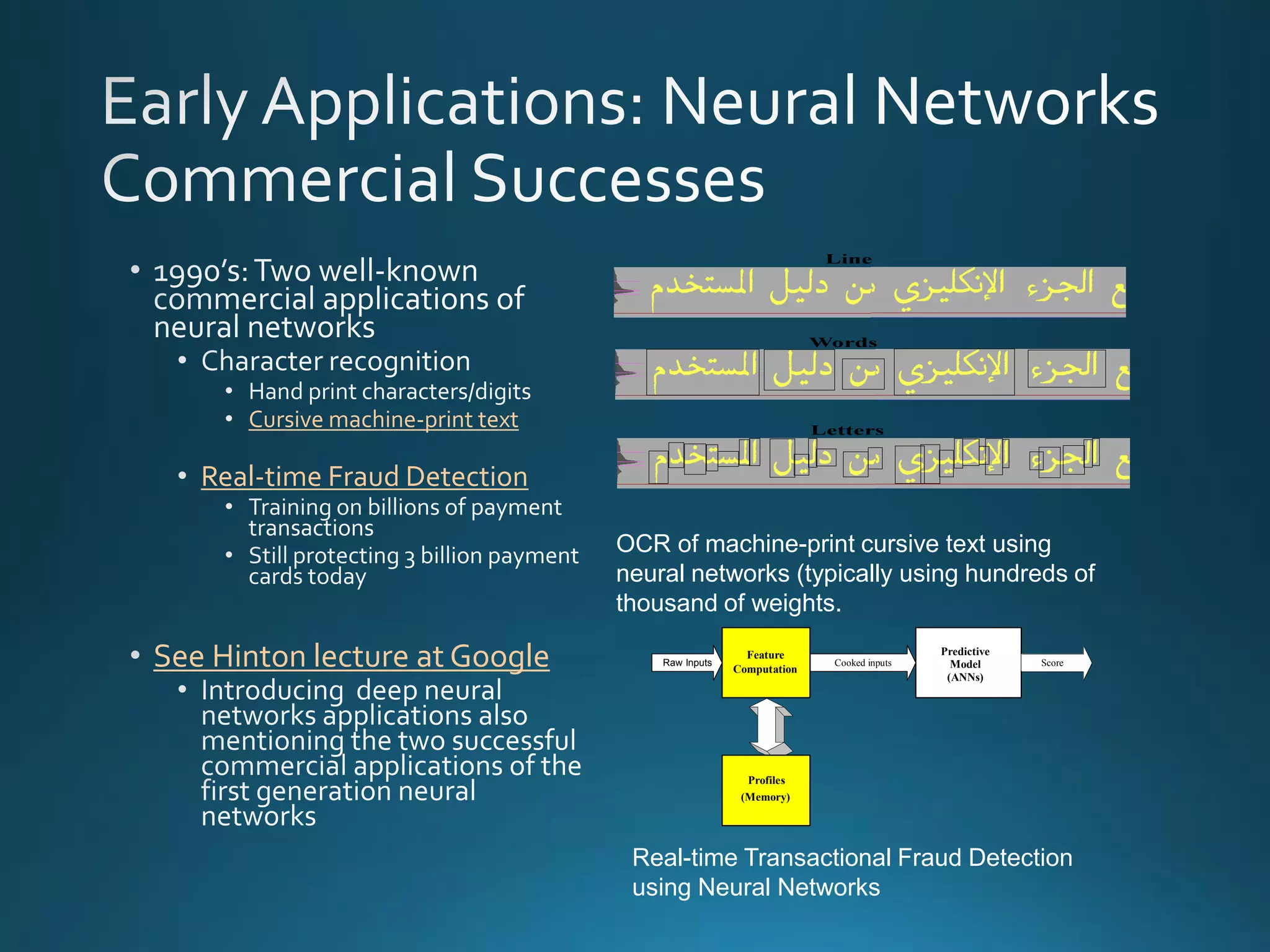
The document discusses the evolution and comparison of data science, machine learning, and traditional statistics, highlighting their distinctive goals and methodologies. It emphasizes the trend towards advanced analytics in business, marked by a need for real-time processing and a culture of data abundance, contrasted with traditional data analysis techniques that prioritize reduced input features. Additionally, it presents the progression of analytics sophistication, capacities for big data environments, and various myths related to data and analytics.