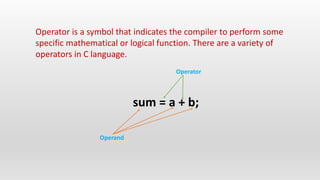
The document explains the various types of operators in C programming, including arithmetic, increment/decrement, assignment, relational, logical, bitwise, and special operators. Each operator is described with examples demonstrating their use in mathematical and logical operations. The document emphasizes how operators function and their purpose within the programming language.